Beginners guide robots txt – Beginner’s Guide Robots.txt lays out the fundamentals of this essential file for website optimization. Understanding robots.txt is crucial for controlling how search engines and other web crawlers interact with your site. It’s a simple text file that tells these bots which pages to crawl and which to ignore, affecting your and website performance.
This comprehensive guide will cover everything from the basics of robots.txt structure and directives to advanced techniques for managing complex websites. We’ll explore how to optimize for different crawlers, handle dynamic content, and implement security measures. Plus, we’ll discuss common issues and troubleshooting strategies, along with best practices for maintaining an effective robots.txt file.
Introduction to Robots.txt
The robots.txt file is a crucial part of website management, acting as a guide for web crawlers. It’s a simple text file located in the root directory of a website that instructs search engine bots, and other web crawlers, on which parts of your site they are allowed to access and which they should ignore. This control is essential for maintaining website integrity and preventing unwanted indexing or crawling of sensitive data.Understanding robots.txt is vital for (Search Engine Optimization) and website security.
It allows you to selectively control which parts of your site are crawled and indexed, protecting resources and improving the overall website experience. This document clarifies how crawlers interact with your website, enabling you to optimize its visibility and safety.
Purpose and Function
The robots.txt file serves as a communication channel between your website and web crawlers. It Artikels which parts of your website should be crawled and indexed, and which should be excluded. This selective crawling process can be critical for preventing excessive crawling, preserving server resources, and safeguarding sensitive content. It’s a fundamental part of website management for and security.
So, you’re diving into a beginner’s guide to robots.txt? Understanding how to optimize your website’s robots.txt file is crucial for search engine visibility. This directly ties into broader user optimization principles, like those outlined in the helpful article on 8 principles of user optimization that’ll increase your search rankings. By properly directing search engine crawlers, you’re laying the groundwork for better search engine results, which ultimately improves user experience.
Mastering robots.txt is a foundational step in a comprehensive SEO strategy.
Role in Web Crawlers and Search Engine Indexing
Web crawlers, also known as spiders or bots, are automated programs that browse the web to discover and index new content. Robots.txt plays a crucial role in guiding these crawlers. By specifying which parts of your site should be ignored, you can prevent the indexing of irrelevant or unwanted content. This ensures that only relevant and valuable information is included in search engine results.
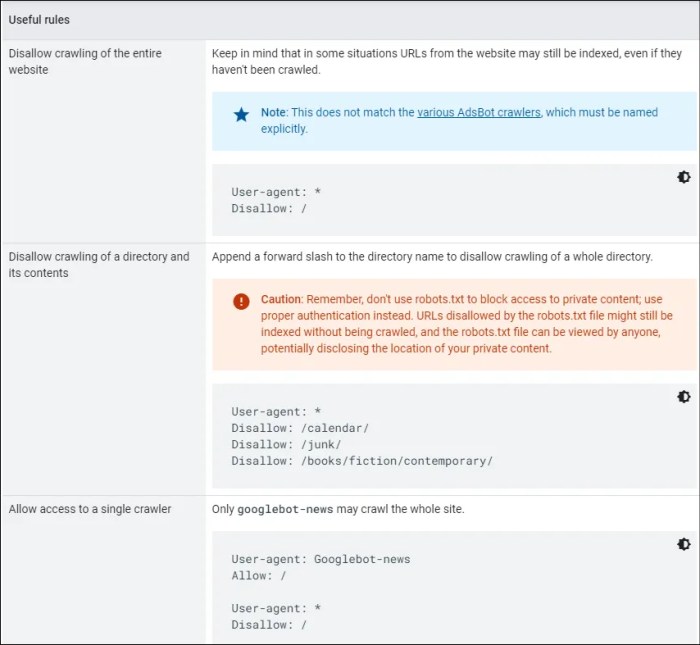
Basic Structure and Syntax
A robots.txt file follows a specific format. It consists of directives that tell crawlers how to behave. These directives are typically written in all-lowercase letters, and each directive must be on a new line. The structure is simple, with directives followed by optional parameters.
Simple Example
“`User-agent:Disallow: /private/Allow: /“`This example demonstrates a basic robots.txt file. The `User-agent:
` directive instructs all web crawlers to follow the rules below. `Disallow
/private/` prevents crawlers from accessing any files or directories within the `/private/` folder. `Allow: /` specifies that all other parts of the website are accessible.
Common Directives
| Directive | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| User-agent | Specifies the web crawler or bot that the directive applies to. A wildcard (*) applies to all crawlers. | User-agent: Googlebot |
| Disallow | Specifies URLs that should not be crawled by the specified user-agent. | Disallow: /admin/ |
| Allow | Specifies URLs that should be crawled by the specified user-agent. If present, it overrides any Disallow directive for the specified URL. | Allow: /products/ |
| Sitemap | Specifies the location of a sitemap file, which contains a list of URLs on your website. | Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap.xml |
This table Artikels the common directives used in a robots.txt file, with clear examples for each. Understanding these directives is key to effectively managing your website’s visibility and security.
Directives and Usage: Beginners Guide Robots Txt
The robots.txt file is a crucial tool for website owners to control how search engine crawlers interact with their site. Understanding its directives is essential for optimizing search engine visibility and preventing unwanted indexing of certain pages. This section delves into the specifics of these directives, focusing on their function and proper usage.The directives within a robots.txt file essentially act as instructions for web crawlers.
They define which parts of your website are accessible and which are not. Proper use of these directives can help you manage how search engines crawl your site, ensuring that only relevant and valuable content is indexed.
User-agent Directive
The `User-agent` directive specifies which web crawlers the directives that follow apply to. This is crucial because different search engines and web crawlers may have varying needs and priorities. By specifying the `User-agent`, you can tailor your instructions to specific bots.For example, if you want to prevent a particular crawler from accessing a directory, you can specify that crawler’s name in the `User-agent` directive.
A common practice is to use a wildcard `*` to apply the rules to all crawlers. This is useful for basic site-wide rules.Example:“`User-agent: GooglebotDisallow: /private/“`This example instructs Googlebot to not crawl the `/private/` directory.
Disallow Directive
The `Disallow` directive is used to block access to specific pages or directories. This is a fundamental aspect of robots.txt management. By specifying a path, you prevent crawlers from indexing that particular section of your site.For instance, you might want to block access to pages containing sensitive data or temporary content that is not meant for public consumption.
A precise path is essential for effective blocking. Incorrect paths or overlapping rules can lead to unintended consequences.Example:“`User-agent:Disallow: /admin/Disallow: /temp/“`This example blocks access to both the `/admin/` and `/temp/` directories for all crawlers.
Allow Directive
The `Allow` directive complements the `Disallow` directive. It permits access to specific pages or directories, even if `Disallow` rules are in place for the same crawler. This is useful for granting access to specific sections of a website that you may have blocked previously. `Allow` directives are crucial for maintaining control over indexing and crawl behavior.Example:“`User-agent:Disallow: /private/Allow: /private/documents/“`This example blocks access to the `/private/` directory for all crawlers but allows access to the `/private/documents/` subdirectory.
Sitemap Directive
The `Sitemap` directive directs crawlers to a sitemap file, a file that lists all the URLs on your website. This is a significant optimization technique for websites with extensive content. A sitemap makes it easier for crawlers to discover and index all relevant pages, improving your site’s discoverability. Proper use of sitemaps can be a significant contributor to .Example:“`Sitemap: https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml“`This example directs crawlers to the sitemap file located at `https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml`.
Disallow vs. Allow Directives
| Directive | Effect | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Disallow | Blocks access to specified URLs or directories. | Preventing indexing of sensitive data, temporary content, or non-essential pages. |
| Allow | Grants access to specified URLs or directories, even if blocked by a `Disallow` rule. | Allowing access to specific sections of a site, despite broad `Disallow` rules. |
The `Disallow` directive is used to block crawlers from accessing certain parts of your website. Conversely, the `Allow` directive is used to permit access to specified locations, even if a broader `Disallow` rule is present. Understanding the interaction between these directives is essential for controlling crawl behavior.
Advanced Techniques
Robots.txt, while a fundamental tool for website management, can become quite sophisticated when dealing with complex structures. Understanding advanced techniques is crucial for effectively controlling how search engines crawl and index your site. This section dives into strategies for handling dynamic content, complex URLs, managing multiple sites, and internationalization.Advanced techniques in robots.txt go beyond basic directives, addressing the nuanced needs of modern websites.
Mastering these methods allows for precise control over which parts of your site are crawled and indexed, ultimately improving search engine optimization and user experience.
Handling Dynamic Content and Complex URL Structures
Dynamic websites often feature URLs that change based on parameters or user interactions. A crucial aspect of robots.txt in this context is the use of wildcards to specify which parts of the dynamic structure should be excluded.For example, a site with URLs like `/product/123`, `/product/456`, and `/product/789` could use a `Disallow` rule like `Disallow: /product/*` to prevent indexing of all product pages.
This approach is effective, but more nuanced handling is possible.
Using Wildcards in User-agent and Disallow Directives
Wildcards are powerful tools in robots.txt, enabling broad control over crawling behavior. They can be used within the `User-agent` and `Disallow` directives.The `User-agent` directive allows targeting specific search engine crawlers. For example, `User-agent: Googlebot` targets only Googlebot, while `User-agent:` targets all crawlers. The `Disallow` directive, in combination with wildcards, enables exclusion of specific parts of the website.
Managing Multiple Robots.txt Files for Different Types of Websites
Large websites often have diverse sections, such as a public storefront and a member’s area. Using multiple robots.txt files is a practical approach to control crawling for these distinct parts.This allows for fine-grained control over different sections of the site. Each file can be tailored to the specific needs of the respective sections. For example, a separate robots.txt for a member’s area can restrict access for non-members, preventing unwanted indexing.
Handling Internationalization or Multilingual Websites with Robots.txt
Internationalization often involves multiple language versions of a website. Robots.txt can help control crawling and indexing for these different versions.Implementing language-specific rules in robots.txt allows site owners to control the visibility of different language versions to search engines. This ensures search engines don’t crawl unnecessary pages.
Robots.txt Configurations for Different Website Types
This table Artikels typical robots.txt configurations for various website types. These are examples and may need adaptation to specific needs.
| Website Type | Example Configuration |
|---|---|
| E-commerce | `User-agent:
/cart/* |
| Blogs | `User-agent:
/wp-admin/* |
| News Sites | `User-agent:
/comments/* |
Common Issues and Troubleshooting

Robots.txt files, while seemingly straightforward, can harbor subtle errors that significantly impact a website’s visibility and accessibility to search engine crawlers. Understanding common pitfalls and troubleshooting strategies is crucial for optimizing website indexing and preventing unwanted content from being crawled. Incorrectly configured robots.txt files can lead to missing pages, blocked essential resources, or even complete indexation issues.
Identifying Errors in Robots.txt Files
Common errors include typos in the file path, incorrect syntax, or directives that inadvertently block crucial parts of the website. Analyzing the file for these issues is the first step in resolving them. Carefully reviewing the file structure, verifying the accuracy of paths, and ensuring correct syntax is critical for avoiding problems. Syntax errors or improperly formatted directives can prevent crawlers from understanding the intended instructions, resulting in unpredictable behavior.
A beginner’s guide to robots.txt can be surprisingly helpful, especially if you’re trying to keep your SEO rankings high. Understanding how to properly utilize this file can help your website stay visible and maintain its position in search results. After all, you want to continue performing well, like in stay put how to maintain your seo rankings after reaching the top , so make sure you have a well-structured robots.txt file in place.
This will help your site stay on top of search engine results pages, ensuring your hard work doesn’t go to waste.
Analyzing Robots.txt Files for Issues
Thorough inspection is vital to detect errors. Start by checking for missing or malformed directives. Ensure that the file’s syntax adheres to the standard specifications, confirming that all directives are correctly formatted and use the appropriate syntax. A simple text editor can help in visualizing the structure of the robots.txt file and identifying potential syntax issues. Look for typos, missing semicolons, and inconsistent use of characters.
Missing or extra spaces within the directives can also cause errors. Verify that all file paths are correct and match the actual file structure on your server.
Debugging and Resolving Robots.txt Errors
Troubleshooting robots.txt errors involves systematic analysis and correction. If a crawler encounters an error, the error messages can provide valuable insights. Carefully review the error messages for clues about the nature of the problem. Use a web browser’s developer tools to inspect the robots.txt file and identify any discrepancies or inconsistencies. Comparing the robots.txt file against the actual file structure can reveal mismatches.
A thorough review of the robots.txt file and the website’s directory structure is crucial.
Testing Robots.txt Files for Proper Functioning
Testing is essential to ensure the robots.txt file correctly guides crawlers. Use a dedicated robots.txt testing tool to simulate crawler behavior. Verify that the tool returns the expected results. Checking the response headers for successful validation is important. Manual testing by requesting the robots.txt file directly through a web browser can also confirm its accessibility and readability.
A simple way to test is by using a web browser to directly access the robots.txt file, ensuring the file is accessible and correctly formatted.
Summary of Typical Robots.txt Errors and Solutions
| Error | Potential Consequences | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect or Missing Directives | Blocked essential content, improper indexing | Verify correct syntax and ensure all necessary directives are present |
| Typographical Errors | Misinterpretation of instructions, incorrect blocking | Double-check all file paths and directives for accuracy |
| Incorrect File Paths | Failure to access intended resources | Verify that all file paths in the directives match the actual file structure on the server |
| Inconsistent Use of Characters | Crawler confusion and improper parsing | Adhere to the standard syntax and formatting rules of robots.txt |
| Unnecessary Blocking | Crawlers missing important pages | Review and remove any unnecessary blocking rules |
Best Practices and Recommendations
A well-maintained robots.txt file is crucial for optimizing search engine crawling and website performance. Proper implementation ensures that search engines effectively crawl and index your website’s content, leading to improved visibility and better user experience. This section details best practices for creating an effective robots.txt file and strategies for maintaining it in large website environments.
Creating an Effective robots.txt File
Effective robots.txt files prioritize essential content while excluding unnecessary files. This includes preventing crawlers from accessing sensitive data, temporary files, or dynamically generated content that doesn’t contribute to user value. The file structure should be clear, concise, and easily understandable for search engine crawlers. Avoid using complex or ambiguous directives; keep it simple and direct.
Regular Updates for Optimal Performance, Beginners guide robots txt
Regular updates to the robots.txt file are essential to reflect changes in website structure and content. This includes removing directives for outdated pages, adding new sections, or modifying access permissions for specific files. Failing to update the file can lead to search engines indexing outdated information or failing to index new content, hindering efforts. Consider implementing a system to track changes and automatically update the robots.txt file when necessary.
Impact on and Website Performance
A properly configured robots.txt file directly impacts by guiding search engine crawlers. It helps ensure that crawlers focus on valuable content, leading to better rankings. A well-structured file contributes to faster website loading times by excluding unnecessary files from being processed, thus enhancing user experience. Search engines often prioritize websites with fast loading times in search results.
So, you’re diving into a beginner’s guide to robots.txt? Understanding how search engines crawl your site is key, and a crucial aspect of that is ensuring your robots.txt file is correctly configured. To truly maximize your SEO efforts, a strong understanding of SEO reporting and tracking is essential. This often involves checking how well your robots.txt file is performing in conjunction with tools and reports from a platform like seo reporting tracking guide.
By reviewing these reports, you can better fine-tune your robots.txt settings, leading to improved SEO results. Ultimately, a well-structured robots.txt file is a cornerstone of any successful SEO strategy for beginners.
Managing Robots.txt in Large Websites
Managing a robots.txt file in a large website environment requires a systematic approach. Use a centralized system for managing updates, allowing for easy tracking and rollback capabilities. Implement a version control system to track changes and facilitate reverting to previous versions if necessary. Consider using tools and plugins designed to manage robots.txt files for large websites, which often provide features for automated updates and monitoring.
A well-organized approach ensures that robots.txt effectively controls crawling and indexing across the entire website, maintaining consistent performance.
Crawling Speed and Indexing Efficiency
The robots.txt file plays a crucial role in optimizing crawling speed and indexing efficiency. By instructing search engines to prioritize specific content, you guide the crawling process. This leads to faster indexing of important content and a more efficient use of search engine resources. The result is improved visibility for relevant content and a faster overall crawling experience for the search engines.
Best Practices Summary
- Prioritize essential content: Focus on directing crawlers to the most valuable pages and resources.
- Avoid unnecessary content: Exclude files or directories that don’t contribute to user value or are dynamically generated.
- Maintain a clear structure: Use clear and concise directives, avoiding complex or ambiguous syntax.
- Regular updates: Implement a system for tracking and updating the robots.txt file in response to changes in the website’s structure and content.
- Centralized management for large websites: Utilize a centralized system for managing updates and tracking changes.
Robots.txt and Security
Robots.txt, while primarily a tool for website management, plays a surprising role in enhancing website security. It allows webmasters to control which parts of their site search engines and other automated tools can access, thereby limiting the potential exposure of sensitive data. This control can significantly mitigate vulnerabilities and safeguard against unwanted access.Implementing robots.txt effectively can act as a first line of defense against unauthorized access to sensitive areas of a website.
This proactive approach is crucial in protecting against automated attacks and accidental exposure of confidential information.
Strategies for Safeguarding Sensitive Areas
Proper implementation of robots.txt directives can prevent unwanted access to sensitive data. By blocking access to specific directories, files, or even entire sections of a website, webmasters can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized data retrieval. This is particularly important for areas containing personally identifiable information (PII), financial data, or proprietary information.
- Blocking Specific Directories: Directing crawlers to not access directories containing sensitive information, like user profiles or financial transaction records, is a fundamental security strategy. This ensures that automated systems cannot retrieve these sensitive files. For example, a robots.txt file could include a directive like
Disallow /user_profiles/to prevent crawlers from accessing this directory. - Filtering Specific File Types: Robots.txt can also prevent the retrieval of specific file types, such as databases or configuration files, that might contain sensitive information. This helps mitigate the risk of exposing confidential data through accidental or malicious access. The directive
Disallow /files/*.dbwould prevent access to all files ending with “.db” extension. - Controlling Access to Specific URLs: The ability to control access to specific URLs is another powerful technique. This allows you to protect specific pages containing sensitive information from being indexed or accessed by unauthorized agents. A directive like
Disallow /admin/login.phpwould block access to a login page, preventing potential brute-force attacks.
Mitigating Potential Vulnerabilities
By carefully crafting the robots.txt file, webmasters can prevent automated tools from accessing sensitive areas of the website, significantly reducing the risk of data breaches and security vulnerabilities. This approach, while not a complete security solution, provides an essential first line of defense.
- Preventing Automated Attacks: By blocking access to login pages or sensitive directories, robots.txt can prevent automated attacks that aim to exploit vulnerabilities in web applications. This strategy is often combined with other security measures, such as strong passwords and secure coding practices.
- Minimizing Accidental Data Exposure: Robots.txt helps prevent accidental data exposure. By limiting what search engines or other automated systems can access, the risk of confidential information being inadvertently indexed and made publicly accessible is minimized.
Robots.txt Security Strategies Table
| Security Strategy | Robots.txt Directive | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Block Sensitive Directories | Disallow /sensitive_data/ |
Prevents crawlers from accessing a directory containing sensitive information. |
| Restrict File Types | Disallow /files/*.conf |
Prevents access to configuration files that might contain sensitive data. |
| Control Specific URLs | Disallow /admin/access.php |
Prevents access to specific URLs containing sensitive information. |
| Block User Agent | User-agent:
|
Blocks all user agents from accessing the entire website. (A strong, but potentially limiting strategy). |
Robots.txt and Crawling
Robots.txt is a crucial file for website owners to control how search engine crawlers interact with their site. It acts as a guide, instructing crawlers on which parts of your site they are allowed to access and which they should ignore. Understanding how crawlers operate and how robots.txt impacts their behavior is essential for optimizing your website’s visibility and performance.This file isn’t a complete solution to all issues, but it is a significant factor in how your website is indexed and ranked.
By carefully crafting your robots.txt file, you can influence crawl patterns and frequency, directing crawlers to focus on the most important aspects of your site.
Crawler Interaction with Robots.txt
Crawlers systematically visit websites, following links to gather information and update their indexes. The robots.txt file acts as a digital gatekeeper, allowing or prohibiting access to specific directories and files. When a crawler encounters a robots.txt file, it parses its directives and adjusts its crawling behavior accordingly.
Impact on Crawl Frequency and Depth
Robots.txt can directly impact how often and how deeply crawlers explore your website. Disallowing access to specific directories or files can significantly reduce the number of pages crawled. This is particularly useful for:
- Preventing Crawling of Sensitive Data: Disallowing access to directories containing sensitive information like user accounts or internal documentation is crucial for maintaining security.
- Controlling Crawl Frequency: The robots.txt file allows you to specify how often crawlers should revisit specific pages, optimizing for the website’s structure and content updates.
- Controlling Crawl Depth: By disallowing access to specific directories, you can limit the depth of the crawl, preventing crawlers from indexing irrelevant or outdated content. This is particularly valuable for new or large websites.
Different Crawl Strategies and Their Impact
Crawlers employ various strategies to discover and index content. These strategies influence how they interpret the robots.txt file. Some crawlers might prioritize speed over depth, while others might focus on comprehensively indexing the entire website. Understanding these strategies is key to effectively configuring robots.txt.
- Breadth-first crawling: Crawlers visit all pages at a given level before moving to the next level. This strategy often requires careful robots.txt management to prevent crawling irrelevant content.
- Depth-first crawling: Crawlers explore a single branch of the website as deeply as possible before moving to another branch. A well-defined robots.txt file can help guide crawlers to the most valuable pages.
- Seed URL crawling: Crawlers start from a specified set of URLs and follow links from those pages. This approach requires a robots.txt file that prioritizes essential content and excludes less important sections.
Crawler Behaviors and Robots.txt Optimization
Different search engine crawlers have unique behaviors. Optimizing robots.txt involves considering these variations. Some crawlers might be more sensitive to certain directives than others.
- Googlebot: Googlebot is the most common crawler. Its behavior is well-documented, allowing for targeted robots.txt optimization for Google’s search index.
- Bingbot: Bingbot’s crawling behavior, while similar to Googlebot’s, might have nuances that require specific considerations in robots.txt configuration.
- Other Crawlers: Various other crawlers exist, each with potential differences in their interpretation of robots.txt. A generalized robots.txt approach often suffices.
Crawl Patterns and Robots.txt Strategies
Understanding different crawl patterns and how they affect robots.txt is crucial for optimizing website indexing. This table illustrates various patterns and corresponding strategies.
| Crawl Pattern | Robots.txt Strategy |
|---|---|
| Breadth-first | Prioritize important pages at the root level, disallow less important directories. |
| Depth-first | Allow access to the deepest pages while excluding shallow, less relevant directories. |
| Seed URL | Specify seed URLs in the robots.txt file and disallow irrelevant branches from those starting points. |
| Sitemap | Include sitemaps in robots.txt to guide crawlers to specific content or pages. |
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, mastering robots.txt is a fundamental step in optimizing your website for search engines and managing crawler behavior. By understanding the directives, best practices, and common pitfalls, you can create a robots.txt file that efficiently directs crawlers, enhances your , and ultimately improves your website’s performance. This guide equips you with the knowledge to confidently navigate the world of robots.txt and achieve optimal results.