9 AB tests that you can run tomorrow to double your conversions. Ready to supercharge your website’s performance? This guide unveils nine actionable A/B tests you can implement immediately, promising a significant boost in conversions. We’ll explore everything from identifying improvement areas to interpreting results and implementing winning variations, all designed for maximum impact and efficiency.
A/B testing is a cornerstone of effective conversion rate optimization. By meticulously comparing different variations of website elements, we can identify which designs resonate most strongly with your target audience, ultimately leading to increased conversions. This detailed guide will equip you with the knowledge and strategies to execute these tests successfully and confidently.
Introduction to A/B Testing
A/B testing is a powerful method for optimizing website performance and increasing conversions. It involves comparing two versions of a webpage or marketing campaign (A and B) to determine which performs better. This systematic approach allows businesses to make data-driven decisions, rather than relying on assumptions or guesswork.By meticulously analyzing user interactions and responses to different variations, A/B testing provides a clear picture of what resonates most effectively with target audiences.
This crucial information can be used to refine website design, improve marketing copy, and enhance overall user experience.
Fundamental Principles of A/B Testing for Conversion Rate Optimization
A/B testing hinges on the principle of controlled experimentation. This involves carefully manipulating variables (e.g., button color, headline text) while keeping all other factors constant. The primary goal is to isolate the impact of the specific change being tested, ensuring accurate results. This controlled environment helps to eliminate external influences and attribute any observed differences directly to the variation introduced.
A/B testing is fundamentally about testing a hypothesis: Does changing X improve Y?
Importance of Controlled Experiments in A/B Testing
Controlled experiments are essential for accurate A/B testing results. They minimize the influence of confounding variables, allowing marketers to confidently attribute observed changes in conversion rates to specific modifications. Without controlled experiments, it’s difficult to definitively state that a particular change caused an improvement. External factors, like seasonal trends or changes in advertising campaigns, could be responsible for the observed results, leading to inaccurate conclusions and poor decision-making.
Different Types of A/B Tests
Understanding the various types of A/B tests helps marketers select the most appropriate approach for their specific needs. A comprehensive understanding of these methods enables more effective targeting and campaign optimization.
| Type of Test | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| A/B Testing | Simplest form; compares two versions of a webpage or element. | Testing two different headlines for a landing page. |
| Multivariate Testing | Tests multiple variations of multiple elements simultaneously. | Testing different headlines, button colors, and images on a product page. |
| Split-URL Testing | Tests different versions of a webpage on different groups of users. | Directing users to different landing pages with varying designs or offers. |
Identifying Potential Areas for Improvement
A/B testing is a powerful tool for optimizing website performance and boosting conversion rates. However, effective testing hinges on a clear understanding of the areas most likely to yield significant improvements. Identifying potential pain points and areas of friction for users is crucial for designing impactful experiments. This section will explore common website elements that influence conversions, user pain points, and the vital role of user research and data analysis in pinpointing testing priorities.Understanding user behavior and common obstacles is fundamental to successful A/B testing.
By identifying areas needing improvement, you can design targeted tests that yield meaningful results. Focusing on user experience is paramount to improving conversions.
Common Website Elements Impacting Conversion Rates
Understanding which website elements influence conversions is essential for effective A/B testing. Significant improvements can often be found in seemingly minor adjustments to crucial components.
Ready to boost your blog conversions tomorrow? Nine A/B tests are waiting to be run! These quick tests can make a real difference in turning visitors into customers. Want a deeper dive into converting blog visitors? Check out this article on a simple yet effective way to convert blog visitors into customers for a few more tips and tricks.
Ultimately, these 9 A/B tests will help you on the road to doubling your conversions.
- Call-to-Action (CTA) Buttons: The design, placement, and wording of CTAs are crucial for driving conversions. Clear, concise, and visually appealing CTAs significantly impact user engagement and encourage desired actions. Examples include using compelling language (“Get Started Now”) or contrasting colors to make buttons stand out.
- Forms and Input Fields: Complex or lengthy forms can deter users. Streamlining form fields, reducing required information, and providing clear instructions can substantially improve conversion rates. An example would be reducing the number of fields in a contact form if not all fields are necessary.
- Product Pages: Detailed and engaging product pages are essential. High-quality images, persuasive descriptions, and clear pricing structures are vital. Consider adding customer testimonials or videos to build trust and credibility. Example: including user reviews on an e-commerce product page.
- Navigation and Site Structure: Intuitive navigation is key to keeping users engaged and enabling them to easily find the information they need. A well-organized website structure improves user experience and increases the likelihood of conversions. An example is a well-structured menu that easily guides users to different sections of the site.
- Website Design and Aesthetics: A visually appealing and user-friendly website design significantly impacts user experience. This encompasses factors such as page load speed, color schemes, typography, and overall aesthetics. An example is optimizing website images to load quickly to reduce bounce rate.
Common User Pain Points
Identifying and addressing user pain points is critical to improving conversion rates. Understanding the common frustrations users experience when interacting with a website is crucial for designing targeted A/B tests.
- Lack of Clarity: Users often abandon a purchase or fail to complete a task due to a lack of clear instructions, confusing navigation, or unclear information on a page. Example: a lack of clear instructions on how to proceed in a checkout process.
- Security Concerns: If users perceive a website as insecure, they might hesitate to provide personal information or complete transactions. Example: the absence of security badges or trust symbols on an e-commerce site.
- Inconvenient Processes: Users are often frustrated by complex or time-consuming processes. Streamlining procedures, reducing steps, and offering convenient payment options can improve conversion rates. Example: a lengthy checkout process with multiple steps can lead to abandonment.
Importance of User Research
Understanding user needs and motivations is fundamental for identifying potential areas for improvement and designing effective A/B tests. Comprehensive user research provides invaluable insights into user behavior and pain points.User research methods like surveys, usability testing, and interviews can reveal key insights into user behavior and preferences. This knowledge helps tailor A/B tests to address specific needs and improve the overall user experience.
Significance of Data Analysis in Determining Testing Priorities
Data analysis plays a critical role in determining which areas to prioritize for A/B testing. Analyzing existing website data reveals patterns, trends, and areas where conversions are low. This data helps determine which areas are most likely to yield significant improvements.Data analysis provides insights into user behavior and conversion funnels. By identifying areas with the lowest conversion rates or highest drop-off points, you can focus A/B testing efforts on these specific areas.
Metrics to Track During A/B Testing
Tracking the right metrics is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of A/B tests. A clear understanding of these metrics provides insights into user behavior and the impact of changes.
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Click-Through Rate (CTR) | The percentage of users who click on a specific element (e.g., a button). |
| Bounce Rate | The percentage of users who leave a website after viewing only one page. |
| Conversion Rate | The percentage of users who complete a desired action (e.g., making a purchase). |
| Average Session Duration | The average time users spend on the website. |
| Pages Per Session | The average number of pages a user visits during a session. |
Selecting the Right Metrics for Your Tests
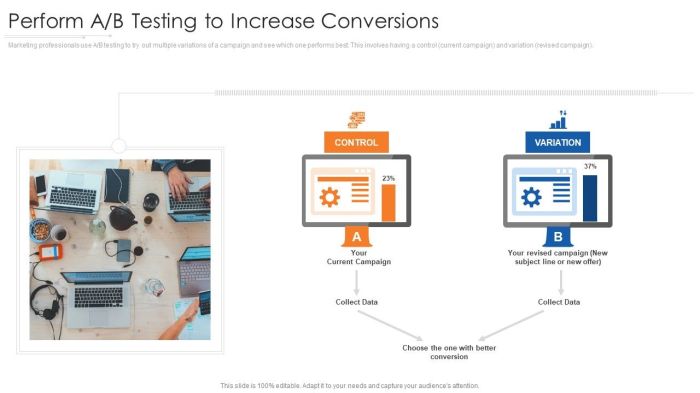
Defining clear goals is crucial for any A/B test. Without specific objectives, it’s impossible to measure success effectively. This clarity allows you to focus your efforts on the metrics that truly matter, leading to actionable insights and improved results. Choosing the right metrics directly impacts the interpretation of your test results and ultimately, your ability to optimize for conversions.Choosing the right metrics is paramount for A/B testing success.
The metrics you select should align directly with your defined goals, ensuring that the results accurately reflect the desired outcomes. By selecting relevant metrics, you avoid drawing misleading conclusions from your data and can make informed decisions based on reliable information. Aligning metrics with business objectives ensures the chosen measurements are valuable and contribute to achieving the desired outcomes.
Defining Clear Goals for Each A/B Test
A well-defined goal for an A/B test provides a clear target. This target serves as a compass, guiding the selection of appropriate metrics and ensuring that the results directly address the business objective. Examples of goals include increasing conversion rates, reducing bounce rates, or improving customer engagement. These clearly defined goals should drive the selection of metrics to measure success.
Choosing Relevant Metrics to Measure Success
The success of an A/B test hinges on the selection of appropriate metrics. Conversion rate, click-through rate, and average order value are all examples of relevant metrics that can be used to assess the success of an A/B test. Metrics should directly reflect the goals set for the test, enabling a precise evaluation of its effectiveness. For example, if the goal is to increase conversions, then conversion rate should be a key metric.
Calculating Statistically Significant Results
Statistical significance is crucial for determining whether the observed differences in A/B test results are genuine or due to random chance. A common method for calculating statistical significance is using a statistical hypothesis test, like a Z-test or a t-test. These tests evaluate the likelihood of observing the results under the assumption that there’s no real difference between the variations.
A p-value below a predetermined significance level (typically 0.05) indicates statistical significance. Understanding statistical significance allows you to confidently determine if observed changes are genuine improvements.
A p-value less than 0.05 usually indicates statistical significance, meaning the observed difference between the variations is unlikely due to random chance.
Setting Up Control and Experimental Groups
A well-structured A/B test relies on the creation of a control group and an experimental group. The control group serves as a benchmark, representing the current version or baseline. The experimental group receives the variation or change being tested. This controlled setup allows for a direct comparison of the two groups and helps isolate the impact of the variation.
A robust experimental design is crucial to draw meaningful conclusions from the A/B test results.
Ready to boost your conversions tomorrow? 9 A/B tests can make a huge difference, but understanding common mobile app pitfalls like those detailed in 11 mobile app pitfalls is crucial. These tests, focusing on things like button placement and call-to-action wording, can significantly improve user engagement and ultimately double your conversions. So, get ready to optimize!
Selecting Appropriate Sample Sizes
Determining the appropriate sample size is essential for ensuring reliable results. A larger sample size generally leads to more precise estimates and greater statistical power. A sample size that is too small may fail to detect a real difference if one exists. Conversely, an excessively large sample size may be unnecessary and costly. Tools and calculators are available to estimate the necessary sample size, given the desired level of confidence and expected effect size.
Proper sample size selection ensures that the test yields meaningful results with sufficient confidence.
Creating Variations for Each Test
Crafting effective variations is crucial for successful A/B testing. It’s not enough to simply change a color or button text; you need to understand the underlying reasons behind potential improvements and craft variations that genuinely resonate with your target audience. A well-designed variation can significantly impact conversion rates, while a poorly executed one can lead to wasted effort and potentially negative outcomes.A critical aspect of variation creation is anticipating user behavior and anticipating how different design elements might influence their decision-making process.
For instance, a subtle change in button color might inadvertently make it less noticeable, leading to a drop in clicks. Conversely, a bold variation might create a positive impression but also potentially overwhelm the user. Careful consideration of user experience (UX) principles is paramount.
Button Variation Strategies
Understanding the different types of button variations is essential for generating compelling and effective A/B test variations. Variations should focus on clarity, call to action, and user engagement. Consider these approaches when designing variations for a button:
- Color Variations: A change in button color can significantly impact visibility and perceived urgency. Testing different shades, hues, and saturation levels can identify which color resonates most with your target audience. For example, a button that transitions to a brighter shade upon hover can highlight its importance. A muted color variation may be suitable for a less prominent call to action.
- Text Variations: The wording on a button is critical for driving engagement. Testing different phrasing and length of text can uncover the most effective way to prompt users to take action. Examples include “Buy Now,” “Learn More,” “Get Started,” and different word choices to improve user engagement.
- Shape Variations: Modifying the shape of a button can change its visual appeal and usability. Testing round buttons, rectangular buttons, or other shapes can be beneficial. For instance, a rectangular button might be more practical for larger quantities of text, while a rounded button can appear more inviting. These variations can be crucial for improving user engagement.
User Experience Considerations in Design Changes
User experience (UX) should be a core element in your design variations. Changes should prioritize clarity, ease of use, and a visually appealing experience. When making modifications, consider the following:
- Navigation: Ensuring smooth and intuitive navigation throughout the design is paramount. Users should easily find what they need, and the layout should support a seamless user flow.
- Accessibility: Consider the needs of users with disabilities. Ensure sufficient contrast between text and background, and ensure all content is accessible to those using assistive technologies.
- Clarity and Readability: Use clear and concise language that is easily understood by the target audience. Employ legible fonts and appropriate spacing to enhance readability. Avoid overly complex or cluttered layouts that could confuse users.
Design Variation Examples
The following table Artikels different design variations for a webpage element, focusing on headlines and form fields:
| Element | Original Design | Variation 1 | Variation 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Headline | Limited-Time Offer! | Exclusive Discount! | Save Now! |
| Form Field (Email) |
Implementing and Monitoring the Tests
A/B testing is only as good as its execution. Proper implementation and meticulous monitoring are crucial for extracting meaningful insights and driving real conversion improvements. A poorly implemented test can lead to misleading results, wasting time and resources. Careful planning and execution, along with thorough monitoring, are key to ensuring the validity and reliability of your findings.The success of A/B tests hinges on meticulous implementation, consistent monitoring, and a robust analysis of the collected data.
This ensures that you’re not only making data-driven decisions but also making informed decisions based on accurate results.
Implementing the A/B Test
Implementing an A/B test involves strategically deploying different variations of your website or landing page to distinct segments of your audience. This controlled rollout allows you to compare the performance of these variations and identify the most effective option. This is a critical step in the process and must be done with precision and attention to detail. Careful setup and implementation ensure that the test is accurate and unbiased.
Tracking Variation Performance
Accurate tracking of each variation’s performance is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of your changes. This involves implementing robust analytics tools to meticulously record key metrics. This detailed tracking allows for a granular understanding of how different variations affect user engagement and conversion rates. Utilize web analytics tools to monitor user interactions, page views, bounce rates, and conversion events for each variation.
These tools provide the necessary data for analysis and improvement.
Monitoring and Analyzing Results
A step-by-step approach to monitoring and analyzing A/B test results is vital for extracting actionable insights. Start by defining a clear timeframe for your tests, ensuring sufficient data collection to avoid drawing conclusions from limited or incomplete results. Regularly check the performance metrics of each variation. Identify any patterns or trends emerging from the data, and analyze them to determine which variation is outperforming others.
Analyzing Data Over Time
Analyzing data over a sufficient timeframe is critical for avoiding misleading results. A short test period may not provide enough data to discern meaningful differences in performance between variations. A longer test period allows for a more comprehensive understanding of user behavior and conversion rates, thereby preventing inaccurate conclusions. Consider the variability in user behavior over time; some metrics may fluctuate significantly, potentially impacting the results.
Avoid jumping to conclusions based on short-term trends; look for consistent performance across a longer period.
Interpreting Statistical Significance
Statistical significance is crucial for determining the winning variation in an A/B test. Interpreting statistical significance involves assessing whether the observed differences in performance between variations are likely due to chance or a genuine difference in effectiveness. Statistical analysis tools can help in this assessment, enabling a more accurate interpretation of the data. Tools and software are readily available for conducting these analyses.
Look for a statistically significant difference in the conversion rates between variations.
Looking to boost your conversions? 9 A/B tests are ready to go, and you can run them tomorrow! To really nail down your content strategy, dive into the advanced guide to custom content marketing. the advanced guide to custom content marketing will show you how to create truly unique content that resonates with your audience.
These tests, combined with a well-crafted strategy, can lead to a significant jump in conversions.
Determining Winning Variations
To identify the winning variations, analyze the collected data and identify the variation with the highest conversion rate, alongside other key metrics. Consider A/B tests to be a continuous process, and analyze the data over a sufficient timeframe to ensure accuracy. Consider the impact on other key performance indicators (KPIs), such as bounce rate or time on site, when determining the winning variation.
Look for consistent improvements in conversion rates and other metrics, confirming the effectiveness of the winning variation.
9 Specific A/B Test Ideas
Ready to supercharge your conversion rates? Let’s dive into 9 actionable A/B test ideas you can implement tomorrow. These tests are designed to be quick to set up and analyze, allowing you to see results swiftly and make data-driven adjustments to your website. Remember, consistent testing and iteration are key to optimizing your online presence and driving significant growth.
A/B Test Ideas for Increased Conversions
These tests target different aspects of your website, from calls to action to product descriptions. Understanding which elements resonate most with your audience is critical for boosting conversions. By isolating and testing specific elements, you can identify what works best and what needs improvement.
- Headline Variations: Test different headline options to see which captures attention and encourages clicks. Variation 1: A concise, benefit-driven headline. Variation 2: A more intriguing, question-based headline. Variation 3: A headline that highlights a unique selling proposition. This test isolates the headline’s impact on click-through rates.
Improved conversion rates are directly linked to the headline that effectively communicates value to your target audience.
- Call-to-Action (CTA) Button Color and Text: Experiment with different colors and text for your CTA buttons. Variation 1: A vibrant, attention-grabbing color. Variation 2: A more subtle, yet noticeable color. Variation 3: Text that explicitly states the benefit (e.g., “Get Started Now”). This test isolates the impact of visual cues and persuasive language on click-through rates.
The most effective CTA will yield the highest click-through rate, leading to increased conversions.
- Product Image Variations: Test different product images to determine which evokes greater interest and desire. Variation 1: A high-quality, professional product shot. Variation 2: A more lifestyle-focused image that showcases the product in use. Variation 3: A product image with customer testimonials incorporated. This test isolates the impact of visual appeal on purchase intent.
The most compelling image will likely increase engagement and lead to more conversions.
- Pricing Structure: Test different pricing tiers and descriptions to see which resonate best. Variation 1: A tiered pricing model with clear benefits for each level. Variation 2: A more competitive pricing structure with a lower entry-level price. Variation 3: A “premium” option emphasizing higher quality or additional features. This test isolates the impact of perceived value and pricing on purchase decisions.
The most attractive pricing plan should drive more sales.
- Form Length: Test different form lengths for collecting customer information. Variation 1: A concise form with only essential fields. Variation 2: A form with additional optional fields. Variation 3: A form that incorporates a progress bar. This test isolates the impact of form length on completion rates.
A shorter, more straightforward form will likely encourage higher completion rates.
- Social Proof: Test different levels of social proof (e.g., testimonials, customer reviews, ratings). Variation 1: A page with no social proof. Variation 2: A page showcasing 2-3 customer testimonials. Variation 3: A page showcasing a large number of customer reviews and ratings. This test isolates the impact of social validation on trust and purchase intent.
Positive social proof will often increase customer confidence and drive conversions.
- Checkout Process: Test different checkout flow options to determine which is the easiest and most efficient. Variation 1: A standard checkout process. Variation 2: A streamlined checkout with fewer steps. Variation 3: A checkout with an option to save payment information. This test isolates the impact of the checkout experience on completion rates.
A smoother checkout process will likely result in fewer abandoned carts and more completed purchases.
- Product Description Variations: Test different product descriptions to see which is most persuasive. Variation 1: A concise, benefit-driven description. Variation 2: A detailed description that highlights features and specifications. Variation 3: A description that incorporates customer testimonials. This test isolates the impact of the product description on purchase intent.
A more engaging description will improve the likelihood of customers making a purchase.
- Homepage Layout: Test different homepage layouts to see which highlights key information and offers a seamless user experience. Variation 1: A traditional homepage layout. Variation 2: A homepage that features a prominent call to action. Variation 3: A homepage with a carousel of product features. This test isolates the impact of the homepage layout on engagement and conversions.
A more intuitive and engaging homepage will lead to higher conversion rates.
A/B Test Structure and Metrics
| Test | Variations | Metrics to Improve |
|---|---|---|
| Headline Variations | Different headlines | Click-through rate, conversion rate |
| CTA Button | Color, text | Click-through rate, conversion rate |
| Product Image | Different images | Engagement, purchase intent, conversion rate |
| Pricing Structure | Tiered pricing, competitive pricing | Purchase decisions, average order value |
| Form Length | Concise, detailed | Form completion rate |
| Social Proof | Different levels | Trust, purchase intent |
| Checkout Process | Standard, streamlined | Completion rate, cart abandonment |
| Product Description | Concise, detailed | Purchase intent, average order value |
| Homepage Layout | Traditional, prominent CTA, carousel | Engagement, conversions |
Analyzing and Interpreting Results
A/B testing is only as good as your ability to interpret the results. Simply running tests isn’t enough; you need a clear understanding of what the data is telling you. Effective analysis allows you to confidently determine which variation performs best and justify your decisions. This section will delve into the crucial steps for interpreting your A/B test results.Effective analysis of A/B test results involves several key steps, from understanding statistical significance to comparing different variations.
By mastering these techniques, you can gain valuable insights and make data-driven decisions that optimize your conversion rates.
Identifying Statistically Significant Results
To determine if a difference in performance between variations is real and not just due to chance, you need to look at statistical significance. A statistically significant result means that the observed difference is unlikely to have occurred by random chance. This is typically measured using a p-value.
Understanding Confidence Intervals and P-Values
Confidence intervals provide a range of values within which the true population parameter (like conversion rate) likely lies. A narrower interval indicates a more precise estimate. P-values represent the probability of observing results as extreme as, or more extreme than, those seen in the test if there were no real difference between the variations. A low p-value (typically below 0.05) suggests a statistically significant difference.
A p-value of 0.05 means there’s a 5% chance the observed difference is due to random chance.
Interpreting A/B Test Results
Interpreting results involves more than just looking at numbers. Consider the context of your test, the specific variation, and the overall goals of your campaign. Don’t just focus on the absolute difference in conversion rates; consider the percentage change and how it relates to your current conversion rates. For example, a 10% increase in conversion rate on a low-conversion website might be more significant than a 1% increase on a high-conversion website.
Comparing Different Variations and Understanding Their Performance Relative to Each Other
A crucial aspect of analysis is comparing the performance of different variations. Consider the overall context of your test, not just the statistical significance. For instance, a variation might have a significantly higher conversion rate but a lower average order value, leading to a potentially lower overall revenue.
Table Illustrating A/B Test Results Comparison
This table demonstrates how to compare A/B test results and draw conclusions. Remember, the specific metrics and conclusions will vary depending on your particular test.
| Variation | Conversion Rate | Average Order Value | Revenue | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variation A | 10% | $50 | $500 | Good overall performance, but potential for improvement in AOV. |
| Variation B | 12% | $45 | $540 | Higher conversion rate, but lower AOV. May be a better choice depending on the target audience and desired outcome. |
| Variation C | 11% | $55 | $605 | Excellent balance between conversion rate and AOV. Likely the best option. |
Implementing Winning Variations
Congratulations on identifying the winning variations in your A/B tests! Now comes the crucial step of implementing those changes and monitoring their impact. This process isn’t just about clicking a button; it’s about strategically rolling out improvements and tracking their effect on your website’s performance.Successfully implementing winning variations requires a methodical approach, ensuring a smooth transition and accurate measurement of results.
It’s essential to document the process and learn from each iteration to optimize future tests. This meticulous approach will help you maximize the impact of your A/B testing efforts.
Implementing Winning Variations Across the Website
Implementing the winning variations requires careful planning and execution to avoid disrupting the website’s functionality. A phased rollout approach is recommended, starting with a small segment of users to test the impact on a controlled scale. This allows for identification of any unforeseen issues before a wider implementation.
Documenting Results and Lessons Learned
Thorough documentation is vital for continuous improvement. Detailed records of each test, including the variations, metrics used, results, and any unexpected outcomes, are essential. This information provides valuable insights for future tests.
Importance of Continuous Improvement and Iterative Testing
Continuous improvement and iterative testing are crucial for ongoing success. A/B testing should not be a one-time event; rather, it’s an ongoing process of refinement. By analyzing results and incorporating feedback from tests, businesses can continuously optimize their website’s design and functionality.
Integrating A/B Testing into Ongoing Website Maintenance
Integrating A/B testing into ongoing website maintenance requires establishing a routine for identifying potential areas for improvement. Regular reviews of key performance indicators (KPIs) and user feedback can reveal opportunities for optimization.
Measuring Impact of Implemented Changes, 9 ab tests that you can run tomorrow to double your conversions
Measuring the impact of implemented changes involves tracking key metrics over time. This includes conversion rates, bounce rates, time on page, and other relevant data. Tools like Google Analytics can provide valuable insights into the performance of the winning variations. Regular monitoring allows for adjustments to the implemented changes as needed, ensuring optimal performance.
Advanced A/B Testing Strategies: 9 Ab Tests That You Can Run Tomorrow To Double Your Conversions
A/B testing, while powerful for optimizing conversions, often requires more sophisticated approaches than simple variations. Moving beyond basic comparisons, advanced strategies allow for more nuanced understanding of user behavior and better conversion optimization. These techniques can reveal insights into complex interactions and preferences, leading to significantly improved results.Advanced A/B testing methods go beyond comparing two options. They explore combinations, user journeys, and feedback to fine-tune user experiences and ultimately drive conversions.
These methods can be particularly valuable in complex systems where the impact of multiple elements needs to be evaluated.
Multivariate Testing
Multivariate testing (MVT) explores the impact of multiple variations of multiple elements simultaneously. It moves beyond testing one variable at a time, allowing marketers to understand how different combinations of elements affect user behavior. Instead of testing a single button color, for instance, MVT can simultaneously test different button colors, text variations, and image placement. This approach reveals which combinations perform best.
This significantly broadens the scope of optimization by evaluating the synergistic effects of different elements. By systematically testing variations of several elements simultaneously, MVT provides a comprehensive understanding of how different combinations affect user behavior. This, in turn, leads to more holistic optimization decisions, maximizing the potential for improved conversion rates.
Sequential Testing
Sequential testing is a dynamic approach to A/B testing. It allows you to stop a test early if the results are conclusive, rather than waiting for a pre-determined number of visitors. If a variation is significantly outperforming the control group early on, sequential testing allows you to stop the test and implement the winning variation, thereby saving time and resources.
This methodology leverages statistical significance calculations to determine when the test can be stopped. The advantage is that you can gain results quickly, potentially implementing improvements sooner than with traditional methods. For example, if a new checkout flow significantly increases conversions within the first 24 hours, a sequential test can stop the test, allowing for a quick launch of the improved flow.
Incorporating User Feedback
Incorporating user feedback into A/B testing can enhance the insights derived from data analysis. User feedback provides qualitative information that complements the quantitative data collected from tests. Collecting feedback on variations can provide valuable insights into why certain changes are effective or ineffective, and can help tailor subsequent tests based on specific user needs. For instance, analyzing user feedback on a redesigned website can identify pain points that weren’t apparent in the initial data, leading to improvements that align more closely with user expectations.
Integrating user feedback helps to improve the usability and relevance of the product/service.
Utilizing Different Testing Tools
Employing a variety of A/B testing tools offers a comprehensive approach to optimization. Different tools provide varying features and capabilities. Using a combination of tools can ensure comprehensive data collection and analysis. For instance, a tool specializing in multivariate testing can complement a tool focusing on user journey analysis, resulting in a more thorough understanding of user behavior and conversion funnels.
Advanced Testing Methods
- Multivariate Testing (MVT): Simultaneously tests multiple variables and their interactions to identify optimal combinations. This approach provides a deeper understanding of complex user behavior by considering the synergistic effect of changes.
- Sequential Testing: Dynamically stops tests early if a clear winner emerges, saving time and resources. This is especially valuable for rapid iterations and quicker implementation of winning variations.
- User Feedback Integration: Incorporating qualitative data from users alongside quantitative test results provides a more holistic understanding of the effectiveness of changes and identifies potential areas for improvement.
- Multi-Channel Testing: Testing variations across different marketing channels (e.g., social media, email, search ads) to understand how variations perform across diverse user segments.
- A/B Testing for User Journeys: Analyzing variations across multiple steps of a user journey (e.g., signup process, checkout flow) to optimize conversions at each stage.
- Testing for Personalization: Using A/B testing to personalize user experiences based on individual characteristics, preferences, and behavior. This creates tailored experiences that resonate with specific user segments.
- Testing for Accessibility: Optimizing website and application design for users with disabilities, ensuring that all users have a positive experience. This approach improves inclusivity and broadens the target audience.
- Testing for Localization: Optimizing content and design for different cultures and languages to appeal to global audiences. This can include variations in wording, imagery, and layout.
- Testing with Machine Learning: Leveraging machine learning algorithms to analyze test results and predict which variations are most likely to succeed, thereby improving the efficiency and effectiveness of the optimization process.
Closing Summary
We’ve journeyed through the world of A/B testing, equipping you with the tools and techniques to elevate your website’s conversion rates. By implementing these nine powerful tests, you’re not just optimizing for immediate results; you’re laying the foundation for continuous improvement and long-term growth. Embrace the data, refine your approach, and watch your conversions soar.