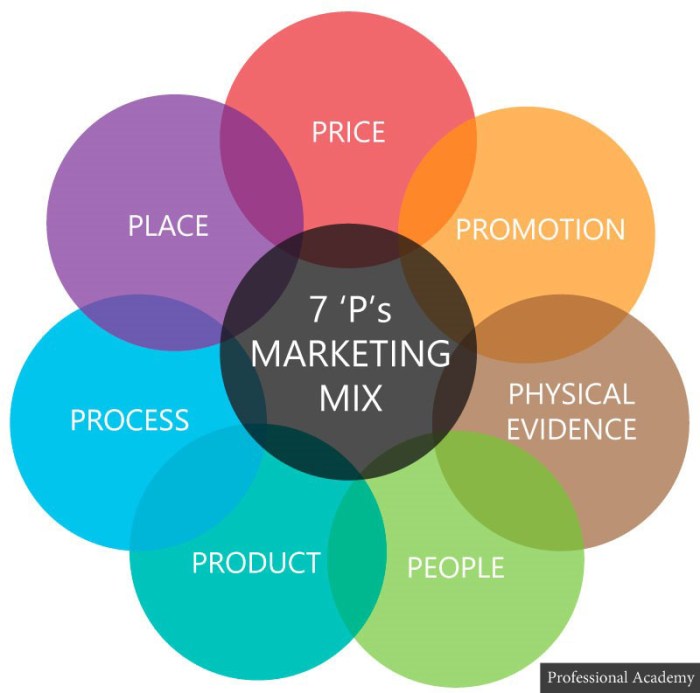
7Ps of marketing mix is a crucial framework for businesses to understand and implement effective marketing strategies. This comprehensive guide delves into the seven key elements—product, price, place, promotion, people, process, and physical evidence—that form the backbone of any successful marketing plan.
From understanding the historical context and core principles of the marketing mix to examining each element in detail, this discussion offers valuable insights into how these interconnected elements drive customer engagement and achieve business objectives. We’ll explore successful strategies, common challenges, and practical examples to provide a well-rounded perspective on the 7Ps.
Introduction to the 7Ps of Marketing Mix

The 7Ps of marketing mix are a crucial framework for businesses to effectively develop and implement marketing strategies. This framework goes beyond traditional product and price considerations to encompass the entire customer experience. It provides a holistic view of the marketing process, allowing businesses to tailor their offerings to specific customer needs and market demands.The concept of the marketing mix evolved over time, building upon earlier models and recognizing the increasing complexity of the modern marketplace.
Initially focusing on the four Ps (product, price, place, and promotion), the framework expanded to include people, process, and physical evidence, reflecting the growing importance of customer interactions and tangible aspects of the brand experience.
Historical Context and Evolution
The 7Ps framework represents a significant advancement in marketing theory. It builds upon the earlier 4Ps model, which primarily focused on the controllable elements of a marketing strategy. The evolution from 4Ps to 7Ps reflects a deeper understanding of the complexities of modern marketing, recognizing the crucial role of people, processes, and physical evidence in creating a successful customer experience.
The 7Ps framework recognizes that customers don’t just interact with a product or service; they interact with the entire system, including the people delivering it, the processes involved, and the tangible aspects of the environment.
Core Principles of the 7Ps
The 7Ps framework is built upon several core principles. It emphasizes the importance of a holistic approach to marketing, viewing the entire customer journey as a series of interconnected elements. It stresses the importance of adapting to changing market conditions and customer needs. Finally, it recognizes the importance of consistency and integration across all marketing activities. This approach allows businesses to tailor their strategies to meet the needs of specific customer segments and market environments.
The 7Ps Framework
This table Artikels the seven elements of the marketing mix, providing a concise description for each.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Product | This encompasses the tangible and intangible attributes of the offering. It includes features, design, quality, branding, and packaging. A crucial aspect is understanding customer needs and desires to create a product that meets those expectations. |
| Price | This involves the monetary value assigned to the product or service. Factors influencing price include production costs, market competition, perceived value, and customer demand. Pricing strategies can significantly impact profitability and market share. |
| Place | This refers to the distribution channels used to make the product or service available to customers. It includes physical stores, online platforms, and other distribution networks. Effective place strategies ensure accessibility and convenience for customers. |
| Promotion | This involves the communication strategies used to promote the product or service. Methods include advertising, public relations, social media marketing, and sales promotions. Effective promotion builds brand awareness and generates customer interest. |
| People | This focuses on the employees and customer service representatives who interact directly with customers. Their knowledge, skills, and attitude significantly impact the customer experience. Training and development programs for personnel can positively affect customer satisfaction. |
| Process | This refers to the systems and procedures involved in delivering the product or service. Efficient and effective processes contribute to a smooth customer journey and higher customer satisfaction. Optimizing these processes can improve operational efficiency. |
| Physical Evidence | This encompasses the tangible elements that customers interact with during the purchase and consumption process. This includes the physical environment, packaging, and visual communications. Creating a positive and consistent brand image through physical evidence can build trust and brand recognition. |
Product
The product is the core offering of any business. It’s the tangible or intangible item, service, or experience that a company provides to satisfy a customer’s needs or wants. A well-defined product strategy is crucial for success, as it directly impacts the perception of the brand and drives sales. Understanding the nuances of product development, differentiation, and positioning is key to a strong marketing strategy.A successful product is more than just a functional item.
It needs to resonate with the target market, address their pain points, and offer a compelling value proposition. The product’s attributes, features, and benefits should be clearly communicated to potential customers, highlighting what sets it apart from competitors.
Role of Product in Marketing Strategy
The product is the cornerstone of any marketing strategy. It’s the offering that directly addresses the customer’s needs. A well-defined product strategy translates into a strong brand image and ultimately, drives sales. Without a compelling product, marketing efforts are largely ineffective.
Product Differentiation and Positioning
Product differentiation involves distinguishing a product from competitors in the market. This could be through unique features, superior quality, or a compelling brand story. Positioning, on the other hand, is the process of establishing a clear and distinct image of the product in the minds of the target audience. Strong product differentiation and positioning allow the product to stand out from competitors, making it more attractive to the target audience.
The 7Ps of marketing mix are crucial for any successful strategy, but understanding how companies like Amazon execute their strategies is key. Amazon’s incredible success in content creation, as explored in how amazon a content works , highlights the importance of adapting these principles. Ultimately, a nuanced understanding of the 7Ps is vital for businesses looking to compete effectively in today’s market.
A clear understanding of the competitive landscape is essential to effectively differentiate a product.
Factors to Consider When Developing a New Product
Several factors need careful consideration during the new product development process. Understanding the target market, their needs, and their preferences is paramount. Market research, including surveys, focus groups, and competitor analysis, should inform the development process. The feasibility of the product, considering production costs, marketing costs, and potential returns, must be assessed. Furthermore, the product’s lifecycle, from introduction to maturity and decline, should be anticipated.
Finally, legal and regulatory considerations must be thoroughly evaluated.
Examples of Successful Product Launches and Strategies
Successful product launches often involve a multi-faceted approach. Consider the iPhone’s launch, which utilized extensive marketing campaigns and created a strong sense of anticipation and desire among consumers. The strategy included carefully managed product information releases and limited-availability tactics. Another successful example is the “Gillette Fusion Razor.” Its unique features and innovative design positioned it as a superior product in the market, leading to high adoption rates.
A clear understanding of the target audience and its needs is fundamental in any successful launch strategy.
Tangible vs. Intangible Products
| Category | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Tangible Products | Physical goods that can be seen, touched, and used. | Cars, smartphones, clothing, furniture |
| Intangible Products | Services, experiences, or ideas that cannot be physically possessed. | Consultancy services, education, insurance, entertainment |
Developing a strong product, whether tangible or intangible, requires a deep understanding of the target market’s needs and desires. Both categories demand careful attention to detail in design, features, and ultimately, the value proposition.
Price
Pricing is a critical element of the marketing mix, directly impacting profitability and market share. A well-defined pricing strategy not only reflects the value proposition but also influences customer perception and purchasing decisions. Understanding various pricing strategies, the factors influencing them, and the relationship between price and perceived value is crucial for successful product positioning.Pricing decisions are complex, considering numerous factors.
Competition, market demand, production costs, and desired profit margins all play a role in determining the optimal price point for a product or service. The price must resonate with the target audience’s perceived value of the product, ensuring profitability while maintaining a competitive edge.
Pricing Strategies
Various pricing strategies exist, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these approaches allows businesses to choose the strategy best aligned with their specific objectives and target market.
- Cost-Plus Pricing: This method involves calculating the total cost of producing a product and adding a markup to arrive at the selling price. It’s straightforward to implement but may not always reflect the true value of the product or consider market dynamics. For example, a simple manufacturing process might rely on cost-plus pricing to ensure a reasonable profit margin, while a high-tech product might be better suited for value-based pricing.
- Value-Based Pricing: This approach focuses on the perceived value of the product to the customer. It considers factors like product features, benefits, and brand reputation to establish a price that aligns with customer expectations. A premium price can be justified by a strong brand reputation and exceptional product features, which directly correlate with customer perception of value. For instance, luxury goods often use value-based pricing.
- Competitive Pricing: This strategy sets prices based on the pricing of competitors’ products. It’s crucial to thoroughly analyze competitors’ offerings and market position to ensure the price is competitive while still maintaining profitability. Consider a local coffee shop adjusting its prices to match those of its neighboring establishments.
- Penetration Pricing: Used to quickly gain market share by setting a low initial price. This attracts a large number of customers and creates significant demand, but it may limit short-term profits. New smartphone brands often employ penetration pricing to quickly establish a presence in the market.
- Premium Pricing: This involves setting a high price for a product or service to position it as a luxury or exclusive item. The price reflects the perceived value, exclusivity, and quality of the product. Think of high-end fashion brands that use premium pricing to differentiate their products.
Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions
Numerous factors influence pricing decisions. Understanding these factors allows for more informed and strategic pricing strategies.
The 7Ps of marketing mix are crucial for any business strategy, but even the best strategies can be affected by privacy concerns. For instance, if you’re using Google Fonts, you might want to consider how to make your website more privacy-friendly, like how to make Google Fonts privacy friendly. Ultimately, a strong marketing mix needs to be sensitive to user privacy for long-term success.
- Market Demand: Demand plays a significant role in determining the optimal price point. Understanding the elasticity of demand—how sensitive demand is to price changes—is essential. If demand is inelastic, a price increase may not significantly impact sales volume. A company selling essential medications, for instance, likely faces inelastic demand.
- Competition: The presence and pricing strategies of competitors are critical considerations. A thorough analysis of competitors’ offerings and pricing is essential to ensure the price remains competitive and attractive. A retail store might consider the pricing of similar products offered by competitors in the same area.
- Production Costs: Production costs, including raw materials, labor, and overhead, directly influence the minimum price a product can be sold at. A company needs to carefully balance production costs with desired profit margins. The cost of ingredients, for instance, plays a role in the pricing of food items.
- Government Regulations: Government regulations, such as taxes and price controls, can affect pricing strategies. Businesses need to understand and adapt to these regulations to maintain compliance and competitiveness. The pricing of certain pharmaceuticals, for example, may be subject to government regulations.
Price and Perceived Value
Price and perceived value are closely related. A product’s price should reflect the value it delivers to the customer. A perceived high value can justify a higher price, while a low perceived value may require a lower price to attract customers.
Cost-Plus vs. Value-Based Pricing
- Cost-plus pricing focuses on the costs associated with producing a product. The price is determined by adding a markup percentage to the total cost. A simple formula for cost-plus pricing is: Selling Price = Cost + Markup. This method is straightforward but may not accurately reflect the value a customer places on the product.
- Value-based pricing focuses on the value the customer perceives from the product. The price is determined by considering the product’s features, benefits, and competitive landscape. This method often leads to higher prices than cost-plus pricing if the product has a strong value proposition.
Pricing Models Comparison
| Pricing Model | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Cost-Plus | Simple to calculate, predictable | May not reflect market value, ignores competition |
| Value-Based | Reflects perceived value, higher potential profits | Requires market research, difficult to quantify value |
| Competitive | Easy to implement, avoids price wars | May not maximize profit, lacks differentiation |
| Penetration | Quick market entry, high volume | Lower profit margins, potential for price wars |
| Premium | High profit margins, positions product as premium | Requires strong brand recognition, susceptible to economic downturns |
Place (Distribution): 7ps Of Marketing Mix
Reaching your target customers effectively hinges on a well-defined distribution strategy. This crucial element of the marketing mix ensures your product or service is accessible and convenient for potential buyers. A robust distribution network not only expands your market reach but also builds brand awareness and ultimately drives sales. This section will delve into the importance of distribution channels, various options available, and the factors influencing your choice.
Importance of Distribution Channels
Distribution channels act as the bridge connecting your product or service to the end consumer. They facilitate the movement of goods from the point of origin to the point of consumption, enabling businesses to efficiently reach their target market. A well-structured channel strategy optimizes the flow of goods, minimizing delays and ensuring timely delivery. Effective distribution also enhances customer satisfaction by offering convenient access to products, thereby strengthening brand loyalty.
Types of Distribution Channels
Distribution channels can be broadly categorized into online and offline options. Offline channels include traditional methods like retail stores, wholesalers, and distributors. These channels have been the mainstay of commerce for decades, offering a tangible experience and a physical presence for brands. Online channels, such as e-commerce platforms, direct sales websites, and social media marketing, have become increasingly prevalent in recent years, offering a global reach and 24/7 accessibility.
Factors Influencing Channel Choice
Several key factors influence the selection of a distribution channel. These include target market characteristics, product attributes, budget constraints, and competitive landscape. Businesses catering to a niche market might opt for specialized distribution channels, while those aiming for mass appeal might favor broader channels. The product’s complexity and technical nature also play a role, influencing the choice of channel.
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations
Effective distribution demands a robust logistics and supply chain strategy. This includes meticulous planning for warehousing, inventory management, transportation, and order fulfillment. Streamlined processes and efficient supply chain management minimize costs and ensure timely delivery, crucial factors in today’s fast-paced marketplace. Technological advancements have significantly enhanced logistics, offering real-time tracking and optimized delivery routes.
Comparison of Distribution Channels
| Distribution Channel | Reach | Cost | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Sales | Limited (local/regional) | High (initial setup) | High-end electronics retailer with showrooms |
| Retail Stores | Broad (local/regional) | Moderate (rent, staffing) | Clothing store chains |
| Wholesalers | Broad (regional/national) | Moderate (negotiation, commissions) | Food distributors supplying grocery stores |
| E-commerce | Global | Low (digital infrastructure) | Online retailers like Amazon |
| Social Media | Moderate (depending on strategy) | Low (often part of marketing budget) | Direct sales through influencer marketing |
This table provides a concise overview, highlighting the reach and costs associated with various distribution channels. The specific costs and reach can vary considerably depending on the specific implementation and market conditions.
Promotion
Promotion is the crucial element of the marketing mix that bridges the gap between a company’s offerings and its target audience. It encompasses all the activities aimed at communicating the value proposition of a product or service and persuading potential customers to purchase it. Effective promotion strategies are vital for building brand awareness, driving sales, and ultimately achieving business objectives.
Promotional Tools and Their Effectiveness
Various tools are used in promotional strategies, each with its unique strengths and weaknesses. Advertising, public relations, sales promotions, direct marketing, and digital marketing are key components. The effectiveness of each tool depends on factors like target audience, budget, and overall marketing goals. For instance, a young, tech-savvy audience might respond better to targeted social media campaigns, while an older demographic might be more receptive to print advertising.
Elements of a Comprehensive Promotional Strategy
A robust promotional strategy requires careful consideration of several key elements. It’s essential to define specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. Understanding the target audience’s needs, preferences, and buying behavior is fundamental. Consistent messaging across all channels builds brand recognition and trust. The strategy should integrate various promotional tools, ensuring a cohesive and impactful communication approach.
Ultimately, a well-defined promotional strategy should align with overall business objectives.
Branding and Advertising in Promoting Products, 7ps of marketing mix
Branding plays a pivotal role in shaping customer perception and loyalty. A strong brand identity, including a memorable logo, consistent visual style, and compelling brand story, fosters trust and recognition. Advertising, a crucial component of promotion, is used to communicate the brand message and highlight product benefits to a wider audience. Effective advertising campaigns utilize persuasive language, compelling visuals, and a clear call to action to drive consumer engagement and purchase decisions.
For example, a strong brand like Nike consistently conveys a message of athleticism, performance, and inspiration through its advertising campaigns.
Successful Promotional Campaigns
Numerous successful promotional campaigns demonstrate the power of strategic promotion. For example, Dove’s “Real Beauty” campaign, focusing on body positivity, resonated with a broad audience and enhanced the brand’s image. Similarly, Red Bull’s campaigns, emphasizing extreme sports and adrenaline, have successfully positioned the brand as a symbol of energy and excitement. These examples show how effectively crafted campaigns can create a strong emotional connection with consumers and drive brand loyalty.
Table of Promotional Methods and Target Audiences
| Promotional Method | Target Audience | Effectiveness Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Television Advertising | Mass market, broad reach | High cost, limited targeting |
| Social Media Marketing | Young adults, tech-savvy consumers | Highly targeted, cost-effective |
| Print Advertising (Magazines/Newspapers) | Specific demographics, niche markets | Lower reach, potentially higher engagement |
| Public Relations | Building brand image, creating awareness | Requires strong media relationships |
| Sales Promotions (Discounts, Coupons) | Incentivizing immediate purchase | Can impact perceived value, potentially decrease profit margins |
People
The human element is the lifeblood of any successful marketing strategy. Beyond products, pricing, and promotion, the interactions between your brand and customers are fundamentally shaped by the people involved. Effective marketing hinges on building genuine connections and fostering trust, and this often comes down to the people representing your brand. Employees are the face of your company, and their attitude, skills, and knowledge directly impact customer experience and ultimately, your bottom line.The role of employees in customer interactions extends far beyond simply fulfilling orders or answering questions.
They are ambassadors of your brand, representing its values and personality. A positive interaction with a knowledgeable and helpful employee can create a lasting positive impression, potentially leading to repeat business and brand advocacy. Conversely, a negative interaction with an unhelpful or unmotivated employee can damage your brand reputation and deter future customers.
The 7Ps of marketing mix are crucial for any successful business strategy, focusing on product, price, place, promotion, people, process, and physical evidence. A key aspect of effective marketing is ensuring easy access to important information, like product details. To make your WordPress site user-friendly, consider adding a seamless PDF viewer, such as the one explained in this helpful guide: how to add a pdf viewer in wordpress 2.
This directly impacts the ‘product’ element of the 7Ps by enhancing the customer experience and improving the overall effectiveness of your marketing efforts.
Employee Role in Customer Interactions
Employees are the first and often the last point of contact customers have with a company. Their interactions directly shape customer perception of the brand. From handling customer inquiries to resolving complaints, employees play a crucial role in building relationships and fostering loyalty. Excellent customer service, often a direct result of skilled and well-trained employees, leads to customer satisfaction and positive word-of-mouth referrals.
Importance of Customer Service and Employee Training
Exceptional customer service is essential for building and maintaining a loyal customer base. It’s not just about providing a product or service; it’s about the entire experience. Training programs are critical for equipping employees with the knowledge and skills to deliver outstanding customer service. These programs should cover product knowledge, communication techniques, conflict resolution, and problem-solving strategies.
Comprehensive training empowers employees to handle various customer situations effectively, leading to increased customer satisfaction.
Building a Strong Company Culture
A strong company culture that prioritizes customer service creates a positive and productive work environment. It’s about fostering a sense of shared values, purpose, and responsibility within the team. When employees feel valued and supported, they are more likely to provide excellent customer service. Open communication channels, recognition programs for outstanding performance, and opportunities for professional development all contribute to a positive and supportive work environment.
Encourage teamwork, mutual respect, and a willingness to go the extra mile for customers.
Key Skills and Qualities for Marketing Staff
The marketing team is crucial in shaping customer perceptions and experiences. Their effectiveness directly influences sales and brand loyalty. Possessing the right combination of skills and qualities is essential for success.
| Skill/Quality | Description |
|---|---|
| Strong Communication Skills | Effective verbal and written communication are vital for conveying brand messaging, building rapport with customers, and explaining products/services. |
| Problem-Solving Abilities | The ability to identify and resolve customer issues efficiently and effectively. |
| Product Knowledge | Deep understanding of the products/services offered, allowing employees to answer customer questions accurately and provide relevant recommendations. |
| Customer Focus | A genuine concern for customer needs and satisfaction, manifested in a proactive approach to exceeding expectations. |
| Empathy | Understanding and responding to customer emotions and concerns, demonstrating genuine care and concern. |
| Teamwork | Collaboration and cooperation with colleagues, fostering a supportive and efficient work environment. |
| Adaptability | Flexibility and resilience to changing market conditions and customer needs, demonstrating the capacity to adjust strategies and approaches. |
Process
The 7Ps of marketing are crucial for crafting a compelling customer experience. However, no matter how well-defined the product, price, place, promotion, people, and even the physical environment are, if the process of delivering value isn’t streamlined, the entire marketing strategy can falter. Efficient processes are the engine driving customer satisfaction and loyalty.The customer journey is a complex series of interactions, and each step is an opportunity to either enhance or detract from the overall experience.
Processes, from initial contact to final delivery, directly influence customer perception. Optimizing these processes is not just about efficiency; it’s about creating a seamless, positive experience that fosters customer loyalty.
Importance of Efficient Processes
Efficient processes are paramount for delivering value and ensuring customer satisfaction. They minimize delays, reduce errors, and create a positive perception of the brand. Streamlined processes directly impact customer satisfaction, driving repeat business and positive word-of-mouth referrals.
Processes Involved in the Customer Journey
The customer journey encompasses various processes, from initial awareness to post-purchase support. These include:
- Awareness & Research: Customer research often involves online searches, social media engagement, and reviews. Efficient processes here involve ensuring easy access to information about the product or service, clear calls to action, and positive online reviews.
- Inquiry & Engagement: This phase encompasses initial contact, whether through a website form, phone call, or email. Efficient processes here include prompt responses, clear communication, and a user-friendly interface that guides the customer through the inquiry process.
- Order Placement & Fulfillment: This process involves order confirmation, processing, and shipping. Efficient processes are vital for timely delivery, accurate order fulfillment, and effective communication with the customer throughout the process.
- Post-Purchase Support & Service: This includes handling returns, addressing queries, and providing ongoing support. Efficient processes ensure prompt resolution of issues, maintaining a positive customer experience even after the purchase.
Optimizing Processes for Efficiency and Customer Satisfaction
Several strategies can optimize processes for efficiency and customer satisfaction. These include:
- Technology Integration: Utilizing CRM systems, automated workflows, and AI-powered chatbots can significantly improve efficiency and responsiveness.
- Employee Training: Empowering employees with the knowledge and skills to handle various customer interactions effectively is essential for maintaining high standards.
- Data Analysis: Tracking customer interactions and identifying bottlenecks allows for data-driven improvements in processes.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Gathering customer feedback through surveys, reviews, and direct communication can reveal areas needing improvement.
Companies Excelling in Process Optimization
Several companies are known for their exceptional customer service processes. For example, Amazon’s highly efficient logistics network and seamless online ordering experience are well-regarded. Similarly, companies like Zappos are known for their exceptional customer service, with a focus on personalized and prompt responses. These companies prioritize efficiency and customer satisfaction, making them industry leaders.
Example of a Typical Customer Service Process (Flowchart)
A simplified flowchart for a customer service process might look like this:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Customer contacts support |
| 2 | Support agent logs the inquiry |
| 3 | Agent researches and identifies the issue |
| 4 | Agent provides a solution or directs to relevant resources |
| 5 | Customer feedback is collected |
| 6 | Process is closed, and data is analyzed |
Physical Evidence
The physical environment plays a crucial role in shaping customer perception and experience. It’s not just about the aesthetics; it’s about creating an atmosphere that resonates with the brand’s values and communicates its personality effectively. From the design of a retail store to the packaging of a product, every physical element contributes to the overall customer journey and influences their perception of the brand.
A well-designed and thoughtfully executed physical environment can significantly enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.A carefully crafted physical environment fosters a sense of connection and belonging. It transcends mere functionality, transforming the interaction with a brand into a holistic sensory experience. This experience can be influenced by factors like lighting, colors, music, smells, and the overall layout. The right combination of these elements can create a positive and memorable encounter, strengthening the bond between the customer and the brand.
Importance of Visual Merchandising and Store Design
Visual merchandising is a powerful tool for showcasing products and enhancing the overall shopping experience. Strategic placement of products, use of attractive displays, and skillful use of lighting and color all contribute to a compelling visual narrative that attracts customers and motivates them to buy. Effective store design extends beyond aesthetics; it considers customer flow, ease of navigation, and the overall experience.
Well-designed stores are easy to navigate, which reduces frustration and encourages exploration. This, in turn, fosters a positive shopping experience.
Impact of Packaging on Brand Perception
Packaging is a crucial element of the physical evidence strategy. It’s often the first interaction a customer has with a product, and it significantly influences their perception of the brand. The design, materials, and information conveyed on the packaging communicate brand values, quality, and target audience. Effective packaging can enhance product appeal, improve shelf presence, and ultimately drive sales.
For instance, minimalist packaging can project a sophisticated image, while vibrant colors and bold designs can appeal to a younger audience.
Creating a Consistent Brand Image Across All Touchpoints
Consistency in brand image across all touchpoints is vital for building a strong and recognizable brand identity. This means ensuring that the brand’s visual identity, tone of voice, and overall messaging are consistent in every interaction a customer has with the brand, whether online or offline. This consistency fosters trust and reliability, creating a unified and memorable brand experience.
Inconsistencies in branding can lead to confusion and a diluted brand image.
Table Contrasting Physical Environments
| Physical Environment | Impact on Customer Perception |
|---|---|
| A modern, minimalist coffee shop with natural light and minimalist furniture. | Creates a sense of calm, sophistication, and exclusivity. Customers perceive the shop as high-quality and stylish. |
| A brightly lit, bustling clothing store with a wide array of displays and seasonal collections. | Creates a vibrant, energetic, and exciting shopping experience. Customers perceive the store as trendy and up-to-date with the latest fashion trends. |
| A traditional, family-owned bookstore with comfortable seating and a curated selection of books. | Creates a welcoming, nostalgic, and intellectual atmosphere. Customers perceive the bookstore as a community hub and a source of knowledge and cultural experience. |
Final Review
In conclusion, the 7Ps of marketing mix provide a robust framework for businesses to craft comprehensive marketing strategies. By carefully considering each element, from the product itself to the physical environment, companies can create a cohesive and impactful approach that resonates with their target audience. This deep dive into the 7Ps offers actionable insights and practical tools for businesses seeking to optimize their marketing efforts and achieve lasting success.