Common Marketo implementation challenges to avoid sets the stage for a deep dive into potential pitfalls and how to navigate them successfully. From data collection snags to resource allocation issues and competitive pressures, this guide highlights critical hurdles and actionable strategies for a smoother Marketo rollout. Understanding these potential obstacles is key to ensuring your Marketo implementation is not only successful but also efficient and cost-effective.
This article will explore the common issues encountered during Marketo implementations, categorized into data collection, market entry strategies, resource management, competitive dynamics, and communication breakdowns. We’ll also examine the root causes of these challenges and offer practical mitigation strategies for each, ensuring your team is well-equipped to tackle any obstacle.
Defining Common Market Implementation Challenges
Market implementation, while crucial for business success, is fraught with potential obstacles. These challenges, often nuanced and varying across market segments, demand careful planning and proactive mitigation strategies. Understanding the root causes of these problems is key to developing effective solutions and avoiding costly delays or failures.Implementing a new market strategy is a complex undertaking. It involves numerous interconnected elements, from adapting products or services to changing consumer needs, to adjusting marketing approaches, and establishing effective distribution channels.
Avoiding common Marketo implementation pitfalls is key to success. One often overlooked area is ensuring your marketing automation strategy aligns with your overall business goals. A deeper dive into Google Discover result study findings can highlight how crucial it is to create content that resonates with your target audience. Understanding user intent and content relevance is vital, as well as avoiding generic approaches in Marketo implementation.
By focusing on these crucial aspects, you can create a more effective and successful Marketo setup. google discover result study
Failures in any of these areas can create significant hurdles. Successfully navigating these challenges hinges on a thorough understanding of the specific market landscape and the potential pitfalls inherent in the chosen implementation plan.
Common Implementation Obstacles
Understanding the diverse obstacles encountered during market implementation is crucial for effective planning. This includes not just technical issues, but also challenges stemming from market dynamics, organizational factors, and unforeseen circumstances. A comprehensive analysis requires consideration of a wide range of potential roadblocks.
- Lack of Market Research: Insufficient or inaccurate market research can lead to misaligned product offerings, ineffective marketing strategies, and poor customer engagement. For instance, failing to properly assess customer preferences and needs can result in products or services that fail to resonate with the target market. Furthermore, neglecting competitor analysis can leave a company vulnerable to market shifts and emerging threats.
Avoiding common Marketo implementation pitfalls is key for success. One often overlooked challenge is ensuring seamless integration with other marketing tools. Luckily, the new Google Click to Call extension is now available in Australia, offering a powerful way to streamline customer engagement, which can directly impact your Marketo strategy. By understanding these nuances and staying ahead of the curve, you can avoid many of the implementation challenges that often plague marketers.
This exciting new tool, detailed in the google click to call extension now in australia article, is a fantastic example of how adapting to new technology can strengthen your marketing efforts. Ultimately, thorough planning and understanding your audience’s needs are essential to successfully deploying Marketo.
- Poor Product-Market Fit: A product or service that does not effectively meet the needs of the target market is destined for failure. This often stems from a lack of understanding of the target market’s specific requirements, resulting in a product that does not solve a problem or offer a compelling value proposition. Examples include over-engineered products that are too complex or overpriced for the market, or products that fail to cater to the unique preferences of specific customer segments.
- Inadequate Distribution Channels: An ineffective distribution strategy can limit access to the target market, significantly hindering sales and market penetration. Challenges can range from logistical difficulties in reaching customers to a lack of suitable retail partnerships or online presence. For example, a product designed for a global market might struggle to reach consumers in remote areas or underserved regions without a robust global logistics network.
- Insufficient Marketing and Sales Efforts: Weak marketing and sales strategies can fail to generate sufficient customer interest or drive sales. This can arise from a lack of targeted marketing campaigns, poor brand messaging, or an ineffective sales process. Companies might fail to capture the attention of potential customers or communicate the value proposition of their products effectively.
- Poor Change Management: Resistance to change within an organization can hinder market implementation efforts. Employees may be hesitant to adopt new processes or procedures, or the company culture may not be receptive to the required transformations. This can be exacerbated by a lack of clear communication, inadequate training, or insufficient support for employees during the transition.
Challenges Across Market Segments
The nature and severity of implementation challenges vary significantly across different market segments. Understanding these variations is essential for developing tailored strategies.
| Market Segment | Common Challenge | Root Cause | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consumer Goods | Changing consumer preferences | Evolving tastes, emerging trends, and economic fluctuations | Agile market research, continuous product development, and rapid response to market shifts |
| B2B Services | Complex sales cycles and decision-making processes | Multiple stakeholders, lengthy negotiations, and intricate contracts | Dedicated account managers, streamlined sales processes, and strong relationship building |
| Technology | Rapid technological advancements | Continuous innovation and obsolescence | Strategic investments in R&D, proactive adaptation to new technologies, and continuous learning |
| Healthcare | Regulatory compliance and ethical considerations | Stringent regulations, patient privacy concerns, and ethical dilemmas | Strong legal expertise, robust compliance procedures, and transparent communication with stakeholders |
Data Collection and Analysis Issues
Market implementation hinges on accurate data. Without robust data collection and insightful analysis, even the best strategies can falter. This section delves into the critical aspects of data collection, potential pitfalls, and various analysis techniques, illustrating how flawed data interpretation can lead to poor decisions. We also provide strategies for ensuring data quality.
Critical Data Collection Methods
Data collection is fundamental to understanding market dynamics. Various methods are employed, including surveys, interviews, focus groups, and secondary research. Surveys offer a broad reach, while interviews provide in-depth insights. Focus groups can reveal nuanced consumer perceptions. Secondary research leverages existing data sources like market reports and government statistics.
Careful selection of the appropriate method, or combination of methods, is crucial to gathering the right information.
Potential Pitfalls in Collecting Accurate Market Data, Common marketo implementation challenges to avoid
Collecting accurate market data isn’t always straightforward. Common pitfalls include poorly designed surveys that lead to biased responses, sampling errors that skew results, and inaccurate data entry. Interviewer bias during interviews can also affect the collected information. Insufficient or unclear survey questions can lead to misinterpretations and inaccurate responses. Inaccurate data entry, especially in large datasets, can introduce significant errors that affect the reliability of the entire analysis.
Data Analysis Techniques
Several data analysis techniques are available, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Descriptive analysis summarizes existing data, providing a foundational understanding. Inferential analysis uses sample data to make inferences about a larger population. Predictive analysis forecasts future trends based on historical data. Choosing the right technique depends on the research question and the type of data available.
Examples of Inaccurate Data Interpretation
Misinterpreting data can lead to disastrous implementation decisions. For instance, assuming a positive correlation between two variables when there is none can lead to a misdirected marketing campaign. Overgeneralizing findings from a small, unrepresentative sample can also lead to poor strategy. Another example is failing to account for external factors like economic downturns when analyzing market trends.
Inaccurate interpretation can lead to lost revenue, wasted resources, and ultimately, project failure.
Methods for Ensuring Data Quality and Integrity
Ensuring data quality is crucial. Clear data definitions, well-defined collection procedures, rigorous data validation, and regular audits are vital. Data validation checks ensure that the data conforms to specified rules and standards. Data audits provide a comprehensive review of data quality and identify any issues. Employing data quality management software can significantly streamline the process.
Common Data Errors and Their Impact
| Data Error Type | Description | Impact on Implementation | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inaccurate Data Entry | Errors in inputting data from surveys or other sources. | Misleading analysis, incorrect targeting, and ineffective campaigns. | Use validation rules, data entry checks, and automated data entry tools. |
| Sampling Bias | The sample does not accurately reflect the target population. | Incorrect conclusions and misleading projections. | Employ stratified sampling, random sampling, and ensure sample size is appropriate for the population. |
| Missing Data | Incomplete data sets. | Incomplete analysis, distorted results, and inaccurate conclusions. | Imputation methods, data collection improvements, and prioritization of missing data. |
| Inaccurate Data Definition | Vague or inconsistent definitions of key variables. | Confusing analysis, inconsistent conclusions, and ineffective targeting. | Clearly define variables and establish consistent measurement criteria. |
Market Entry Strategies and Their Challenges
Choosing the right market entry strategy is crucial for a company’s success in new markets. A poorly chosen strategy can lead to significant financial losses and wasted resources. This section delves into various market entry strategies, their associated challenges, and how adapting to the specific market environment is key to achieving optimal results.
Market Entry Strategy Options
Different market entry strategies cater to various business needs and market conditions. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each is vital before making a decision.
- Exporting: This strategy involves selling products or services directly to customers in a foreign market. It’s often a good starting point for companies looking to test international waters. It typically involves minimal upfront investment and allows for a gradual expansion into new markets. However, exporting can be complicated by tariffs, import regulations, and the need to find reliable distributors or agents in the target market.
This strategy is suitable for companies with established domestic operations and limited resources, as it allows for a measured approach to international expansion. For instance, a small artisan crafts company could begin by exporting their goods to online marketplaces in other countries.
- Licensing: This involves granting a foreign company the right to use a company’s intellectual property, such as patents, trademarks, or copyrights, in exchange for royalties. Licensing is an attractive option for companies that want to minimize their investment in foreign markets but still benefit from the potential for high returns. However, maintaining control over the quality and image of the product or service in a foreign market can be a challenge.
This strategy is particularly relevant for companies with proprietary technologies or strong brand recognition that can be leveraged in new markets. For example, a software company might license its software to a foreign company in a particular region.
- Franchising: This approach involves granting a foreign company the right to operate a business using a company’s brand and business model. It offers the potential for rapid expansion into new markets while relying on the local expertise of the franchisee. However, maintaining brand consistency across different locations can be challenging. Franchising is ideal for companies with established brand recognition and a proven business model, as it leverages local expertise and potentially high profit margins.
A coffee shop chain, for example, might franchise its business in a new country.
- Joint Ventures: This involves creating a new company with a foreign partner. This strategy allows for the sharing of resources and expertise, which can be especially beneficial in complex markets. However, conflicts of interest or disagreements between partners can arise. This is ideal for businesses seeking to leverage the expertise and resources of a foreign partner to overcome barriers in a new market.
A technology company, for example, might enter a foreign market through a joint venture with a local telecommunications provider.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): This involves establishing a physical presence in a foreign market, such as setting up a manufacturing facility or a retail store. It offers the most control over operations and allows for a strong brand presence. However, FDI requires significant capital investment and is subject to local regulations and political risks. This is a significant commitment for a company and is most appropriate for companies seeking complete control over their operations in a new market, such as a large multinational corporation establishing a manufacturing plant in a foreign country.
Comparing Implementation Challenges
The challenges associated with each market entry strategy vary significantly. Exporting faces challenges with logistics and tariffs, while licensing requires careful management of intellectual property rights. Franchising demands brand consistency, joint ventures necessitate strong partnerships, and FDI presents considerable financial and political risks. Choosing the wrong strategy can lead to wasted resources and missed opportunities.
Pitfalls of Choosing the Wrong Strategy
Implementing an inappropriate market entry strategy can lead to numerous problems. For example, trying to enter a highly regulated market with a licensing agreement might prove ineffective. A lack of local market research can lead to a poor understanding of consumer needs and preferences.
Adapting Strategies Based on the Market
No single strategy is universally applicable. Companies must carefully assess the specific market environment, including cultural norms, economic conditions, and political stability, before selecting a market entry strategy. A successful strategy must be adaptable to changing market conditions. A company that ignores these factors risks failure.
Summary Table
| Market Entry Strategy | Description | Potential Challenges | Success Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exporting | Selling products/services to foreign customers | Tariffs, regulations, finding reliable distributors | Established domestic operations, limited resources |
| Licensing | Granting rights to use intellectual property | Maintaining brand consistency, control over quality | Proprietary technologies, strong brand recognition |
| Franchising | Granting rights to operate a business using a brand | Maintaining brand consistency across locations | Established brand, proven business model |
| Joint Ventures | Creating a new company with a foreign partner | Conflicts of interest, disagreements between partners | Leveraging partner expertise, overcoming market barriers |
| Foreign Direct Investment | Establishing a physical presence in a foreign market | Significant capital investment, local regulations, political risks | Complete control over operations, strong brand presence |
Resource Management and Allocation
Effective market implementation hinges on meticulous resource management. Without a well-defined plan for allocating resources, projects can falter, budgets can be exceeded, and deadlines missed. This section explores the critical role of resource management in market implementation, highlighting common issues, budget constraints, optimization strategies, and successful examples.Resource allocation is not merely about assigning funds; it encompasses the careful deployment of all resources – human capital, technology, materials, and time – towards achieving specific objectives.
A poorly managed allocation can lead to bottlenecks, wasted efforts, and ultimately, failure to meet the desired market penetration goals.
Avoiding common Marketo implementation pitfalls is key to success. One often overlooked aspect is ensuring your freelance ghost writer, like those highlighted in 4 ways to increase ROI freelance ghost writer , is effectively integrated into your overall marketing strategy. Poorly defined goals and a lack of clear KPIs can lead to wasted budget and missed opportunities.
Focusing on these critical elements, you can steer clear of common mistakes and optimize your Marketo ROI.
Common Resource Allocation Issues
Resource allocation problems often stem from inadequate planning and poor communication. Unclear project scope, lack of defined roles and responsibilities, and a failure to anticipate resource needs during different project phases contribute to these issues. Moreover, competing priorities within the organization can divert resources from market implementation initiatives, causing delays and hindering progress.
Budget Constraints and Their Impact
Budget constraints severely limit the scope and speed of market implementation. Insufficient funding can lead to inadequate staffing levels, the purchase of inferior technology, or a reduced marketing campaign budget. These limitations directly impact the project’s ability to reach its target audience effectively and achieve its desired market share. For instance, a limited marketing budget might force the team to prioritize one channel over another, impacting the potential reach and return on investment.
Strategies to Optimize Resource Utilization and Allocation
Several strategies can optimize resource utilization and allocation. Developing a detailed project plan outlining specific tasks, required resources, and timelines is crucial. Regular monitoring and reporting on resource consumption are vital for identifying and addressing potential bottlenecks. Implementing a robust project management system, with clear communication channels, facilitates efficient resource allocation and ensures everyone is aware of their responsibilities.
Prioritizing tasks based on their impact on project objectives is essential for maximizing return on investment.
Examples of Successful Resource Management
Successful resource management in market implementations often involves a collaborative approach. For example, organizations that have successfully launched new products or services in new markets often utilized a phased approach, allocating resources incrementally as the project progressed. This allowed them to adapt to evolving market conditions and adjust resource allocation as needed. Furthermore, organizations that have consistently achieved high market share often utilized a data-driven approach, utilizing market research and customer insights to optimize their resource allocation strategies.
Allocating Resources for Specific Tasks
Effective resource allocation for specific tasks involves understanding the resource requirements for each task. This includes estimating the time needed for each task, identifying the skills required, and determining the budget necessary. Project managers should create detailed task breakdowns, assigning specific resources to each, and tracking progress regularly.
Table: Common Resource Constraints and Their Impact
| Resource Constraint | Description | Impact on Implementation | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insufficient Budget | Limited financial resources available for the project. | Reduced marketing efforts, inadequate staffing, inferior technology, delays in project completion. | Seek additional funding, prioritize essential tasks, explore cost-effective solutions. |
| Lack of Skilled Personnel | Inadequate expertise or skillsets within the team. | Delayed task completion, inaccurate data analysis, compromised quality of work. | Recruit skilled personnel, outsource tasks, provide training and development. |
| Limited Access to Technology | Inability to utilize necessary software or tools. | Data entry errors, reduced productivity, delayed project completion. | Invest in necessary technology, explore cloud-based solutions, utilize open-source alternatives. |
| Inadequate Time | Insufficient time allocated for project completion. | Missed deadlines, rushed work, reduced quality, increased errors. | Refine project timeline, prioritize tasks, allocate appropriate time for each task. |
Competition and Market Dynamics: Common Marketo Implementation Challenges To Avoid
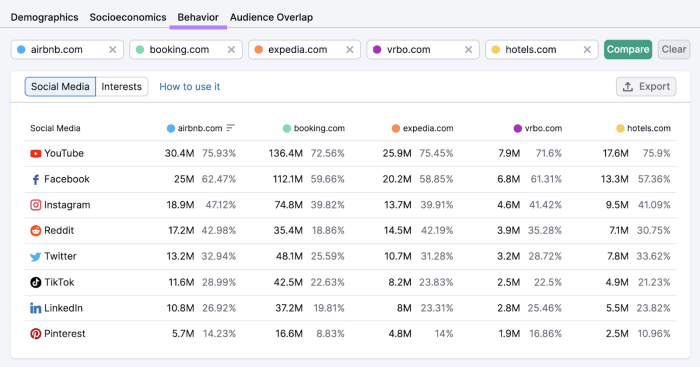
Navigating a competitive market requires constant vigilance and adaptability. Market implementation strategies must be resilient enough to withstand unforeseen shifts in consumer preferences, technological advancements, and competitor actions. Ignoring these dynamics can lead to significant setbacks and ultimately, failure in achieving objectives.Understanding the competitive landscape is not just about identifying rivals; it’s about comprehending the underlying forces driving market behavior.
This involves analyzing not only current competitors but also potential future entrants, as well as emerging technologies and shifting customer needs. Market implementation plans must be flexible enough to accommodate these evolving realities.
Competitive Pressures and Market Implementation
Competitive pressures significantly influence market implementation strategies. High levels of competition often force companies to adopt aggressive pricing strategies, invest heavily in marketing and product development, and prioritize customer service to maintain market share. A company’s ability to adapt to these pressures directly affects its success in the market.
Understanding Market Trends and Competitor Analysis
A thorough understanding of market trends and competitor analysis is crucial for effective market implementation. This involves tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) such as sales figures, market share, and customer acquisition costs. Regular competitor analysis provides insights into their strategies, strengths, and weaknesses, enabling proactive adjustments to one’s own approach. This intelligence allows companies to anticipate potential threats and capitalize on opportunities.
For instance, monitoring social media trends can reveal emerging customer preferences, while analyzing competitor websites can unveil new product features or marketing campaigns.
Impact of Market Shifts on Implementation Plans
Market shifts, such as economic downturns, technological disruptions, or regulatory changes, can significantly impact implementation plans. For example, a sudden increase in raw material costs could necessitate price adjustments or sourcing changes. Technological advancements can render existing products obsolete, necessitating product redesigns or new product development. Implementation plans must be agile enough to adapt to these unexpected events.
A flexible approach, including contingency plans, is essential for navigating unforeseen market disruptions.
Adapting to Unexpected Changes in Market Dynamics
Adapting to unexpected changes in market dynamics requires a flexible and proactive approach. This includes regularly monitoring market trends, actively seeking feedback from customers, and maintaining open communication channels with stakeholders. Building a culture of continuous improvement within the organization is critical for reacting to dynamic shifts. Companies must be prepared to pivot their strategies when necessary, and to learn from both successes and failures.
Maintaining a Competitive Edge in the Target Market
Maintaining a competitive edge in the target market requires a continuous cycle of innovation, adaptation, and improvement. This includes investing in research and development to create new products or services, focusing on building strong customer relationships, and actively seeking feedback to identify areas for improvement. Companies should focus on differentiation, whether through unique product features, exceptional customer service, or a strong brand identity.
Differentiating oneself through innovative solutions is essential for maintaining a competitive advantage.
Competitive Landscape and Implications
| Competitor | Strategy | Market Share | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Company A | Focus on low-cost, high-volume production | 30% | Potential for price wars, pressure on margins |
| Company B | Premium pricing, high-quality products | 20% | Strong brand loyalty, but less price sensitive customers |
| Company C | Niche marketing, targeting specific customer segments | 10% | May offer a smaller but more loyal customer base |
| New Entrant | Aggressive marketing, disruptive pricing | 0% | Potential for market share shift, need for competitive analysis |
Communication and Collaboration Issues
Effective communication and seamless collaboration are crucial for the success of any market implementation project. Without clear and consistent communication channels, misunderstandings, conflicts, and ultimately project failure can arise. Poor internal communication can lead to duplicated efforts, missed deadlines, and a lack of shared understanding of project goals. External communication breakdowns can damage the company’s reputation and hinder the relationship with stakeholders.
This section will delve into the common communication breakdowns in market implementation, the significance of internal and external communication, conflict resolution strategies, successful collaboration examples, and the vital role of clear communication channels.
Common Communication Breakdowns
Misunderstandings often arise from unclear or incomplete information, differing interpretations of instructions, and a lack of active listening. Poorly defined roles and responsibilities can also lead to confusion and conflict. Different communication styles, such as varying levels of formality or preferred methods of communication, can create barriers. Technological glitches, language barriers, and time zone differences can also hinder effective communication.
Importance of Effective Internal Communication
Internal communication is vital for project success. A well-informed team, working cohesively towards a shared goal, increases productivity and efficiency. Open channels of communication facilitate the timely exchange of information, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring everyone is on the same page. Regular updates, transparent decision-making processes, and opportunities for feedback foster a positive and collaborative work environment.
Importance of Effective External Communication
External communication plays a critical role in building and maintaining strong relationships with stakeholders, including customers, partners, and investors. Clear and consistent messaging builds trust and reinforces the company’s commitment to its market strategy. This includes conveying a clear understanding of the project’s objectives, progress updates, and any potential challenges. Transparency and proactive communication manage expectations and prevent misunderstandings.
Methods for Resolving Conflicts and Maintaining Team Cohesion
Effective conflict resolution is critical in maintaining team cohesion. Open dialogue, active listening, and a focus on finding common ground are essential. Mediation or facilitation can be employed to guide discussions and facilitate constructive solutions. Establishing clear procedures for handling disagreements, providing opportunities for team building, and promoting a culture of respect and understanding are essential.
Examples of Successful Collaboration in Market Implementation Projects
Successful collaboration in market implementation projects is often characterized by a shared understanding of project goals, well-defined roles and responsibilities, and consistent communication channels. For example, a project might employ a project management software that tracks progress, tasks, and communication threads, ensuring everyone has access to the latest information. Another project might use a dedicated communication platform for external stakeholders, such as a customer portal or an online forum, to keep them updated and address their concerns promptly.
Furthermore, projects that prioritize clear, concise communication, use multiple channels to reach various stakeholders, and create a safe space for feedback are more likely to succeed.
Importance of Clear Communication Channels for Project Success
Clear communication channels ensure that information flows effectively and efficiently throughout the project lifecycle. A robust system of communication channels, including email, instant messaging, project management software, and regular meetings, enables teams to share updates, address concerns, and maintain momentum. Choosing the right channels for different stakeholders is essential for effective communication.
Communication Strategies for Diverse Stakeholders
| Stakeholder Group | Communication Channel | Communication Goal | Communication Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customers | Email newsletters, dedicated customer portal, social media | Maintain customer satisfaction, provide updates on project progress | Weekly/monthly |
| Partners | Regular meetings, shared project documentation, dedicated communication platform | Foster collaboration, ensure alignment on project goals | Bi-weekly/monthly |
| Investors | Financial reports, presentations, investor relations materials | Maintain transparency, demonstrate project progress and ROI | Quarterly/as needed |
| Internal Teams | Project management software, team meetings, internal communication channels | Ensure alignment on project goals, maintain transparency on tasks and progress | Daily/weekly |
Final Summary
Successfully implementing Marketo requires a proactive approach to anticipating and addressing potential challenges. By understanding the common obstacles Artikeld in this guide, you can significantly improve your chances of a smooth and effective implementation. From meticulous data collection to strategic resource allocation and robust communication, the key is to plan ahead and have a comprehensive strategy in place. This knowledge empowers you to create a tailored plan that addresses the unique needs of your specific market segment and ensures your Marketo implementation yields a significant return on investment.