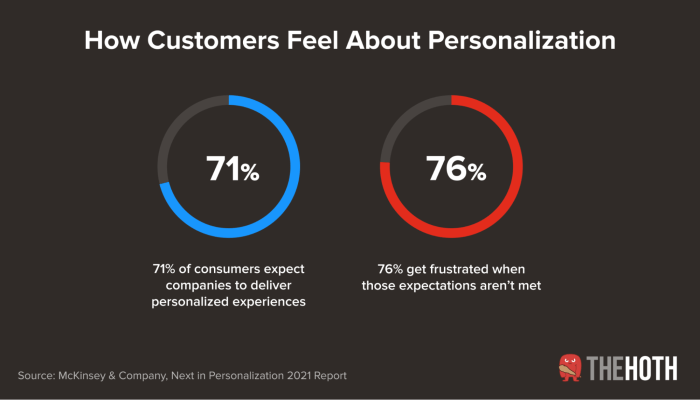
Content personalization what is it? It’s about tailoring online experiences to individual users, making websites, apps, and emails more relevant and engaging. This involves understanding user needs, preferences, and behaviors to deliver content that resonates with each person. From websites to emails, personalization is increasingly crucial for grabbing attention and fostering stronger connections with customers.
By understanding what content personalization what is it, you can craft tailored experiences that boost engagement, drive conversions, and ultimately strengthen customer relationships. This detailed exploration will dive into defining personalization, outlining different types, and discussing implementation strategies.
Defining Content Personalization
Content personalization is no longer a futuristic concept but a crucial element in modern digital strategies. It’s about tailoring online experiences to individual users, recognizing their preferences, needs, and behaviors to deliver highly relevant content. This approach moves beyond generic messaging and creates a more engaging and valuable experience for the user. It’s about understanding the user’s journey and proactively adapting the content to meet their specific requirements.Content personalization goes beyond simply remembering past actions.
It involves analyzing user data, including browsing history, purchase patterns, demographics, and even social media activity, to create a comprehensive profile. This allows for dynamic content adjustments in real-time, ensuring that each user interacts with content that resonates with them. This personalization significantly increases user engagement and conversion rates, ultimately driving better business outcomes.
Core Principles of Content Personalization
Content personalization is built upon several key principles. First, it demands a deep understanding of the target audience, going beyond basic demographics to include interests, values, and pain points. Second, it necessitates the collection and analysis of user data in an ethical and transparent manner, adhering to privacy regulations and gaining informed consent. Third, it requires the implementation of sophisticated technologies that can process and interpret vast amounts of data to generate personalized recommendations.
Content personalization is all about tailoring your content to individual users, right? It’s a key part of modern content marketing, and understanding best practices like content marketing best practices is crucial. Ultimately, if you want to engage your audience effectively, personalized content is a powerful tool in your arsenal.
Finally, it necessitates continuous monitoring and evaluation to refine strategies and adapt to evolving user needs.
Methods of Content Personalization Across Platforms
Personalization strategies are implemented across various digital touchpoints, including websites, mobile apps, and email marketing campaigns. On websites, personalization manifests in tailored product recommendations, dynamic content displays, and personalized search results. Mobile apps leverage personalized content feeds, targeted notifications, and customized user interfaces. Email marketing campaigns employ personalized subject lines, customized content, and targeted offers.
Importance of Understanding User Needs
Effective content personalization hinges on a profound understanding of user needs. This involves identifying the specific pain points and desires of different user segments. By understanding user needs, businesses can craft content that directly addresses those needs, leading to a more meaningful and impactful user experience. This deeper understanding of user preferences fosters stronger engagement and brand loyalty.
Benefits of Tailoring Content to Individual Users
Personalization offers numerous benefits. Increased user engagement is a key advantage, as users are more likely to interact with content that resonates with them. This engagement often leads to higher conversion rates, as personalized recommendations and offers are more likely to motivate purchases. Personalization also enhances brand loyalty and fosters a more positive user experience, building stronger customer relationships.
Improved customer satisfaction results from content that caters to individual preferences, making users feel understood and valued.
Different Approaches to Content Personalization
Different approaches exist for personalizing content. The table below highlights some key methods and their characteristics.
| Approach | Description | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic-Based | Content tailored based on user demographics (age, gender, location). | Relatively easy to implement, inexpensive. | Limited personalization, may not capture individual preferences. |
| Behavioral-Based | Content personalized based on user behavior (website activity, purchase history). | More accurate personalization, higher engagement potential. | Requires more data collection, potentially raising privacy concerns. |
| AI-Powered | Content personalized using AI algorithms that analyze vast amounts of data to predict user preferences. | Highly accurate and adaptable personalization, scalable solutions. | Can be complex to implement, requires significant data. |
Types of Content Personalization
Content personalization isn’t a one-size-fits-all approach. It leverages diverse techniques to cater to individual user needs and preferences, ultimately boosting engagement and conversion rates. Understanding the various types allows businesses to craft highly targeted experiences.Personalized content goes beyond simply displaying different products. It involves tailoring the entire user journey, from initial interaction to post-purchase follow-up, ensuring a seamless and relevant experience for each individual.
User-Based Personalization
This type of personalization focuses on individual user profiles, extracting insights from their past behavior and interactions. Understanding past browsing history, purchase decisions, and engagement levels are key to crafting personalized recommendations and experiences. This deep understanding allows for a more proactive and relevant approach. For example, a user who frequently visits a gardening section on an online retailer’s website will likely receive tailored recommendations for gardening tools and supplies.
Contextual Personalization
Contextual personalization focuses on understanding the immediate situation of the user. This might involve their location, device, time of day, or even the specific webpage they’re currently viewing. For instance, a user browsing a clothing store from a mobile device in a specific region will see product recommendations and promotions relevant to their location and device type. Contextual factors provide a dynamic layer of personalization.
Demographic Personalization
Demographic personalization uses broad characteristics like age, gender, location, and interests to segment users and deliver tailored content. This method can be highly effective in reaching specific user groups with targeted marketing messages and product recommendations. For instance, a company targeting teenagers might use demographic data to showcase products and promotions appealing to that particular age group.
Behavioral Personalization
This approach relies heavily on the user’s past actions and interactions. Analyzing website browsing patterns, purchase history, and engagement levels reveals insights into user preferences and interests. This allows for dynamic and responsive content adjustments. A user who frequently purchases a particular type of product will likely see more recommendations and promotions for similar items.
Algorithmic Personalization
Algorithms are essential tools in the personalization process. They analyze vast amounts of user data to identify patterns and predict user preferences. These algorithms use complex mathematical models and machine learning techniques to provide personalized content recommendations. For example, a movie streaming service utilizes algorithms to suggest movies based on a user’s viewing history and ratings, predicting what they might enjoy.
Table of Personalization Types
| Type of Personalization | Methods | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| User-Based | Analyzing user profiles, browsing history, purchase history | Recommending products based on past purchases, suggesting similar items |
| Contextual | Leveraging location, device, time of day, current webpage | Showing location-specific deals, recommending products based on current browsing page |
| Demographic | Segmenting users by age, gender, location, interests | Targeting specific age groups with relevant promotions, showcasing products tailored to interests |
| Behavioral | Analyzing user interactions, website browsing patterns, engagement levels | Recommending products based on recent browsing behavior, suggesting similar products purchased by others |
| Algorithmic | Using machine learning and complex algorithms to predict preferences | Recommending movies based on viewing history, suggesting articles based on past reads |
Implementing Personalization Strategies
Content personalization isn’t just a buzzword; it’s a crucial component of modern marketing and customer experience. Successfully implementing personalization requires a well-defined strategy, meticulous execution, and a deep understanding of your audience. This section delves into the practical aspects of developing and executing a content personalization strategy.Effective personalization goes beyond simply tailoring content to demographics. It’s about understanding individual user behavior, preferences, and needs to deliver highly relevant and engaging experiences.
This results in increased customer satisfaction, higher conversion rates, and stronger brand loyalty.
Developing a Content Personalization Strategy
A robust personalization strategy begins with a clear understanding of your target audience. Identifying key characteristics, behaviors, and motivations is critical. Data collection and analysis are essential steps in creating detailed user profiles. This understanding should drive decisions about content relevance and delivery methods. Consider how different segments respond to various types of content and tailor your approach accordingly.
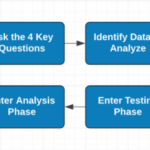
Process Flow for Implementing Personalized Content
A structured process is crucial for effective content personalization. A typical process flow involves these stages:
- Data Collection and Analysis: Gathering data from various sources, such as website interactions, purchase history, and surveys, is vital for building detailed user profiles. Analyzing this data identifies patterns and preferences to understand customer behavior.
- Segmenting the Audience: Dividing your audience into distinct segments based on shared characteristics or behaviors allows for tailored content delivery. This approach maximizes the relevance and impact of personalized messages.
- Content Creation and Customization: Creating a library of personalized content tailored to each segment is a key step. The content should address specific needs and interests within each segment.
- Delivery and Measurement: Implementing tools and platforms to deliver personalized content to the right users at the right time is essential. Track and measure the effectiveness of personalized content through key metrics such as conversion rates, engagement rates, and customer satisfaction.
- Continuous Optimization: Regular monitoring and analysis of the performance of personalized content is essential for ongoing optimization. Adjusting strategies based on feedback and results ensures continued improvement.
Tools and Technologies for Content Personalization
Several tools and technologies can facilitate content personalization.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems: CRMs store and manage customer data, enabling the creation of detailed user profiles and the targeting of personalized messages.
- Marketing Automation Platforms: These platforms automate the delivery of personalized content based on predefined rules and user behavior.
- Personalization Engines: These tools allow for the dynamic creation and delivery of personalized content based on real-time data and user profiles.
- Analytics Platforms: Tools like Google Analytics track user behavior and provide insights into what content resonates best with different segments.
Challenges in Implementing Effective Personalization Strategies
Implementing effective personalization strategies isn’t without challenges.
- Data Privacy and Security Concerns: Collecting and using user data responsibly is paramount. Strict adherence to data privacy regulations is crucial to avoid legal and reputational risks.
- Scalability Issues: Personalization can become complex as the volume of data and the number of users increase. Choosing the right tools and technologies to manage scalability is essential.
- Maintaining Content Quality: Ensuring the relevance and quality of personalized content across different segments is a key challenge. Maintaining a consistent brand message while tailoring content for specific groups is critical.
- Keeping Up with Evolving User Needs: User preferences and behaviors change over time. A robust personalization strategy must adapt to these changes to maintain relevance and engagement.
Examples of Content Personalization in Action
Several companies successfully utilize personalization in their marketing efforts.
- Amazon: Their personalized product recommendations based on purchase history and browsing behavior are well-known examples.
- Netflix: Their recommendation system suggests movies and shows based on viewing history and preferences.
- Spotify: Their personalized playlists and recommendations based on user listening habits are another example.
Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing Content Personalization on a Website
- Define Goals and Objectives: Clearly articulate what you want to achieve with content personalization.
- Identify Target Audience Segments: Determine the characteristics and behaviors of different user groups.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Gather data from various sources to create user profiles.
- Choose the Right Tools and Technologies: Select the tools that align with your needs and resources.
- Develop Personalized Content: Create content that resonates with each segment’s interests and needs.
- Implement and Test: Gradually roll out personalized content and monitor its performance.
- Measure and Analyze Results: Track key metrics and adapt the strategy based on data.
Measuring the Impact of Personalization
Content personalization, while powerful, needs robust measurement to demonstrate its value. Simply implementing personalized content isn’t enough; understanding its impact on user behavior and business outcomes is crucial for optimization. Effective personalization relies on a data-driven approach that tracks key metrics and analyzes user interactions. This allows for continuous improvement and ensures that personalized experiences align with business goals.Measuring personalization effectiveness isn’t just about tracking vanity metrics; it’s about understanding how personalized content influences user actions, from engagement to conversions.
This requires a multifaceted approach that combines quantitative and qualitative data analysis to gauge the true impact of these tailored experiences.
Key Metrics for Assessing Personalization Success
Effective personalization relies on a comprehensive understanding of user behavior and how personalized content impacts that behavior. This necessitates tracking a range of metrics to paint a complete picture of success.
Content personalization, in a nutshell, is tailoring your content to resonate with individual users. It’s about understanding your audience’s needs and preferences, and delivering the right information at the right time. This often involves using data to create unique experiences, and a crucial aspect of that is selecting the perfect visuals for your blog posts. For a comprehensive guide on crafting compelling blog post images, check out our helpful resource: blog post image guide.
Ultimately, the goal of personalization is to create a more engaging and effective online experience for your audience.
- Conversion Rates: Personalized content should drive higher conversion rates than generic content. Tracking the conversion rate for different segments exposed to personalized content versus those exposed to generic content is essential. For instance, if a personalized email campaign increases the purchase rate by 15% compared to a generic campaign, that signifies a successful personalization strategy.
- Engagement Metrics: Engagement metrics, such as time spent on a page, click-through rates, and the number of interactions, are critical indicators of content effectiveness. Personalized content should inherently be more engaging, thus leading to higher interaction rates. For example, if a personalized product recommendation section increases the average time spent on the product page by 10%, it demonstrates the effectiveness of the personalized content.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): The long-term value a customer brings to a business is directly impacted by personalization. Analyzing CLTV for segments exposed to personalized content versus generic content allows businesses to assess the overall impact of personalization on revenue generation over time. For instance, if a segment receiving personalized recommendations shows a 20% increase in CLTV compared to a control group, the personalization strategy is likely successful.
Analyzing User Engagement with Personalized Content
Understanding how users interact with personalized content is vital for refining the strategy. This involves tracking specific user behaviors to gain valuable insights.
- A/B Testing: A/B testing personalized content against generic content is a crucial method to determine the effectiveness of different personalization strategies. For example, testing different personalized product recommendations against generic recommendations can identify which approach results in higher purchase rates.
- Heatmaps and Clickstream Data: Analyzing heatmaps and clickstream data provides valuable insights into where users are focusing their attention on personalized content. Identifying areas of high engagement or areas of confusion helps in optimizing the design and presentation of the personalized content.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Personalization, Content personalization what is it
Identifying and tracking KPIs specific to personalization efforts is essential for measuring success and continuous improvement.
| KPI | Description | How to Track |
|---|---|---|
| Conversion Rate (Personalized vs. Generic) | Percentage of users who complete a desired action (e.g., purchase, signup) after interacting with personalized content versus generic content. | Use analytics platforms to segment users and track conversions for each group. |
| Average Session Duration (Personalized vs. Generic) | Average time spent by users on a page or within a personalized experience compared to generic experiences. | Utilize website analytics tools to measure session duration for different content types. |
| Click-Through Rate (CTR) | Percentage of users who click on a specific element (e.g., a link, a button) within the personalized content. | Track clicks on different elements within personalized content using analytics tools. |
| Bounce Rate (Personalized vs. Generic) | Percentage of users who leave a page or experience after viewing the initial page or personalized content. | Compare bounce rates for users interacting with personalized content to those interacting with generic content. |
Tracking User Behavior to Optimize Personalization
Optimizing personalization requires constant monitoring and analysis of user behavior. This involves leveraging various tools and techniques to gain valuable insights into how users interact with personalized content.
- User Feedback Mechanisms: Incorporating feedback mechanisms, such as surveys or feedback forms, can provide valuable insights into user experiences with personalized content.
- Data Analysis Tools: Leveraging analytics tools like Google Analytics or other dedicated platforms allows for the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data related to user behavior.
Ethical Considerations in Content Personalization
Content personalization, while offering tailored experiences, raises significant ethical concerns regarding user data. The increasing reliance on user data for targeted content necessitates a careful consideration of privacy, security, and potential biases within personalization algorithms. A responsible approach to personalization requires a strong ethical framework to ensure fair and equitable treatment for all users.
Ethical Implications of Using User Data
The collection and use of user data for personalization raise important ethical implications. Data breaches, misuse of personal information, and the potential for discriminatory practices are all potential risks. For example, if a company collects sensitive data like health information or financial details for personalization purposes, a security breach could have severe consequences for the user. Furthermore, personalized content might inadvertently reinforce existing societal biases, if not carefully monitored and controlled.
The potential for manipulation through personalized content also necessitates careful consideration.
Ensuring User Privacy and Data Security
Robust data security measures are crucial for safeguarding user privacy. Implementing strong encryption protocols, limiting data access to authorized personnel, and regularly auditing data practices are essential steps. Users should be provided with clear and comprehensive privacy policies that Artikel how their data will be collected, used, and protected. Regular security assessments and compliance with relevant data protection regulations are essential to mitigate risks.
User consent and transparency are critical components of any ethical personalization strategy.
Content personalization, simply put, is tailoring your website’s content to individual users. It’s about understanding your audience’s needs and preferences to deliver a more relevant and engaging experience. This directly impacts how your site looks and feels, including the crucial role of typography in conveying your message effectively. For instance, consider how how typography affects conversions can significantly impact conversions.
Ultimately, by understanding and implementing effective personalization strategies, you’re creating a more satisfying and impactful user experience.
Identifying Potential Biases in Personalization Algorithms
Personalization algorithms can perpetuate existing societal biases if not designed and trained carefully. For example, if an algorithm is trained on data reflecting historical gender or racial biases, it might reinforce those biases in its recommendations. This can lead to unequal access to information or opportunities for certain groups. Regular audits and testing of algorithms for bias are essential to ensure fairness and inclusivity.
Guidelines for Responsible Use of User Data
To ensure responsible data use, companies should establish clear guidelines for data collection, storage, and use. These guidelines should include restrictions on the types of data collected, the purposes for which it can be used, and the duration for which it will be retained. Transparency and user control over their data are paramount. Users should be empowered to review, correct, and delete their data as needed.
Importance of Transparency with Users
Transparency regarding personalization practices is essential to build trust and maintain user confidence. Clear communication about how data is collected, used, and protected is crucial. Users should be informed about the specific types of content being personalized, the criteria used for personalization, and the potential consequences of these practices. This transparency fosters user agency and empowers them to make informed decisions about their data.
Ethical Considerations List
- Data Minimization: Collect only the necessary data for personalization purposes. Avoid collecting excessive or sensitive data.
- Data Security: Implement robust security measures to protect user data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, alteration, or destruction.
- Transparency and Consent: Clearly communicate data practices to users and obtain informed consent before collecting and using their data.
- Bias Mitigation: Regularly audit and test personalization algorithms for potential biases and take corrective actions to ensure fairness and inclusivity.
- User Control: Provide users with control over their data, including the ability to access, correct, and delete their data.
- Accountability: Establish clear lines of accountability for data practices and create mechanisms for addressing user concerns.
Future Trends in Content Personalization: Content Personalization What Is It

Content personalization is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing user expectations. No longer simply about displaying different product recommendations, the future of personalization is about creating truly tailored experiences that anticipate and address individual needs. This involves not just presenting relevant content but also understanding the context and intent behind each interaction.The future of content personalization will be deeply intertwined with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), enabling more sophisticated and proactive personalization strategies.
These technologies will enable systems to not only understand user preferences but also predict future needs, allowing for a proactive approach to engagement and satisfaction.
Emerging Technologies and Trends
AI and machine learning are fundamentally changing the way content is personalized. These technologies enable algorithms to analyze vast amounts of data, including user behavior, demographics, and past interactions, to create highly tailored experiences. Natural Language Processing (NLP) is also crucial, enabling AI to understand user intent and sentiment, allowing for more nuanced and effective personalization. The use of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are also emerging as powerful tools to create immersive and personalized content experiences.
Furthermore, the rise of personalized search is set to transform how users discover information, making content more accessible and relevant.
Impact of AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are revolutionizing content personalization by enabling algorithms to understand and predict user behavior with increasing accuracy. This allows for proactive content delivery, anticipating user needs before they are explicitly expressed. For example, an e-commerce platform using AI could recommend products based on not just past purchases, but also browsing history, social media activity, and even current economic trends.
This level of prediction allows for a much more sophisticated and anticipatory personalization approach.
Future of Personalized Content Experiences
Personalized content experiences are moving beyond simple recommendations to encompass more nuanced aspects of user interaction. Users will expect a seamless integration of personalized content into their daily lives, across various platforms and devices. This will require the development of more sophisticated algorithms that can handle complex data sets and adapt to dynamic user behavior. Content delivery will become more proactive, anticipating needs and preferences, rather than simply reacting to explicit requests.
Potential Benefits and Challenges of Advanced Personalization
Advanced personalization techniques offer immense potential for improving user engagement and satisfaction. They can lead to increased conversion rates, higher customer lifetime value, and a more positive brand perception. However, challenges exist. Privacy concerns are paramount, requiring careful consideration of data collection, storage, and usage practices. Ensuring fairness and avoiding bias in algorithms is also critical to maintain a positive user experience for everyone.
Evolution of Personalization with Changing User Expectations
User expectations are rapidly evolving, with a growing demand for personalized experiences across all digital touchpoints. Users expect relevant content, tailored recommendations, and seamless integration across platforms. To meet these evolving expectations, content providers must invest in sophisticated personalization strategies that can adapt to changing user needs and behaviors in real time.
Potential Impact of Technologies on Content Personalization
| Technology | Potential Impact on Content Personalization ||—|—|| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Enables proactive content delivery, anticipating user needs; highly tailored experiences. || Machine Learning (ML) | Improves accuracy of user behavior prediction; enhances dynamic content adaptation. || Natural Language Processing (NLP) | Allows for nuanced understanding of user intent and sentiment; enables more responsive personalization. || Augmented Reality (AR) & Virtual Reality (VR) | Creates immersive and personalized content experiences, enhancing engagement and satisfaction.
|| Personalized Search | Improves discovery of relevant information; makes content more accessible and user-friendly. |
Epilogue
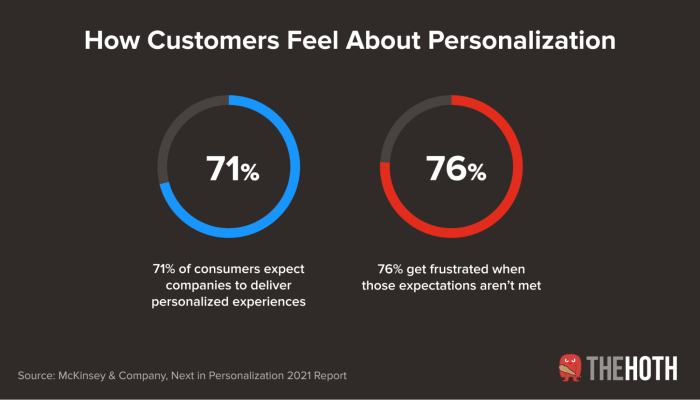
In conclusion, content personalization what is it, ultimately boils down to understanding your audience and adapting your content accordingly. From defining core principles to implementing strategies, and measuring success, content personalization is a powerful tool. By embracing ethical considerations and anticipating future trends, you can leverage this technique to build lasting connections with your users and drive meaningful results.