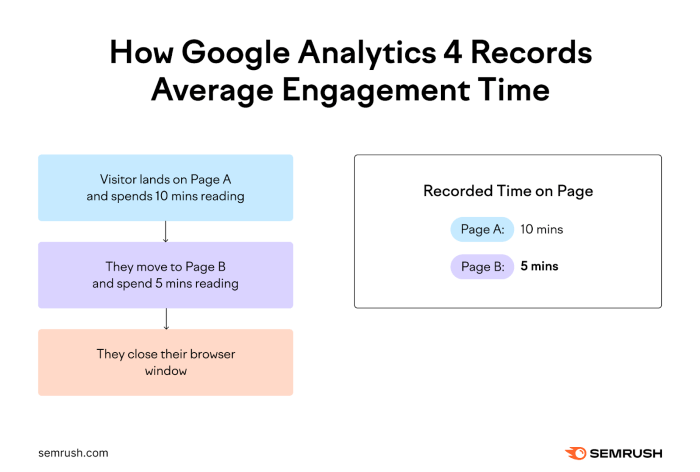
Average time on page Google Analytics is a crucial metric for understanding user engagement on your website. It reveals how long visitors stay on specific pages, offering insights into content effectiveness and user experience. This analysis delves into the factors influencing this metric, helping you optimize your website for better user retention and ultimately, achieving your online goals.
We’ll explore how to interpret average time on page data, identify areas for improvement, and track the impact of changes. From understanding the basics to implementing strategies for maximizing user engagement, this guide provides a comprehensive overview of average time on page Google Analytics.
Analyzing Page Performance
Understanding how users interact with different pages on your website is crucial for optimizing user experience and driving desired actions. Analyzing average time on page data provides valuable insights into which pages are engaging and which might need improvement. This analysis helps pinpoint areas for content enhancement, navigation adjustments, and ultimately, a more effective website.A key aspect of this analysis is comparing the average time spent on various pages.
Significant variations in time spent can highlight areas where your content resonates with users and areas where there might be issues that need addressing. For example, a page dedicated to a popular product might see high average time on page, while a confusing or poorly designed landing page might show significantly lower average time on page.
Comparing Average Time on Page Across Pages
Different pages on a website naturally attract different amounts of user engagement. The average time spent on a page is a reflection of user interaction with the content and design elements. This metric helps determine which pages are effectively communicating their message and which ones might need adjustments.
Identifying Pages with High or Low Average Time on Page Values
Identifying pages with exceptionally high or low average time on page values is a crucial step in understanding user behavior. Pages with high average time on page suggest engaging content and a user-friendly experience, while low average time on page values often indicate areas needing improvement, such as unclear content, slow loading times, or confusing navigation. For example, a blog post with extensive detail and interactive elements may have a high average time on page.
Potential Reasons for Variations in Average Time on Page
Variations in average time on page across different pages can be attributed to several factors. Content quality, page design, and page load speed are key contributing elements. If a page is poorly designed, users might quickly leave. Similarly, if a page’s content is not relevant or compelling, users will spend less time interacting with it.
Impact of Page Load Speed on Average Time on Page
Page load speed is directly correlated with average time on page. Slow-loading pages often lead to users abandoning the page before it fully loads. In contrast, pages that load quickly tend to retain users longer, allowing them to explore the content and engage with it. Studies have consistently shown a strong positive correlation between page load speed and user engagement, measured by metrics like average time on page and bounce rate.
My Google Analytics reports were always a bit vague on average time on page. It was great to see the granular detail now available. The recent update to the Google Search Analytics API, giving hourly breakdowns for the past 10 days, like this article highlights , means I can now pinpoint exactly when users spend the most time on specific pages.
This precision will really help me optimize content and improve user engagement, and ultimately my average time on page.
Average Time on Page by Page Category
| Page Category | Average Time on Page (Estimated) |
|---|---|
| Product Pages | 2-5 minutes |
| Blog Posts | 3-7 minutes |
| Landing Pages | 1-3 minutes |
This table provides a general guideline for the average time on page for different page categories. However, actual times will vary depending on specific content, design, and user engagement. Factors like the product’s complexity or the blog post’s depth will influence the time spent.
Exploring User Engagement: Average Time On Page Google Analytics
Average time on page is a crucial metric for understanding user engagement. It provides insight into how deeply users interact with specific content. By analyzing this metric, we can better understand user behavior and tailor our content strategy to improve user experience. Understanding the relationship between average time on page and other engagement metrics helps in identifying areas for optimization.Understanding user engagement is not just about numbers; it’s about deciphering user behavior.
A high average time on page might indicate that users are finding the content valuable and relevant, while a low average time on page could signal that the content isn’t compelling or is confusing. By combining this data with other engagement metrics, we gain a comprehensive view of how users interact with our website.
Relationship Between Average Time on Page and User Engagement Metrics
Average time on page is closely linked to other user engagement metrics like bounce rate and pages per session. A higher average time on page often suggests a lower bounce rate and a higher number of pages per session, indicating users are actively exploring the site. Conversely, a low average time on page might correlate with a higher bounce rate, signifying that users are not finding the content valuable.
Interpreting Average Time on Page in the Context of User Behavior
Average time on page should be considered in conjunction with other data points. For example, a page with a high average time on page might indicate a high level of user interest and satisfaction. However, this metric alone doesn’t paint a complete picture. It is essential to analyze other factors such as the content’s quality, design, and overall user experience to gain a deeper understanding of user behavior.
Segmenting Users Based on Average Time on Page
Segmenting users based on their average time on page can be a powerful tool for understanding different user groups and their needs. For instance, users who spend a considerable amount of time on a specific page might be highly interested in the information presented. This allows for targeted content strategies and personalized experiences.One approach to segmenting users is to create different groups based on quartiles of average time on page.
This could reveal insights into user preferences and help tailor content to specific segments. Users in the highest quartile might be particularly engaged, and understanding their behaviors can inform strategies to retain and further engage them.
Want to know how engaged your readers are? Average time on page in Google Analytics is a great starting point, but it’s just one piece of the puzzle. Understanding how to effectively measure reader engagement and loyalty using Google Analytics is key to truly grasping audience interaction. For a deeper dive into the metrics that matter, check out this guide on how to measure reader engagement and loyalty using Google Analytics.
Ultimately, a longer average time on page often signifies a more engaged audience, indicating that your content is truly resonating.
Examples of Pages with High Average Time on Page and Why
High average time on page can be seen on pages with engaging content, such as in-depth blog posts, detailed product descriptions, or interactive articles.For example, a detailed blog post about a complex topic, with clear explanations and insightful visuals, is likely to keep users engaged for a longer duration. Similarly, a well-structured and informative product description, with high-quality images and videos, can hold users’ attention.
Interactive content, such as quizzes or polls, encourages longer engagement. These examples showcase how compelling and well-designed content can directly impact average time on page.
Comparing Average Time on Page with Other Engagement Metrics
The following table illustrates the relationship between average time on page and other engagement metrics.
| Metric | Description | High Value Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Average Time on Page | Average time spent on a specific page | Users are deeply engaged with the content. |
| Bounce Rate | Percentage of visitors who leave the site after viewing only one page | Indicates low engagement; users might not find the content relevant or useful. |
| Pages per Session | Average number of pages viewed per session | Indicates higher user engagement; users are exploring multiple pages. |
This table provides a concise overview of the interrelation of these metrics. Analyzing these metrics together offers a holistic understanding of user behavior and content effectiveness.
Identifying Areas for Improvement
Improving average time on page is crucial for a website’s success. It signifies user engagement and signals to search engines that your content is valuable and relevant. A longer average time on page often translates into higher conversion rates and better overall website performance. Understanding why users are spending less time on specific pages is the first step toward improvement.Analyzing the data from Google Analytics reveals areas where user engagement is low.
This information provides actionable insights to optimize website design and content, ultimately leading to increased user satisfaction and improved website performance. We can strategically enhance website elements to better meet user needs and encourage prolonged engagement.
Potential Website Design Issues
Identifying design flaws in underperforming pages is critical for improvement. Poorly structured layouts, slow loading times, or unattractive visuals can quickly discourage users. For example, if a product page is difficult to navigate or the images take too long to load, users may leave before exploring the full product details. Usability testing and user feedback can help uncover these problems and provide solutions.
Google Analytics’ average time on page is a key metric. Understanding how users interact with your site is crucial, and a high average time on page often signals engaged visitors. This directly correlates with improved user experience and, ultimately, business growth. A great example of rapid growth is how Shopify scaled 10x in three years, and you can learn actionable strategies to achieve similar results from this in-depth analysis how shopify grew 10x in 3 years and how you can achieve similar results.
Analyzing how these techniques impact user engagement on your site through time on page will reveal what resonates best with your audience. Ultimately, this insight helps refine your strategy to keep visitors engaged longer and achieve your business goals.
Content Optimization Strategies
Enhancing content quality is vital for maximizing user engagement. Adding more relevant information, visual elements, or interactive components can keep users engaged. For example, adding a helpful FAQ section to a product page can answer customer questions and increase dwell time. High-quality images, videos, and infographics can also significantly enhance engagement.
User Experience Enhancements
Improving user experience is paramount to retaining visitors. Streamlined navigation, intuitive design, and clear calls to action all contribute to a positive user experience. Providing helpful resources, such as related articles or product comparisons, can encourage users to explore further and spend more time on the page.
Examples of Effective Strategies, Average time on page google analytics
Several effective strategies can be implemented to increase average time on page. Implementing a “related products” section on product pages encourages users to explore other offerings and stay on the site. Adding interactive elements, like quizzes or polls, can make the experience more engaging and encourage visitors to spend more time on the page. A well-structured FAQ section, especially for complex products or services, can address user questions and reduce bounce rates.
Recommendations for Different Page Types
| Page Type | Specific Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Product Pages | Enhance product descriptions with high-quality images and videos. Include detailed specifications, customer reviews, and related products. Consider a “frequently asked questions” section. |
| Blog Posts | Use compelling headlines and subheadings to capture attention. Break up large blocks of text with images, videos, and bullet points. Encourage interaction with comments and social sharing options. |
| Landing Pages | Clearly articulate the value proposition and benefits of the product or service. Include a compelling call to action. Optimize the page for mobile viewing and fast loading times. |
| Service Pages | Highlight customer testimonials and case studies. Provide detailed information about the services offered. Use clear and concise language. |
Measuring the Impact of Changes
Tracking improvements in average time on page is crucial for understanding the effectiveness of content optimization efforts. Knowing how these changes impact user engagement provides valuable insights into content effectiveness and user experience. This section details how to monitor these changes, evaluate their impact, and ultimately use data to fine-tune content strategy.A robust process for measuring the impact of changes involves consistent tracking, meticulous analysis, and a clear understanding of the baseline data.
This enables a more accurate assessment of the success of implemented changes, ultimately leading to more effective content strategies.
Tracking Changes in Average Time on Page
Implementing improvements to a website often involves a multifaceted approach, from optimizing content structure to enhancing user interface design. Tracking changes in average time on page post-implementation provides a clear indication of the effectiveness of these efforts. Using Google Analytics or a similar tool, one can monitor the average time users spend on specific pages after modifications.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Implemented Changes
Evaluating the effectiveness of implemented changes is not a one-time task. It requires consistent monitoring and analysis of data to understand the long-term impact of the adjustments. Key metrics to consider include not just the average time on page, but also bounce rate and other engagement metrics. Comparing these metrics before and after the changes allows for a nuanced understanding of the improvements’ effectiveness.
Using Data to Measure the Impact of Content Optimization
Analyzing the data collected from analytics tools is crucial for understanding the impact of content optimization on user engagement. Identifying patterns and correlations between changes in content and corresponding changes in average time on page provides a strong foundation for future content strategies. For example, if optimizing a product page leads to a significant increase in average time on page, this suggests the optimization was successful.
Monitoring and Analyzing Average Time on Page Over Time
Monitoring average time on page over time reveals trends and patterns in user engagement. This continuous analysis helps in understanding how user behavior evolves over time and allows for the adaptation of content strategies based on observed patterns. By tracking the average time on page for different pages, we can pinpoint areas for improvement and adapt content strategies accordingly.
Pre- and Post-Improvement Average Time on Page
| Page | Pre-Improvement Avg. Time on Page (seconds) | Post-Improvement Avg. Time on Page (seconds) | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Product Page A | 50 | 75 | 25 seconds |
| Blog Post B | 200 | 250 | 50 seconds |
| Landing Page C | 10 | 15 | 5 seconds |
| About Us Page | 60 | 70 | 10 seconds |
This table showcases a hypothetical comparison of average time on page before and after implementing content improvements across various pages. The differences highlight the impact of these adjustments on user engagement. Note that these values are examples and may vary based on the specific website and the nature of the improvements.
Contextualizing Average Time on Page
Average time on page, a seemingly straightforward metric, can be easily misinterpreted if not considered within a broader context of user behavior and website design. While it offers a glimpse into user engagement, it’s crucial to understand its limitations and the importance of evaluating it alongside other metrics. A high average time on page doesn’t automatically equate to a successful website, and conversely, a low average time on page doesn’t necessarily signal failure.Understanding the nuances of average time on page requires a more holistic approach to website analysis.
Simply focusing on this one metric can lead to misinterpretations, particularly when other important aspects of user interaction are ignored. For instance, a user might spend a long time on a page browsing through a large product catalog, but ultimately not convert into a purchase. This highlights the need for a comprehensive analysis of user engagement encompassing various factors.
Misinterpretations of Average Time on Page
Average time on page can be misleading because it doesn’t inherently indicate user satisfaction or engagement. A user might spend a significant amount of time on a page simply navigating through the site’s content or interacting with complex forms, without necessarily understanding or absorbing the information. This can be especially true for informational websites or those with extensive product listings.
A long time spent scrolling through a page doesn’t necessarily imply that the user is actively engaging with the content in a meaningful way.
Importance of Considering Other Metrics
Focusing solely on average time on page provides an incomplete picture of user engagement. It’s crucial to consider other metrics such as bounce rate, pages per session, conversion rate, and user flow. A low bounce rate, coupled with a high number of pages per session, and high conversion rates, are all strong indicators of user engagement, regardless of average time on page.
Examples of Websites Where Average Time on Page is Not a Reliable Indicator
Consider a website selling high-value products like luxury cars. Users might spend a considerable amount of time browsing through detailed specifications, but that prolonged time doesn’t always correlate with a purchase. A user might spend hours comparing models and options, but ultimately, the decision is often complex and time-consuming. Similarly, a website dedicated to complex financial information or scientific research might see high average time on page figures, but these lengthy sessions might not translate into substantial conversions or engagement with the site’s core purpose.
Limitations of Using Average Time on Page as the Sole Measure of User Engagement
Average time on page, in isolation, provides a limited understanding of user behavior. It fails to account for the complexity of user interactions and the various reasons behind prolonged or brief visits. A user might spend a short time on a page because they quickly find the information they need or because the design is confusing and they quickly exit.
Consequently, focusing exclusively on average time on page overlooks other crucial aspects of user engagement.
Importance of Multiple User Engagement Metrics
| Metric | Description | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Average Time on Page | Average duration of user interaction on a specific page. | Provides a basic measure of user engagement, but limited in isolation. |
| Bounce Rate | Percentage of users who leave a website after viewing only one page. | Highlights whether users are finding the desired information quickly. |
| Pages per Session | Average number of pages visited by a user during a session. | Indicates the depth of engagement and user exploration of the website. |
| Conversion Rate | Percentage of users who complete a desired action (e.g., purchase, signup). | Measures the effectiveness of the website in achieving its goals. |
| User Flow | Sequence of pages visited by a user during a session. | Reveals user journey and identifies areas where users drop off. |
Comprehensive analysis of user engagement requires considering multiple metrics in conjunction with average time on page. This holistic approach allows for a deeper understanding of user behavior and identification of potential areas for improvement.
Epilogue
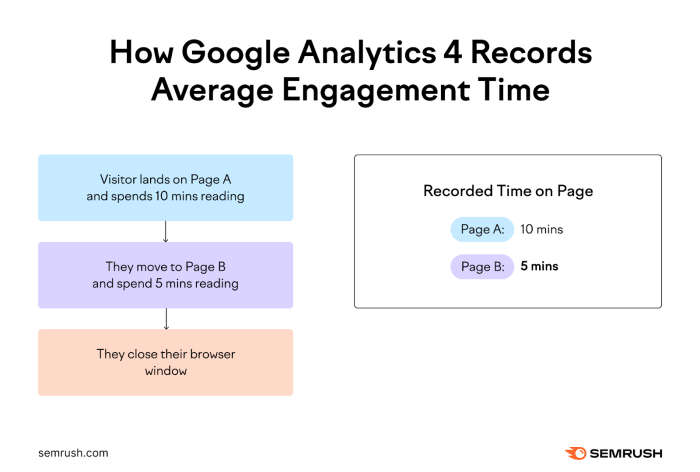
In conclusion, understanding average time on page in Google Analytics is essential for website optimization. By analyzing page performance, user engagement, and identifying areas for improvement, you can create a more engaging and user-friendly website. Remember, average time on page is just one piece of the puzzle; consider other metrics like bounce rate and pages per session for a holistic view of user behavior.
By implementing the strategies discussed, you can effectively enhance user experience and drive better results.