A beginners guide to canonical tags infographics – A beginner’s guide to canonical tags infographics dives deep into the world of , demystifying these crucial elements for website optimization. We’ll unpack how canonical tags work, focusing on how they address duplicate content issues and enhance search engine crawlability. This visual guide will be a powerful resource, helping you understand and implement these essential tags for better search rankings.
This infographic-based guide will simplify the complex world of canonical tags, providing a clear and concise understanding for anyone new to . The step-by-step instructions, combined with visually engaging elements, will make learning about canonical tags a breeze. We’ll cover common pitfalls to avoid, making the entire process much smoother and more effective.
Introduction to Canonical Tags
Canonical tags are crucial for search engine optimization (). They help search engines understand which version of a webpage is the primary or authoritative one, preventing issues caused by duplicate content. This is vital for maintaining a positive search ranking and ensuring that users are directed to the correct and most up-to-date version of a page.Canonical tags essentially tell search engines which URL should be considered the “original” source of a piece of content.
This is particularly important when you have multiple URLs that display largely identical content, such as different versions of a product page or a page available via different means of access.
Understanding Duplicate Content
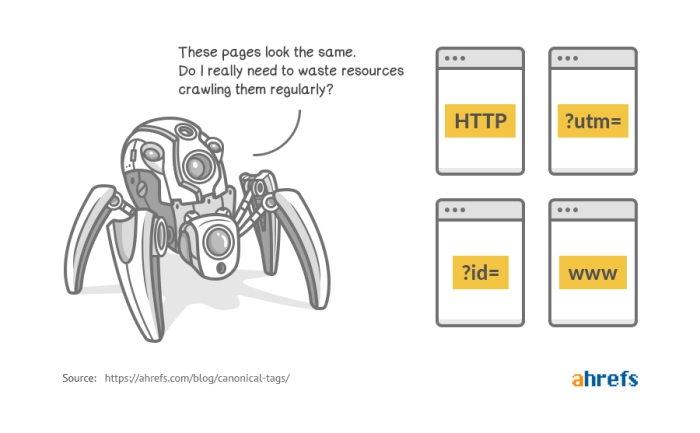
Duplicate content occurs when significant portions of content are identical across multiple URLs. Search engines might penalize websites with duplicate content, potentially affecting their search rankings. Canonical tags address this issue by signaling to search engines which version of the page should be prioritized.
A beginner’s guide to canonical tags infographics is a great starting point for SEO optimization. Understanding how to implement them correctly can significantly improve your website’s search ranking. However, you should also consider the impact of things like Apple’s ad tracking in Safari apple ad tracking safari , as it can sometimes conflict with your canonical tag strategies.
Ultimately, a strong understanding of canonical tags remains crucial for a successful online presence.
How Canonical Tags Work
Canonical tags are HTML meta tags that specify the canonical URL for a page. Search engines use this information to understand which URL represents the authoritative source of the content. When a search engine encounters a canonical tag, it prioritizes the specified URL for indexing and ranking. This ensures that the page with the canonical tag is more likely to appear in search results, thereby improving the website’s .
Importance for Search Engine Crawlers
Canonical tags are vital for search engine crawlers because they prevent the indexing of duplicate content. By directing crawlers to the canonical URL, search engines avoid creating multiple entries for the same content, saving resources and improving the accuracy of their search results. This efficiency translates into a more accurate representation of a website’s content to users.
Implementing Canonical Tags: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Identify duplicate content pages. This involves comparing different versions of pages, including those accessible via different methods or variations in parameters.
- Determine the canonical URL. This is the URL that represents the definitive version of the content. Choose the most complete, updated, and comprehensive version.
- Add the canonical tag to the section of the HTML. This is typically done within the HTML code of the page, which is accessible via a text editor or a website content management system.
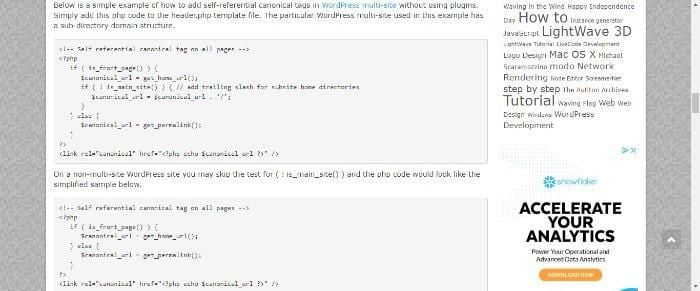
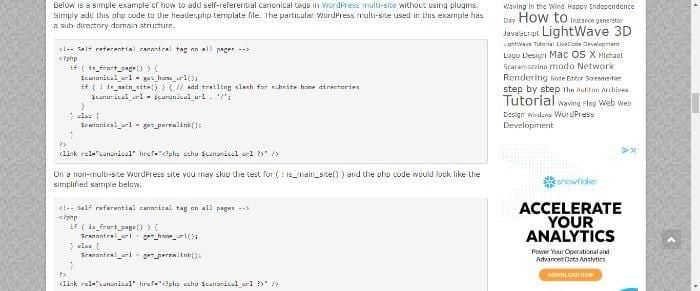
- Example of the canonical tag:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.example.com/canonical-page" />. Replace `https://www.example.com/canonical-page` with the actual canonical URL. - Verify the implementation. Use web developer tools or analysis tools to check if the canonical tag is correctly implemented and that the search engine is acknowledging it.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Incorrect canonical tag placement. The canonical tag must be placed within the ` ` section of the HTML.
- Mismatched canonical URLs. Ensure the canonical URL accurately reflects the definitive page.
- Incorrect or outdated canonical URL. Regularly review canonical tags and update them as needed to avoid inconsistencies.
- Missing canonical tags. If duplicate content exists, canonical tags are essential.
- Using canonical tags for unrelated content. Canonical tags are intended for content that is substantially similar.
Understanding Infographics: A Beginners Guide To Canonical Tags Infographics
Infographics are visual representations of information, designed to make complex data easier to understand and remember. They’re a powerful tool for communicating intricate concepts, such as the nuances of canonical tags, in a way that’s engaging and accessible to a wide audience. They achieve this by combining data with compelling visuals, replacing dense text with easily digestible charts, graphs, and illustrations.
This approach is particularly valuable for beginners and those seeking a quick grasp of technical subjects.Visualizations effectively simplify intricate technical details. By translating complex data points into easily understandable visual formats, infographics transform abstract concepts into tangible, relatable representations. This approach, particularly when combined with clear annotations and concise labels, makes the information more readily absorbed and retained. For example, showing the relationship between canonical tags and website structure through a flow chart or a hierarchical diagram, can significantly enhance comprehension compared to dense paragraphs.
So, you’re diving into canonical tags for the first time? A good visual aid, like an infographic, can be a real game-changer for understanding how they work. But, while mastering canonical tags is crucial, it’s equally important to be aware of situations where your website’s management (MA) strategies could actually damage your brand. For example, if you’re not careful about duplicates, or using incorrect configurations, it can negatively impact your SEO.
Understanding these potential pitfalls, as explored in 5 situations when ma can hurt your brand , is key to using canonical tags effectively. This beginner’s guide to canonical tags infographics will help you avoid those common issues.
Types of Infographics for Canonical Tags
Different infographic types can effectively illustrate canonical tag information. A flowchart, for instance, can visually map the canonical tag implementation process from the initial identification of duplicate content to the final implementation of the canonical tag. A comparison chart can contrast different canonical tag strategies, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses. Another option is an infographic that visually represents the impact of canonical tags on search engine rankings, using graphs to illustrate the potential gains in organic traffic.
A simple diagram depicting a website’s structure and how canonical tags link different pages within that structure is also useful.
Effective Visual Representation of Technical Concepts
Using visuals to simplify technical concepts involves choosing the right type of infographic and carefully designing its elements. Clear and concise labeling of every component is crucial. Avoid using overly complex or intricate designs that might distract from the core message. For example, using consistent colors and fonts across the infographic, and using high-quality images, makes the information more professional and readable.
Use a consistent color scheme to represent different elements and maintain visual clarity. The color coding will effectively highlight and group the various aspects of canonical tags, allowing the reader to follow the relationships easily.
Tools for Creating Infographics
Several tools facilitate the creation of engaging infographics. Canva is a user-friendly platform with a wide array of templates and design elements. Piktochart offers a range of infographic templates suitable for various purposes, including those that represent concepts like canonical tags. Visme is another versatile tool that provides a variety of templates, allowing users to customize their designs and effectively convey their message.
More advanced tools like Adobe Illustrator or Figma can provide more control over design elements, if one has prior experience with design software. Online graphic design tools provide a spectrum of features, ranging from simple layouts to more advanced customization options.
Best Practices for Designing Engaging Infographics
Designing effective infographics requires attention to detail. Maintain a consistent color palette to create a visually appealing and organized presentation. Use high-quality images and visuals that enhance the information without distracting from the core message. Ensure the visual elements are relevant and appropriate to the topic. Clearly label every element to avoid ambiguity and maintain clarity.
Employ a concise and direct language, avoiding jargon or overly complex phrases. Ensure that the infographic’s design complements the content and enhances comprehension.
Infographic Structure for Beginners’ Guide
This infographic will serve as a beginner’s guide to canonical tags, breaking down complex concepts into easily digestible visual components. The structure prioritizes clarity and accessibility, using visuals to illustrate the practical application of canonical tags for . The design will incorporate a responsive layout, ensuring optimal viewing across various devices.
Visual Representation of the Canonical Tag Concept
The infographic will begin with a clear visual representation of the canonical tag’s purpose. A simplified diagram will illustrate how canonical tags direct search engine crawlers to the preferred version of a webpage when multiple URLs exist for the same content. This introductory section will emphasize the importance of avoiding duplicate content and how canonical tags help maintain website structure and health.
A visually appealing graphic, possibly a flowchart, will clearly show the process of a search engine following a canonical tag. The graphic should highlight the flow from the URL to the canonical URL.
Identifying Duplicate Content Issues
This section addresses the identification of duplicate content. A table will visually categorize different types of duplicate content problems, illustrating how canonical tags solve each problem.
| Duplicate Content Type | Description | Canonical Tag Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Exact Duplicate | Identical content on multiple URLs. | Use a canonical tag on the less important URL to point to the primary URL. |
| Near Duplicate | Content with minor differences, like variations in product descriptions. | Use a canonical tag to point to the primary, authoritative version. |
| Dynamic Content Variations | Same content, but generated differently (e.g., different dates or product filters). | Implement a canonical tag to the main, comprehensive page. |
Implementing Canonical Tags Effectively
This section will guide users through the practical steps of implementing canonical tags. A step-by-step guide using bullet points will demonstrate how to correctly add canonical tags to HTML.
- Identify the target URL for each page.
- Determine the preferred version of the page.
- Add the canonical tag meta element to the <head> section of the HTML page. The format should be clear:
<link rel="canonical" href="canonical-url.com"> - Test the implementation to confirm the search engine crawlers are correctly identifying the canonical URL.
Using Canonical Tags for Different Scenarios
This section will present different scenarios where canonical tags are used, with real-world examples and descriptions of the problem.
- Multiple Versions of a Page: A website might have mobile and desktop versions of a page. Using a canonical tag for the desktop version on the mobile page ensures search engines prioritize the desktop content.
- Product Variations: An e-commerce website might have different versions of a product page based on variations in color or size. A canonical tag directs search engines to the primary product page.
- Pagination Issues: When dealing with pages of results, canonical tags are crucial. Using canonical tags ensures that search engines don’t index multiple pages of results as separate entities. A real-world example is pagination on a blog or news site, where canonical tags are used to direct the search engine to the main article page rather than individual pages of results.
Troubleshooting Common Canonical Tag Issues
This section details common errors and their solutions, using visuals like a flowchart or checklist to highlight potential problems. It will cover issues like incorrect implementation, incorrect use of multiple canonical tags, and issues with redirecting or broken links.
Content for the Infographic Sections
This section details the content for each infographic section, focusing on clear explanations and visual aids. We’ll cover topics like defining canonical tags, illustrating their benefits, and showing how to implement them. Each section will be designed for beginner understanding, using simple language and clear examples.To effectively convey complex concepts to beginners, a visual approach is paramount.
Using charts, diagrams, and icons will make the infographic engaging and easy to grasp. We’ll also emphasize the practical advantages of using canonical tags, making the information relatable and valuable for readers.
Defining Canonical Tags
Canonical tags are crucial for search engine optimization (). They help search engines understand which version of a webpage is the primary one. This prevents duplicate content issues, which can harm a website’s ranking. Proper use of canonical tags can improve a site’s by reducing duplicate content penalties.
- What Canonical Tags Are: Canonical tags are meta tags that specify the preferred version of a webpage. They are used to tell search engines which URL is the authoritative version of a page, preventing issues with duplicate content.
- Importance of Uniqueness: Search engines prioritize unique content. Canonical tags help ensure that search engines index only the desired version of a page, preventing duplicate content penalties that could harm search rankings.
- Example: Imagine a product page with different variations like size or color. A canonical tag would point search engines to the main product page, while other variations would link to that main page via a canonical tag. This prevents duplicate content issues, as search engines see the variations as references to the main page.
Benefits of Using Canonical Tags
Implementing canonical tags delivers significant advantages for . They maintain website structure, and improve ranking.
- Improved Ranking: By preventing duplicate content, canonical tags help search engines understand the primary version of a page. This can improve a website’s search engine ranking as search engines index the correct version, without being confused by multiple similar pages.
- Reduced Duplicate Content Issues: Canonical tags explicitly tell search engines which version of a page is the preferred one. This significantly reduces the risk of duplicate content penalties, a major concern for website owners.
- Enhanced Crawling Efficiency: By directing search engines to the primary version of a page, canonical tags enhance the crawling efficiency of search engines. This improves indexing speed and overall website performance.
Implementing Canonical Tags
This section will guide users on the practical application of canonical tags. The infographic will demonstrate the correct implementation using code examples.
- HTML Implementation: The infographic will visually represent the HTML code for adding a canonical tag to a webpage. A simple HTML example will be included, such as placing a ` ` tag within the ` ` section of the relevant HTML file.
- Practical Scenarios: The infographic will showcase how to use canonical tags in various scenarios, like product variations, different language versions of a page, or mobile versions of a website. A table will be used to demonstrate various situations, highlighting the correct canonical implementation for each case.
- Example: The infographic will show an example of a website with different product variations (e.g., a t-shirt in different colors). Each variation page would include a canonical tag pointing to the main product page, preventing search engines from indexing each variation as separate pages.
Visual Elements
The infographic will utilize charts, diagrams, and icons to make the concepts easier to understand.
- Charts: A bar chart can illustrate the impact of using canonical tags on search engine rankings. This would show a significant increase in rankings after implementing canonical tags.
- Diagrams: A flowchart can guide users through the process of implementing canonical tags, visually representing the steps from identifying the main page to adding the canonical tag to the relevant pages.
- Icons: Icons can visually represent the concept of duplicate content and how canonical tags resolve the issue. A visual of a single page with arrows pointing to it from various other pages could represent this.
Example Infographic Sections
This section details how to structure an infographic guide on canonical tags, focusing on clear examples and visual representations. We’ll break down sections dedicated to defining canonical tags, highlighting common issues, and showcasing solutions with practical implementations across various scenarios. Visual elements will be crucial for conveying complex information in a digestible format.
Ever wondered why your canonical tags infographic might not perfectly match your SEO data in Google Analytics and Search Console? It’s a common issue, and understanding the differences between the two tools is key. Learning how these tools work independently, as well as the potential discrepancies, is crucial for any beginner. This often boils down to the way Google interprets and processes data, and a deep dive into why Google Analytics and Search Console sometimes show different data on your SEO performance can help you get a clearer picture.
You can check out this great article explaining why Google Analytics and Google Search Console data can differ why google analytics and google search console show different seo data. Regardless, a solid understanding of canonical tags, as detailed in a beginner’s guide infographic, remains important for optimizing your site’s SEO.
Defining Canonical Tags
This section will concisely explain canonical tags, emphasizing their role in search engine optimization (). A clear and concise definition of canonical tags is paramount for a beginner’s understanding. A simple explanation, perhaps using a metaphor like a “primary address” for a website’s content, will help the reader grasp the concept quickly. The visual representation could include a flowchart depicting how canonical tags function within a website’s structure, showing the relationship between different URLs.
| Term | Definition | Visual Representation |
|---|---|---|
| Canonical Tag | A specific HTML element that tells search engines which version of a webpage is the primary one. | A small tag icon next to a URL, or a box highlighting the canonical URL in a diagram. |
Common Issues with Canonical Tags
This section will cover common problems website owners encounter when using canonical tags, including incorrect implementation and improper use cases. Addressing these issues is crucial for guiding users toward best practices.
| Issue | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect Implementation | Using the incorrect syntax or missing the tag entirely. | |
| Redundant Canonical Tags | Implementing canonical tags on multiple pages for the same content, creating confusion for search engines. | Using canonical tags on both the main page and a specific product page, both pointing to the same content. |
| Incorrect Targeting | Implementing canonical tags to the wrong URLs or incorrectly using different canonical tags for various content. | Pointing a canonical tag on a product page to a category page when the product page is the primary page. |
Implementing Canonical Tags in Different Scenarios
This section will demonstrate how canonical tags are applied in various scenarios. Examples will include scenarios involving multiple URLs with identical content, handling redirects, and managing duplicate content across different domains.
| Scenario | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Duplicate Content on Different Domains | Two separate websites have identical content. | Implement a canonical tag on the primary domain’s URL, pointing to it from the secondary domain. |
| Handling Redirects | Redirecting a URL to another URL. | Use canonical tags to indicate the original URL. |
| Multiple Versions of a Page | A page with various formats or different layouts (mobile, desktop). | Use canonical tags to specify the primary version, ensuring search engines index the desired version. |
Using Examples and Use Cases
This section will highlight practical examples and use cases, providing a visual representation of how canonical tags are implemented in real-world scenarios. The examples will be straightforward and relatable.
A small e-commerce store with multiple product pages. Visual representation: A diagram showing multiple product pages with the same product. The canonical tag would point to a single product page to avoid duplicate content.
A blog with various article formats (mobile, desktop). Visual representation: A simple flowchart showing the relationship between different versions of the blog post. The canonical tag would specify the primary version for indexing.
Visual Elements
Visual elements are key for conveying the information effectively.
- Flowcharts: Illustrate the flow of canonical tags within a website’s structure.
- Icons: Represent canonical tags with simple, easily recognizable icons.
- Color-coding: Highlight primary and secondary URLs.
- Tables: Summarize information about different issues and solutions.
- Diagrams: Show how canonical tags function within various website architectures.
Responsive Design and Visual Appeal
Infographics are most effective when they are easily digestible and visually engaging. A well-designed infographic adapts to different screen sizes and maintains a consistent aesthetic across all platforms. This section will guide you through creating responsive infographics and maximizing visual impact.A key element to achieving this is understanding how to make the infographic adaptable to various screen sizes. Employing responsive design principles ensures that your infographic remains clear and readable on computers, tablets, and mobile devices.
Creating a Responsive Infographic with HTML Tables
Using HTML tables is a practical method for creating a responsive infographic. The structure of tables allows for organized content and flexibility in adapting to different screen widths. By utilizing CSS properties, you can adjust the width and height of table cells and rows dynamically, ensuring your infographic remains visually appealing on various devices. For example, you can adjust the size of the cells containing the infographic elements, such as titles, descriptions, or data visualizations, to accommodate different screen sizes.
This responsive approach makes the infographic readable on smaller screens without compromising its layout.
Consistent Visual Style
A consistent visual style is crucial for a cohesive and professional-looking infographic. This encompasses the use of a unified color palette, font choices, and image styles. A consistent approach reinforces the infographic’s theme and creates a clear visual identity. This consistency will make your infographic more memorable and impactful.
Color Palette, Fonts, and Imagery
The color palette, fonts, and images you choose significantly impact the infographic’s overall appeal and message. Choose colors that complement each other and support the infographic’s theme. Use a limited color palette to avoid visual clutter. Fonts should be legible and visually appealing, matching the tone and style of the infographic. Ensure that the chosen font sizes are suitable for readability on various devices.
Images and icons should be high-quality, relevant to the information being presented, and contribute to the overall aesthetic.
Whitespace for Readability
Proper use of whitespace is essential for creating a clean and easily readable infographic. Whitespace acts as visual breathing room between elements, allowing the eye to focus on specific data points and making the infographic more accessible. Avoid overcrowding by strategically placing whitespace between different sections, data points, and elements within the infographic.
Appropriate Imagery and Icons
Using appropriate imagery and icons enhances understanding and engagement. Icons should be relevant to the data points or sections of the infographic. For example, a financial infographic might use icons representing money or graphs. Images and icons should support the narrative, enhancing comprehension and engagement. The choice of imagery and icons should complement the infographic’s overall design.
The inclusion of relevant visuals should make the infographic more engaging and understandable.
Illustrative Examples for Infographic
Bringing canonical tags to life visually is key for understanding their impact. Infographics offer a powerful way to simplify complex concepts and make data more digestible. This section dives into how to effectively represent canonical tag strategies using various visual elements.Visualizing canonical tag concepts requires a clear understanding of the core ideas. The goal is to present information in a visually engaging way that mirrors the underlying logic and principles of canonical tags.
This section will showcase illustrative examples of different infographic elements, highlighting how to use diagrams, graphs, and flowcharts to depict canonical tag strategies effectively.
Diagrammatic Representations of Canonical Tag Concepts
Effective diagrams can visually represent the relationships between different URLs and their canonical counterparts. A flowchart, for instance, can trace the user journey and show how canonical tags direct users to the intended pages. A hierarchical diagram can showcase the structure of a website, emphasizing how canonical tags maintain consistency across different sections and pages. These diagrams will often include different colored boxes, lines, and arrows, each element signifying a particular action or relationship within the canonical tag strategy.
Graphing Data for Understanding Canonical Tag Impact
Graphs provide a powerful way to present data related to canonical tag effectiveness. A line graph, for example, can track the increase in search engine rankings or the decrease in crawl errors after implementing a canonical tag strategy. Bar graphs can compare the traffic volume from different pages on a website, illustrating the impact of a canonical tag on redirecting traffic to the desired page.
Using colors, patterns, and legends to distinguish different data points is crucial to create a clear and understandable visual representation.
Flowchart Depiction of Canonical Tag Scenarios, A beginners guide to canonical tags infographics
Flowcharts are particularly helpful in illustrating complex scenarios. A flowchart can guide the user through a process, such as how a user interacts with different versions of a page and how canonical tags ensure consistency. The flowchart will use shapes like rectangles, diamonds, and ovals to represent different steps in the process. Arrows connecting these shapes illustrate the flow of information and the actions involved.
For example, a flowchart can depict how a user might access a page from a mobile device or a desktop, and how canonical tags redirect to the appropriate version, ensuring a seamless user experience.
Alternative Infographic Designs for Canonical Tag Concepts
Different concepts demand different visual representations. For example, a mind map might be suitable for illustrating different aspects of canonicalization across various pages on a website, whereas a spider chart could illustrate the relationship between different search queries and the corresponding pages on a website that benefit from the canonical tag implementation. A scatter plot might display the correlation between the number of backlinks and the ranking of pages.
The choice of infographic design depends on the specific data and the message you want to convey. The important thing is to maintain visual clarity and avoid overly complex or cluttered visuals.
Visual Representations for Common Canonical Tag Scenarios
Here are some examples of visual representations for common canonical tag scenarios:
- Duplicate Content on Multiple URLs: A diagram showing multiple URLs with identical content, highlighting the canonical URL and how the others are redirected to it. The diagram might use different shades of a color or unique shapes to represent the various URLs.
- Mobile-Friendly Website: A comparison chart contrasting the mobile and desktop versions of a webpage. The graph might use two columns to visually compare the page structure and the impact of canonical tags on mobile devices.
- Redirecting from Old URLs to New URLs: A flowchart that depicts the process of redirecting users from older URLs to the new, updated version. The flowchart would clearly show the step-by-step process using visual representations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this beginner’s guide to canonical tags infographics offers a comprehensive and visually engaging approach to understanding and implementing these critical elements. By following the detailed structure, examples, and visual aids, you’ll be well-equipped to optimize your website’s content and improve its visibility in search engine results. Remember, consistent implementation of canonical tags leads to a stronger online presence.