Empathy map vs persona unleashing consumer insights is a crucial topic for businesses seeking to understand their customers. This exploration delves into the strengths and weaknesses of both empathy maps and personas, examining how they can be used to uncover customer motivations, needs, and pain points. We’ll compare their data collection methods, creation processes, and the insights they provide, ultimately helping you choose the right approach for your specific business needs.
The discussion covers everything from identifying key customer segments to creating detailed personas and combining the methods for a holistic view.
This detailed guide breaks down the intricacies of each method, providing practical examples, case studies, and a breakdown of the various tools and technologies available. Learn how to use empathy maps to visualize customer journeys, understand consumer behavior, and extract valuable insights. We’ll also examine how personas can help you create detailed representations of your ideal customer, encompassing demographics, psychographics, and motivations.
The article concludes by addressing potential limitations and pitfalls of both methods, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of their application.
Introduction to Empathy Maps and Personas
Understanding your customers is crucial for any business. Empathy maps and personas are powerful tools for achieving this, allowing businesses to delve deeper into customer behavior and motivations. They provide valuable insights that can inform product development, marketing strategies, and overall business decisions.These tools, while complementary, offer different perspectives. Empathy maps focus on visualizing the customer’s experience, while personas create a detailed representation of a typical customer segment.
By exploring both, businesses can develop a comprehensive understanding of their target audience, leading to more effective strategies and improved customer satisfaction.
Empathy Map Definition and Strengths/Weaknesses
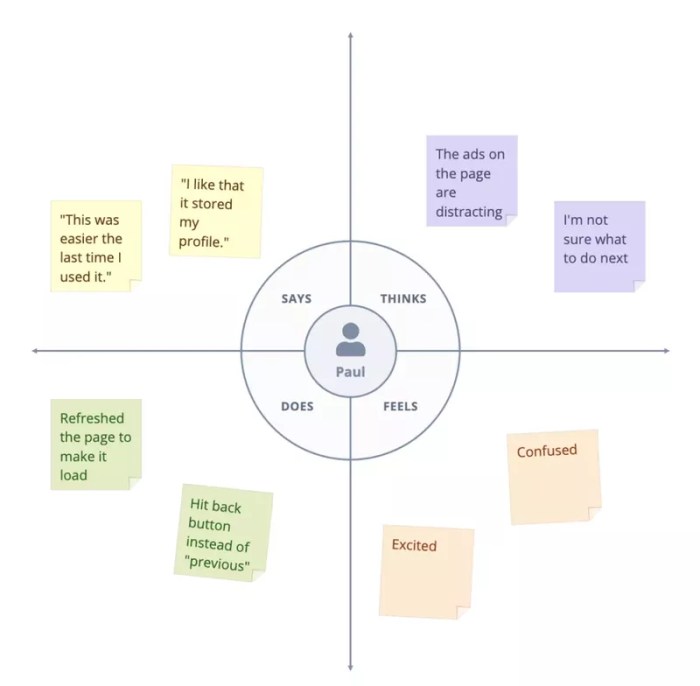
An empathy map is a visual tool used to understand a customer’s perspective. It helps identify a customer’s thoughts, feelings, pains, and gains in relation to a particular product or service. Strengths lie in its ability to quickly capture diverse perspectives and facilitate brainstorming sessions. It’s particularly useful for generating creative ideas and exploring multiple customer viewpoints. A weakness, however, might be its less structured approach, potentially leading to less in-depth analysis compared to personas.
Persona Definition and Strengths/Weaknesses
A persona is a detailed representation of a typical customer within a specific segment. It includes demographic information, psychographic details, motivations, and pain points. Personas provide a more structured and detailed understanding of customer segments, offering specific insights for targeted marketing efforts. A potential weakness is the time and resources needed to create a comprehensive persona, requiring significant data collection and analysis.
This can be a barrier in quickly gaining initial insights.
Comparison of Empathy Maps and Personas
| Feature | Empathy Map | Persona |
|---|---|---|
| Data Collection Method | Qualitative data, including observations, interviews, surveys, and existing data sources. | Quantitative data, including surveys, interviews, and secondary data sources to create detailed profiles. |
| Focus | Understanding the customer’s experience and perspective. | Representing a typical customer within a segment. |
| Depth of Analysis | Broader, more qualitative overview. | More in-depth, structured analysis. |
| Time Investment | Generally quicker to create. | Requires more time and resources. |
Stages in Creating Empathy Maps
Creating an empathy map typically involves these stages:
- Defining the customer segment: Clearly identify the target audience. Consider their demographics, behaviors, and needs.
- Gathering data: Collect information through interviews, surveys, observations, and existing data sources. This data should include both quantitative and qualitative elements to create a holistic view.
- Visualizing the customer experience: Create a visual representation of the customer’s thoughts, feelings, pains, and gains related to the product or service.
- Analyzing the findings: Identify key insights and patterns from the map. This is crucial for generating actionable ideas.
Stages in Creating Personas
Creating a persona typically involves these steps:
- Defining the target market: Identify specific customer segments relevant to the product or service.
- Data Collection: Gather data through interviews, surveys, and analysis of existing customer data. Thorough data collection is essential to create a realistic representation.
- Developing the persona profile: Create a detailed profile that includes demographics, psychographics, motivations, and pain points. This profile should be specific and relevant.
- Validation and refinement: Ensure the persona accurately represents the target customer segment by verifying information with stakeholders and customers.
Key Considerations for Choosing Between Empathy Maps and Personas
- Project Goals: If the goal is a quick understanding of customer perspectives, an empathy map might be sufficient. If a detailed representation of a customer segment is needed, a persona is a better choice.
- Available Resources: Empathy maps are often more manageable in terms of time and resources. Personas require more resources and time for in-depth data collection and analysis.
- Depth of Analysis Needed: Empathy maps provide a broad overview of customer experience, while personas offer a detailed understanding of individual customer segments. Choose the method based on the required level of detail.
Uncovering Consumer Insights using Empathy Maps
Empathy maps are powerful tools for understanding consumers. They go beyond basic demographic data to delve into the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of your target audience. By visualizing these elements, empathy maps provide a holistic view of the consumer, revealing valuable insights into their motivations, needs, and pain points. This understanding is crucial for developing effective marketing strategies, product improvements, and overall business success.Empathy maps provide a framework to move beyond assumptions and truly understand the consumer.
They reveal the unspoken needs and desires, and help identify opportunities for creating products and services that resonate deeply with customers. This shift from assumptions to understanding fosters more effective communication and solutions.
Identifying Consumer Motivations, Needs, and Pain Points
Empathy maps facilitate the identification of consumer motivations, needs, and pain points by focusing on the “why” behind customer actions. They explore the emotional and rational drivers of their decisions, providing a richer understanding of their motivations. For example, a customer might buy a specific product not just because of its features, but because it represents a sense of status or belonging, or because it solves a specific problem.
Empathy maps reveal these deeper motivations. Understanding the pain points, the frustrations and struggles consumers face, allows for the development of solutions that directly address those issues.
Understanding consumer behavior through empathy maps and personas is key, but getting the data right is crucial. To truly uncover those insights, you need accurate analytics. Checking out these 5 GA4 tips to get quality analytics 5 ga4 tips to get quality analytics will help you avoid common pitfalls and ensure your data paints a clear picture.
This data then fuels better empathy maps and personas, ultimately leading to a deeper understanding of your target audience.
Identifying Key Customer Segments
Empathy maps are highly effective in identifying key customer segments. By analyzing the responses and insights gathered from different customer groups, businesses can categorize customers into distinct segments based on shared characteristics and behaviors. This segmentation process allows for tailored marketing strategies and product development that address the unique needs and desires of each segment. It moves beyond a generalized approach and allows for a targeted, individualized approach that drives greater success.
Visualizing Customer Journey Maps with Empathy Maps
Integrating empathy maps with customer journey maps creates a powerful visual representation of the customer’s experience. This combined approach allows for a deep understanding of the emotions, thoughts, and actions of customers at each stage of their interaction with the product or service. By visualizing the customer journey with an empathy map, businesses can identify potential touchpoints for improvement, and uncover areas where the customer experience could be enhanced.
For instance, a customer might experience frustration at a specific step in the purchasing process, and an empathy map can pinpoint this frustration and suggest potential solutions.
Types of Insights Extracted from Empathy Maps
| Insight Category | Example |
|---|---|
| Motivations | Desire for convenience, status, or problem-solving |
| Needs | Functional needs (e.g., durability) or emotional needs (e.g., belonging) |
| Pain Points | Frustrations with a particular process, difficulty understanding instructions, or lack of support |
| Frustrations | Technical glitches, long wait times, or poor customer service interactions |
| Thoughts and Feelings | Positive emotions (e.g., excitement, satisfaction) or negative emotions (e.g., confusion, anxiety) |
| Behaviors | Specific actions taken by the customer, such as researching products online, comparing prices, or contacting customer support |
Analyzing Gathered Information
Analyzing the collected information from empathy maps requires a systematic approach. This involves identifying recurring themes, patterns, and insights that emerge from the combined data. The process should be iterative, with constant feedback loops to ensure accuracy and relevance. This analysis is not a one-time event; it should be an ongoing process that refines understanding of consumer behavior over time.
For example, comparing customer segments through the lens of their frustrations and motivations will allow for identification of opportunities for improvement in the customer experience.
Uncovering Consumer Insights using Personas: Empathy Map Vs Persona Unleashing Consumer Insights
Personas are more than just fictional characters; they’re powerful tools for understanding your customers on a deeper level. They represent archetypal customer segments, allowing businesses to tailor products, services, and marketing strategies to resonate with specific needs and motivations. By stepping into the shoes of these representative customers, businesses can anticipate their behaviors, predict their needs, and ultimately drive more effective and profitable strategies.Creating detailed and realistic personas is crucial for accurate representation of target customers.
These detailed profiles provide a roadmap for understanding customer needs, motivations, and pain points. This understanding fuels the development of more relevant and impactful products and services. Furthermore, personas enable marketers to tailor their messaging and communication channels to resonate with specific customer segments, resulting in increased engagement and conversion rates.
Creating Detailed and Realistic Personas
Personas are not simply lists of demographics; they are richly detailed representations of the customer’s experience. A comprehensive persona should go beyond basic facts and delve into the customer’s motivations, values, and pain points. This nuanced understanding allows businesses to tailor products and services to specific needs, resulting in increased customer satisfaction and loyalty. The key is to move beyond surface-level data to gain a profound understanding of the individual’s motivations and anxieties.
Steps in Identifying and Developing Customer Personas
Developing customer personas involves a systematic approach. It starts with comprehensive research to identify key customer segments. This research may include surveys, interviews, focus groups, and analyzing existing customer data. Next, analyze the collected data to identify patterns and common characteristics among customer segments. This process involves grouping similar customer profiles based on their behaviors, motivations, and needs.
Finally, synthesize the findings into detailed, fictional representations of your target customers. This step involves creating narratives around these personas, incorporating their motivations, aspirations, and frustrations to achieve a complete understanding.
The Role of Demographics and Psychographics
Demographics provide the foundational elements of a persona, like age, gender, location, and occupation. However, a complete understanding of the customer requires incorporating psychographics – the psychological characteristics, values, interests, and lifestyles. These elements provide insight into the customer’s motivations and decision-making processes. For instance, a persona might be a young professional living in a major city, but their psychographics might reveal a strong interest in sustainability and social responsibility, impacting their purchasing decisions.
A successful persona balances factual demographic information with the nuances of individual psychology.
Comparing Empathy Maps and Personas
Empathy maps and personas both provide valuable insights into customer behavior. However, they differ in the level of detail they offer. Empathy maps focus on understanding the customer’s experience from a broader perspective, encompassing their emotions, thoughts, and pain points. Personas, on the other hand, offer a more structured and detailed representation of a specific customer segment, including their motivations, goals, and decision-making processes.
While empathy maps paint a vivid picture of the customer’s experience, personas offer a more actionable framework for product development and marketing. The level of detail provided by personas allows for more precise targeting and messaging strategies, making them valuable tools for businesses seeking to enhance customer understanding and satisfaction.
Combining Empathy Maps and Personas for Enhanced Insights
Combining empathy maps and personas provides a powerful, holistic view of your target customer. Empathy maps delve deep into the customer’s experience, uncovering their motivations, pain points, and emotional responses. Personas, on the other hand, create a more generalized representation of the customer, allowing for a structured approach to understanding their needs and behaviors. Integrating these two powerful tools creates a richer, more actionable understanding that leads to more effective strategies and products.This integrated approach allows for a deeper dive into customer needs.
Instead of relying solely on surface-level data, it helps uncover the underlying motivations and emotions driving customer behavior. This results in a more nuanced understanding, leading to more effective product development, marketing campaigns, and customer service strategies. Understanding the customer’s journey, both emotionally and logically, is critical to developing solutions that truly resonate.
Understanding empathy maps versus personas is key to unlocking consumer insights. These tools help you truly connect with your audience, but creating compelling content that resonates with them requires a strategic approach. For example, delving into the 8 essential steps for effective content marketing, like understanding your target audience, defining your goals, and creating valuable content, will significantly enhance your marketing efforts.
Content marketing 8 essential steps for effective implementation can provide a solid framework. Ultimately, a deep dive into empathy maps and personas allows you to tailor your content to address their specific needs and desires, resulting in a more impactful and engaging marketing strategy.
Integrating Empathy Maps and Personas for a Holistic View
Empathy maps and personas, when used together, create a comprehensive picture of your target customer. The empathy map provides rich qualitative data, revealing the customer’s thoughts, feelings, and behaviors in specific contexts. Personas, on the other hand, provide a generalized, representative view of the customer. By combining these two approaches, you can understand both the specific experiences of a customer and the overall patterns that emerge across different customer segments.
This creates a more powerful framework for informed decision-making.
Leveraging Strengths of Both Methods for Actionable Insights
The strengths of each method complement each other when used in tandem. Empathy maps excel at uncovering the “why” behind customer actions, while personas offer a structured framework for applying those insights across a larger group. This combined approach allows for more insightful predictions about customer behavior, leading to more effective strategies and products. By understanding both the individual experiences and the overall trends, you can tailor your offerings to resonate with specific needs and motivations.
Table: Combined Use of Empathy Maps and Personas
| Aspect | Empathy Map Insights | Persona Insights | Combined Insights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Needs | Specific needs revealed through observed behaviors and stated desires. | General needs and desires of a representative customer segment. | Specific needs of a persona, categorized by their particular circumstances and emotional drivers, revealed through the empathy map. |
| Pain Points | Pain points experienced by the customer in particular situations. | Common pain points experienced by the representative customer segment. | Pain points within a specific persona’s context, including their motivations and emotional reactions. |
| Motivations | Motivations driving the customer’s actions in specific scenarios. | General motivations of the representative customer segment. | Motivations for a specific persona’s actions, considering both external factors and their internal drives. |
| Behaviors | Specific behaviors of the customer in different scenarios. | Typical behaviors of the representative customer segment. | Typical behaviors of a persona, categorized by their circumstances and motivations, revealed through the empathy map. |
Example: Designing a New Fitness App
Imagine designing a new fitness app. An empathy map for a busy professional reveals they struggle with finding time for workouts, often feel overwhelmed by the options available, and value quick, effective routines. Their persona, a “Time-Crunched Professional,” further refines this by highlighting their desire for personalized workout plans and integration with their existing calendar. Combining these insights allows the app to feature tailored workouts that fit into users’ schedules, providing clear, concise options.
This more comprehensive approach results in a product that resonates with the specific needs of the target user group.
Practical Applications and Case Studies
Empathy maps and personas are more than just theoretical tools; they deliver tangible results when applied strategically. Their value lies in the ability to move beyond assumptions and connect with real consumer needs and motivations. Understanding these insights translates directly into better marketing strategies, refined product development, and ultimately, increased profitability. This section will explore real-world examples of how these methods have been successfully implemented in various industries, highlighting the impact they’ve had on business outcomes.Successful application of empathy maps and personas often involves a deep dive into consumer behavior.
This is achieved by considering the entire customer journey, from initial awareness to post-purchase satisfaction. It’s not just about collecting data; it’s about interpreting the data within the context of the customer’s experience and using this understanding to inform every aspect of the business strategy.
Retail Industry Successes
Retailers are prime candidates for utilizing empathy maps and personas. Understanding customer motivations, pain points, and preferences can significantly impact store layout, product selection, and marketing campaigns. A successful implementation involves understanding the different customer segments within a store, from the budget-conscious shopper to the luxury goods enthusiast. This segmentation, informed by detailed persona profiles, allows for tailored product displays, targeted promotions, and personalized customer service experiences.
Example: A clothing retailer using personas to improve online experience.
A major clothing retailer identified distinct customer segments: the “Trendsetter,” the “Classic,” and the “Value Seeker.” By creating detailed personas for each segment, the retailer discovered that the “Trendsetter” valued rapid fashion updates and personalized recommendations. In response, they implemented a dynamic, trend-focused online experience with AI-powered style suggestions, resulting in a 20% increase in sales within the “Trendsetter” segment.
The “Classic” segment, needing more in-depth product information, saw their purchase conversion rates increase by 15% with enhanced product descriptions and detailed styling guides.
Impact on Business Outcomes
Empathy maps and personas contribute to informed decision-making in marketing strategies. By understanding customer needs, preferences, and pain points, businesses can tailor their marketing messages and campaigns to resonate more effectively. This translates into higher engagement rates, improved conversion rates, and ultimately, increased revenue.A key benefit of these tools is the ability to anticipate customer needs. By understanding the customer journey and motivations, businesses can preemptively address potential issues and provide solutions before they arise.
For instance, identifying a recurring pain point in the customer journey can lead to the development of a new product or service to address it, or an adjustment in the existing offering.
Influence on Product Development Strategies
Insights gained from empathy maps and personas directly influence product development strategies. Understanding customer needs, pain points, and desires is paramount for creating products that meet those needs. A company can create a more targeted and efficient product development cycle by understanding who their customers are. This can lead to the development of more relevant products that are aligned with customer expectations, resulting in higher customer satisfaction and ultimately driving sales.
Summary of Case Studies
| Industry | Company | Key Takeaway | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail | Clothing Retailer | Targeted marketing strategies based on customer segments (Trendsetter, Classic, Value Seeker) | 20% increase in sales for Trendsetter segment, 15% increase in conversion rates for Classic segment. |
| Technology | Software Company | Understanding customer pain points regarding software usability | Improved user interface, increased customer satisfaction and retention |
Tools and Technologies for Empathy Map and Persona Creation
Uncovering consumer insights through empathy maps and personas requires the right tools to effectively capture and analyze data. Choosing the right software can streamline the process, from initial brainstorming to final presentation. The selection of tools should consider the team’s specific needs, budget, and technical expertise. This section will explore various tools and platforms, their benefits and limitations, and recommendations for selecting the best fit for your projects.Tools and platforms provide structured templates, data collection mechanisms, and analysis capabilities, enabling more efficient and comprehensive understanding of target audiences.
This facilitates a more nuanced approach to designing products and services that resonate with customer needs.
Software Options for Empathy Map Creation
Various software solutions cater to empathy map creation, each with unique strengths and weaknesses. These tools often offer templates, collaborative features, and data visualization options.
- Spreadsheet Software (e.g., Google Sheets, Microsoft Excel): Spreadsheet software provides a basic but flexible platform for creating empathy maps. Users can organize data into different sections (e.g., thoughts, feelings, pains, gains) and create visualizations. Their adaptability makes them suitable for smaller projects or teams with limited budgets. However, these tools lack the sophisticated features of dedicated design tools. The technical aspects involve manually entering and organizing data into cells and potentially using charts for visualization.
- Specialized Design Tools (e.g., Miro, Mural, Figma): Dedicated design tools like Miro and Mural offer digital whiteboards and collaborative features that facilitate empathy map creation. They often include templates, visual elements, and shared workspaces. Figma, while primarily a design tool, also offers features suitable for empathy mapping, especially for visualizing user flows and interactions. The technical aspects include using the tool’s interface, utilizing its collaborative features, and managing the project through the software’s features.
- Survey Platforms (e.g., SurveyMonkey, Typeform): Survey platforms are valuable for collecting data directly from target audiences to inform empathy maps. This approach allows gathering insights into customer behaviors, motivations, and pain points. This approach is ideal for collecting qualitative data from a large pool of respondents, leading to more comprehensive understanding. The technical aspects include designing surveys, distributing them, analyzing collected responses, and incorporating those insights into the empathy map.
Software Options for Persona Creation
Creating detailed personas often involves more than just data gathering. Tools designed for persona creation provide templates, questionnaires, and visualization tools.
Understanding consumer behavior through empathy maps and personas is crucial for effective marketing. However, the inflated online traffic numbers from click bots and fake traffic, costing online advertisers a staggering $35 billion click bots and fake traffic cost online advertisers 35 billion , can skew these insights. Ultimately, robust, real data gathered through authentic interactions remains essential for accurately developing effective empathy maps and personas to understand consumer needs and desires.
- Persona Creation Software (e.g., UserZoom, Hotjar): These specialized tools provide pre-built templates, questionnaire options, and tools for visualizing persona characteristics. They typically offer sophisticated data analysis and visualization features. The technical aspects involve using the tool’s interface, inputting collected data, and leveraging the software’s analysis and visualization capabilities.
- Presentation Software (e.g., PowerPoint, Google Slides): Presentation software allows the creation of visually appealing persona representations. Tools like PowerPoint and Google Slides can effectively present findings and insights from the empathy map and persona development process. The technical aspects are using the software’s design and presentation tools to create effective visuals that clearly communicate the persona’s characteristics and motivations.
Choosing the Right Tool
Choosing the right tool depends on several factors, including project scope, budget, team size, and desired features. A small team with a limited budget might find spreadsheet software sufficient, while larger projects benefit from specialized design tools.
- Consider project scope: The complexity of the project dictates the sophistication of the tool needed. Smaller projects might benefit from simpler tools, while large-scale projects require more robust platforms.
- Evaluate budget constraints: Some tools are free or have freemium tiers, while others require paid subscriptions. Balancing functionality with budget is crucial.
- Assess team size and technical expertise: Teams with limited technical expertise might prefer user-friendly tools. More advanced tools are best suited for teams with technical proficiency.
Limitations and Considerations
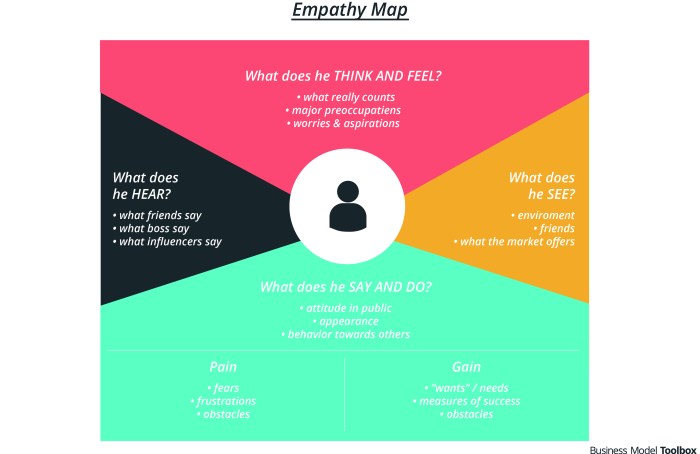
Empathy maps and personas, while powerful tools, are not without their limitations. Understanding these constraints is crucial for using these methods effectively and interpreting the insights they generate accurately. A critical evaluation of the process and data collected is essential for avoiding misinterpretations and ensuring the generated insights are actionable and valuable.
Potential Challenges and Limitations
The accuracy of empathy maps and personas hinges heavily on the quality and quantity of data collected. Insufficient or biased data can lead to inaccurate representations of target audiences. Limited data sources, such as relying solely on surveys or focus groups, might not capture the full spectrum of user experiences or perspectives. Furthermore, the subjective nature of interpretation can introduce bias into the analysis process.
For example, if the researcher has pre-conceived notions about the target audience, these biases could influence the way the data is interpreted, potentially leading to skewed insights.
Mitigation Strategies for Limitations
Addressing these limitations involves a multi-faceted approach. Triangulating data from various sources, including surveys, interviews, observations, and social media analysis, can enhance the validity of the insights. Incorporating diverse perspectives, such as those from different demographics and backgrounds, is vital for creating a more comprehensive understanding of the target audience. Employing rigorous data analysis techniques, such as statistical analysis and qualitative thematic analysis, can help to identify patterns and trends in the data more objectively.
Finally, establishing clear criteria for interpreting the data and documenting the analysis process can improve transparency and reduce bias.
Importance of Cultural and Societal Factors
Cultural and societal factors significantly impact consumer behavior. Empathy maps and personas should explicitly consider these factors. For instance, different cultures have varying communication styles, values, and beliefs. Ignoring these nuances can lead to inaccurate assumptions about consumer needs and motivations. Understanding these differences is vital for creating effective marketing strategies and products that resonate with diverse audiences.
Consider the use of culturally sensitive language and imagery in materials and avoid generalizations.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
One common pitfall is assuming that all individuals within a particular demographic group share the same characteristics and experiences. Empathy maps and personas should avoid oversimplification and stereotyping. Another pitfall is relying on anecdotal evidence or limited data samples to develop a complete picture of the target audience. This can lead to flawed conclusions and ineffective strategies.
Avoid making sweeping generalizations about a group of people based on a few examples. Instead, gather sufficient data from diverse sources and conduct rigorous analysis to support your conclusions. Finally, avoid imposing your own values and biases onto the target audience. Remain objective and allow the data to speak for itself.
Limitations Based on Data Collection Methods and Biases
Different data collection methods, such as surveys, interviews, and observations, each have inherent limitations. Surveys might suffer from response bias, while interviews could be influenced by the interviewer’s presence. Furthermore, the researcher’s own biases can impact the interpretation of data, leading to inaccurate conclusions. To mitigate these issues, employing diverse data collection methods can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the target audience.
Using multiple methods helps to cross-validate the findings and reduce the impact of individual biases.
Examples of Data Collection Method Limitations, Empathy map vs persona unleashing consumer insights
- Surveys: Response bias (only certain types of people responding), limited depth of understanding, and potential for misinterpretation of questions are all potential limitations.
- Interviews: Interviewer bias (leading questions, non-verbal cues), potential for social desirability bias (respondents giving answers they believe the interviewer wants to hear), and limited sample size are all possible limitations.
- Observations: Limited context, potential for observer bias, and difficulty capturing the full range of emotions and motivations are potential limitations.
Closure
In conclusion, understanding the nuances of empathy maps and personas is critical for unlocking actionable consumer insights. Choosing the right method, or a combination of both, empowers businesses to develop more effective marketing strategies, design better products, and ultimately build stronger customer relationships. The detailed comparison, practical applications, and discussion of limitations provided in this guide will equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
Ultimately, the key is to tailor your approach to your specific business needs and goals, recognizing that both empathy maps and personas offer unique advantages in the quest for understanding your customers.