Engaging customers via customer centric message maps – Engaging customers via customer-centric message maps is crucial for modern businesses. This approach goes beyond traditional marketing, focusing on understanding customer needs and crafting personalized messages across various channels. We’ll explore how to define, create, and implement effective message maps, along with case studies and best practices.
This comprehensive guide dives into the practical application of customer-centric message mapping, revealing actionable strategies to tailor your communication for maximum impact. We’ll dissect the essential elements of crafting engaging messages, prioritizing customer needs, and measuring the success of your initiatives.
Defining Customer-Centric Message Maps
Customer-centric message maps are a powerful tool for businesses to understand and connect with their customers on a deeper level. They move beyond traditional marketing tactics, focusing instead on understanding customer needs, motivations, and pain points to craft targeted messaging. This approach builds stronger customer relationships and ultimately drives business success.This approach goes beyond simply promoting products; it’s about tailoring communication to resonate with individual customer segments, leading to increased engagement and loyalty.
It requires a thorough understanding of your target audience and a willingness to adapt your messaging accordingly.
Key Principles of Customer-Centric Message Maps
Customer-centric message maps are built on several key principles, which differentiate them from conventional marketing strategies. These principles guide the creation and implementation of effective communication strategies.
- Customer-focused perspective: Instead of starting with product features, customer-centric message maps begin by understanding the customer’s journey, needs, and pain points. This ensures that messaging directly addresses their concerns and aspirations.
- Segmentation and personalization: Recognizing that not all customers are the same, customer-centric message maps employ segmentation to tailor communications to specific customer groups. This personalized approach increases relevance and engagement, leading to higher conversion rates.
- Multi-channel strategy: Effective communication strategies utilize multiple channels, from social media to email marketing. A customer-centric message map identifies the optimal channels for each segment to maximize impact and efficiency.
- Continuous monitoring and adaptation: Customer feedback and market trends are constantly evaluated to ensure the message map remains relevant and effective. This ongoing evaluation allows for adaptation and optimization to maintain alignment with evolving customer needs.
Differences from Traditional Marketing Strategies
Traditional marketing strategies often focus on product features and benefits, while customer-centric message maps prioritize the customer’s perspective. This fundamental shift allows for more meaningful engagement and builds stronger relationships.
| Feature | Traditional Marketing | Customer-Centric Message Maps |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Product features and benefits | Customer needs, motivations, and pain points |
| Messaging | One-size-fits-all approach | Segmented and personalized messaging |
| Customer Relationship | Transactional | Long-term, relationship-focused |
| Evaluation | Sales figures and ad impressions | Customer feedback and engagement metrics |
Examples of Effective Use
Several companies have successfully implemented customer-centric message maps, demonstrating their effectiveness.
- Netflix: Their recommendation engine and personalized content offerings exemplify a customer-centric approach, allowing users to discover tailored content. This personalized approach drives user engagement and retention.
- Spotify: Spotify’s curated playlists and personalized radio stations are tailored to individual user preferences. This personalized approach enhances user experience and encourages continued usage.
Creating a Simple Framework
Developing a customer-centric message map involves a structured approach.
- Identify Target Audience: Define specific customer segments based on demographics, psychographics, and behaviors.
- Understand Customer Journey: Map out the customer’s steps from initial awareness to purchase and beyond.
- Define Customer Needs and Pain Points: Identify the specific problems customers are facing and the solutions they seek.
- Craft Key Messages: Develop concise and impactful messages that resonate with each segment, addressing their needs and motivations.
- Choose Communication Channels: Select the most effective channels for reaching each segment and delivering tailored messaging.
Identifying Customer Needs and Pain Points
Understanding your customers’ needs and pain points is crucial for any business, especially in today’s competitive landscape. A deep understanding allows businesses to tailor their products and services, improve customer experience, and ultimately, drive sales and loyalty. This insight forms the foundation for effective marketing strategies, product development, and customer service initiatives. By anticipating and addressing customer frustrations, businesses can build stronger relationships and achieve sustainable growth.Customer needs and pain points are not static.
They evolve with changing market trends, technological advancements, and evolving customer expectations. Businesses that remain attentive to these shifts gain a significant advantage in retaining customers and attracting new ones. Constantly monitoring and analyzing customer feedback is essential to staying ahead of the curve and ensuring products and services meet ever-changing demands.
Common Customer Pain Points in Online Retail
Online retail is a dynamic industry, and understanding customer pain points is vital for success. Several recurring issues often frustrate online shoppers. Five prominent pain points include:
- Shipping Delays and Costs: Customers often express frustration over prolonged shipping times and unexpected or high shipping costs. These delays and added expenses can significantly impact the overall shopping experience and make customers reconsider future purchases.
- Inaccurate Product Descriptions and Images: Misleading or inaccurate product descriptions and images can lead to disappointment once the product arrives. Customers may have unrealistic expectations, which negatively impacts their satisfaction and may discourage repeat business.
- Complex or Inaccessible Checkout Process: A cumbersome checkout process with confusing steps can deter customers from completing a purchase. The process should be straightforward, secure, and offer multiple payment options.
- Limited Customer Support Options: Insufficient or unhelpful customer support can severely impact customer satisfaction. Easy access to multiple support channels is crucial for resolving queries and issues efficiently.
- Security Concerns and Data Privacy: Customer concerns regarding data privacy and online security are paramount. Ensuring a safe and secure shopping environment is essential to build trust and encourage customers to return.
Importance of Understanding Customer Needs and Pain Points
Understanding customer needs and pain points is paramount for businesses to thrive. This knowledge allows companies to:
- Improve Product Development: By identifying what customers truly need, businesses can create products and services that meet those specific requirements, leading to greater customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Enhance Customer Experience: Addressing customer pain points through streamlined processes, efficient customer service, and transparent communication can elevate the overall customer experience.
- Drive Sales and Loyalty: Understanding customer needs and addressing their pain points results in higher customer satisfaction, which ultimately drives sales and fosters customer loyalty.
- Gain a Competitive Advantage: Companies that proactively address customer needs and pain points can differentiate themselves from competitors and capture a larger market share.
Gathering Data on Customer Needs and Pain Points
Gathering data on customer needs and pain points is an iterative process. It involves employing various methods to collect feedback and insights.
- Surveys: Surveys provide structured data on customer opinions and preferences, allowing for quantifiable results. A variety of question types can be used, from multiple choice to open-ended questions.
- Customer Interviews: One-on-one interviews offer in-depth qualitative data, enabling businesses to understand the reasons behind customer responses and uncover underlying motivations.
- Focus Groups: Focus groups bring together a small group of customers to discuss specific products or services, offering valuable insights into group opinions and preferences.
- Social Media Monitoring: Monitoring social media platforms for customer conversations and feedback can reveal emerging trends and identify potential issues.
- Customer Feedback Forms: Integrating feedback forms into the online shopping process allows for real-time feedback and quick responses to customer concerns.
Prioritizing Customer Needs and Pain Points
Prioritizing customer needs and pain points is crucial for effective resource allocation. Methods for prioritization often involve assessing the impact and urgency of each issue.
- Impact Analysis: This involves assessing the severity of the impact of each pain point on the customer experience. For example, a high-impact issue would be one that significantly affects customer satisfaction and potentially discourages future purchases.
- Urgency Assessment: This involves evaluating how quickly each pain point needs to be addressed. A high-urgency issue requires immediate attention to prevent further negative impacts on the customer experience.
- Pareto Analysis: This method, also known as the 80/20 rule, helps identify the most significant issues. It prioritizes the 20% of pain points that contribute to 80% of the problems.
Methods for Gathering Customer Feedback
Different methods for gathering customer feedback have varying strengths and weaknesses. A comparative analysis is presented below:
| Method | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surveys | Structured questionnaires | Quantifiable data, easy to analyze | Limited depth, may not capture nuances |
| Interviews | In-depth conversations | Rich qualitative data, deep understanding | Time-consuming, expensive |
| Focus Groups | Group discussions | Diverse perspectives, collaborative insights | Potential for dominant voices, groupthink |
| Social Media Monitoring | Tracking online conversations | Real-time feedback, broad reach | Difficult to analyze, potential for biased opinions |
| Customer Feedback Forms | Embedded forms | Easy to implement, immediate feedback | Limited scope, may not be comprehensive |
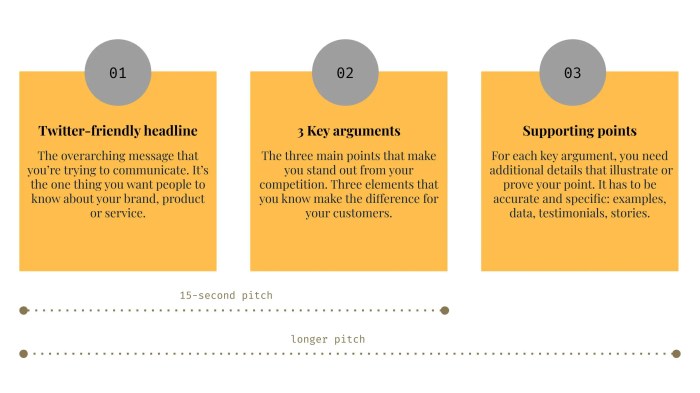
Crafting Engaging Messages

Crafting engaging messages is crucial for resonating with customers and driving desired actions. It’s not enough to simply communicate; you need to connect with your audience on an emotional level and motivate them to take the next step. This involves understanding your customer’s needs, tailoring your message to their specific concerns, and using compelling language and strategies.Understanding your customers’ needs and pain points is the foundation of effective messaging.
Once you’ve identified these, you can construct messages that address those concerns directly and offer solutions. The goal is to move beyond generic marketing speak and create truly meaningful interactions.
Elements of an Engaging Message
Engaging messages possess several key characteristics. They are clear, concise, and focused on the customer’s benefit, rather than just the product or service itself. They use strong verbs and active voice to convey a sense of urgency and action. Moreover, they incorporate storytelling to create an emotional connection and make the message more memorable.
- Clarity and Conciseness: Avoid jargon and technical terms that may confuse or alienate the customer. Get straight to the point and clearly articulate the value proposition. A well-crafted message gets to the heart of the matter quickly and efficiently.
- Customer Focus: Frame the message around the customer’s needs and pain points, not your company’s features. Highlight how your product or service solves their problems and improves their lives.
- Emotional Connection: Use storytelling, evocative language, and imagery to create an emotional connection with the customer. Tap into their desires, fears, and aspirations to create a personal resonance.
Tailoring Messages to Specific Customer Segments
Understanding your target audience is paramount. Different customer segments have different needs, motivations, and concerns. Tailoring your message to each segment ensures your message resonates with the specific audience you are trying to reach.
- Segmentation Strategies: Utilize demographics, psychographics, and behavioral data to segment your customer base. Identify common traits and patterns among different groups. This allows you to craft specific messages for each segment.
- Personalized Messaging: Move beyond generic messages and incorporate personalization. Use data to tailor messages to individual customers, acknowledging their past interactions and preferences.
- Example: A financial institution targeting young professionals might focus on building credit and managing debt. For senior citizens, the message might emphasize retirement planning and legacy strategies.
Compelling Messaging Strategies
Several proven strategies can enhance the impact of your messaging. These strategies use various techniques to capture attention and create a lasting impression.
- Problem/Solution Framework: Clearly define the problem the customer faces and then showcase how your product or service solves it. This is a highly effective approach for highlighting the value proposition.
- Benefit-Driven Messaging: Focus on the benefits your product or service provides, rather than just the features. How will it improve their lives? How will it solve their problems?
- Storytelling: Share real-life examples and stories that resonate with the customer’s experiences. This approach builds trust and creates a stronger emotional connection.
Measuring Message Effectiveness
Measuring the effectiveness of your messages is critical to continuous improvement. Track key metrics to understand what works and what needs refinement.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Track metrics such as open rates, click-through rates, conversion rates, and customer feedback to gauge the effectiveness of different message types.
- A/B Testing: Experiment with different message variations to determine which performs best. This data-driven approach helps refine messaging strategies for optimal results.
Communication Channels and Optimal Message Formats
Choosing the right channel and format is vital for delivering your message effectively.
| Channel | Message Format | Tone | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Short, concise email with a clear call to action. | Professional, friendly. | “Get a free trial today!” | |
| Social Media | Engaging posts with visuals and interactive elements. | Enthusiastic, conversational. | “Share your favorite tips for [topic]!” |
| Website | Clear, concise product descriptions with strong calls to action. | Informative, persuasive. | “Learn more about our premium features.” |
| In-App Notifications | Short, urgent messages to encourage action. | Direct, actionable. | “Don’t miss out on the sale!” |
Implementing and Measuring Success

Bringing your customer-centric message maps to life requires careful implementation and consistent monitoring. This isn’t a one-and-done project; it’s an ongoing process of refinement based on customer feedback and performance data. A well-defined implementation plan ensures that your messaging resonates with your target audience across all touchpoints.This stage is crucial for maximizing the impact of your customer-centric message maps.
By carefully implementing and measuring success, you can identify what works and what doesn’t, allowing you to refine your approach for even greater customer engagement and satisfaction.
Implementation Steps
Implementing customer-centric message maps involves a phased approach, ensuring a smooth transition and maximizing the benefits for your customers. Each phase builds upon the previous one, leading to a comprehensive strategy that aligns messaging across all channels.
- Develop a Communication Plan: Artikel how the message maps will be disseminated across different channels (website, social media, email, customer service interactions). This plan should include specific timelines and responsibilities for each team involved. For example, a company selling software might assign the task of creating blog posts on the website to the marketing team and updating product descriptions to the product development team.
- Train Key Personnel: Equip your customer-facing teams (sales, marketing, customer service) with the message maps and guidelines. Ensure they understand the core messages, the target audience, and how to tailor their interactions accordingly. Training sessions should be interactive and include practical examples to solidify understanding. For instance, role-playing scenarios can demonstrate how to respond to customer concerns using the message map’s language.
- Integrate Messaging Across Channels: Ensure consistency in your messaging across all communication channels. This includes website content, social media posts, email marketing, and customer service interactions. The message should be seamlessly woven into every touchpoint, avoiding inconsistencies that could confuse or frustrate the customer. For example, if the message map highlights the value of customer support, customer service agents should always convey that value in their interactions, even on social media.
- Monitor and Track Progress: Implement a system to monitor how well the message maps are being implemented and their impact on customer engagement. Regularly track key performance indicators (KPIs) and analyze the data to identify areas for improvement. Examples include website traffic from specific marketing campaigns, customer satisfaction scores, and social media engagement.
Consistent Messaging Across Channels
Consistency is paramount in customer-centric communication. A unified message across all channels builds trust and reinforces the brand’s identity.
Consistent messaging across all channels creates a cohesive customer experience. When customers encounter the same message, regardless of the interaction point, they are more likely to trust and engage with the brand. This consistency strengthens brand recognition and fosters a deeper understanding of the brand’s values.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Tracking KPIs is essential for measuring the effectiveness of your message maps and identifying areas for improvement.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) Score: Track customer satisfaction scores through surveys or feedback forms to gauge how well the message maps are resonating. Higher scores indicate that the messaging is effective in addressing customer needs.
- Customer Engagement Metrics: Monitor metrics like website traffic, social media interactions, email open rates, and response times to customer service requests. Increased engagement suggests that the messaging is appealing and relevant.
- Conversion Rates: Measure the rate at which customers complete desired actions (e.g., purchasing a product, signing up for a newsletter). Higher conversion rates often indicate effective messaging that drives desired customer behaviors.
Adapting Message Maps
Message maps are not static documents; they should be reviewed and updated regularly based on performance data. Changes should be based on measurable results and insights gleaned from customer feedback.
Crafting customer-centric message maps is key to engaging customers effectively. Understanding how to effectively measure the impact of these strategies is crucial, and tools like those discussed in measuring social ROI using Adobe and Google can help. Ultimately, a deep dive into these metrics is vital for refining customer engagement strategies and ensuring your message maps resonate with your audience.
- Regular Reviews: Regularly analyze the performance data of your message maps to identify trends and areas for improvement. Look for patterns in customer feedback and engagement metrics to understand how messaging is impacting customer behavior.
- Customer Feedback Integration: Actively collect customer feedback through surveys, reviews, and social media monitoring. This feedback provides valuable insights into how your messaging is perceived and what areas need adjustment.
- Iterative Improvements: Use the insights gathered to make adjustments to the message maps, ensuring they continue to meet the evolving needs of your customers. Iterative improvements are critical to ensuring ongoing relevance and effectiveness.
Measuring and Improving Customer Engagement Flowchart
The following flowchart Artikels the process of measuring and improving customer engagement:
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Define KPIs: Identify key performance indicators to track customer engagement |
| 2 | Collect Data: Gather data on customer interactions and feedback. |
| 3 | Analyze Data: Identify trends and patterns in the data. |
| 4 | Identify Areas for Improvement: Based on the analysis, pinpoint areas where the messaging can be more effective. |
| 5 | Adjust Message Maps: Refine the message maps to address identified areas for improvement. |
| 6 | Retest and Re-evaluate: Re-measure KPIs and evaluate the effectiveness of the adjusted message maps. |
Case Studies and Best Practices: Engaging Customers Via Customer Centric Message Maps
Turning customer-centric message mapping into tangible results requires real-world examples. This section dives into a successful campaign, highlighting key factors, challenges, and the invaluable lessons learned. We’ll also explore how effective message maps manifest in different industries, from finance to healthcare.Customer-centric message mapping isn’t just a theoretical framework; it’s a powerful tool for businesses looking to build stronger connections with their customers.
Engaging customers through customer-centric message maps is crucial for a strong brand connection. Choosing the right digital adoption platform, like those compared in pendo vs walkme unveiling the best digital adoption platform , directly impacts how easily customers can navigate and utilize your offerings. Ultimately, a well-designed customer experience, facilitated by effective message maps, will lead to greater customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Successful implementations demonstrate the significant impact this strategy can have on customer satisfaction, brand loyalty, and ultimately, business growth.
A Successful Campaign in the E-commerce Sector
A leading online retailer, “TechGear,” implemented a comprehensive customer-centric message mapping strategy. Their goal was to enhance the customer experience throughout the entire purchase journey, from initial product discovery to post-purchase support.The campaign focused on understanding customer needs and pain points through extensive surveys, interviews, and website analytics. They identified that customers struggled with navigating the vast product catalog and finding specific items quickly.
Additionally, concerns about shipping times and return policies were highlighted.
TechGear’s message map meticulously defined the key messages for each stage of the customer journey. For instance, the landing page message emphasized the vast selection and ease of navigation. Product pages focused on detailed product descriptions, high-quality images, and customer reviews. Shipping and return pages were clear and concise, addressing customer anxieties directly.
Key Factors Contributing to Success, Engaging customers via customer centric message maps
- Deep Customer Insight: TechGear invested heavily in understanding their customer base through various research methods. This thorough understanding was the bedrock of the entire campaign.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Marketing, sales, customer service, and product development teams collaborated closely to ensure a consistent brand message across all touchpoints. This alignment was critical for a cohesive experience.
- Iterative Improvement: TechGear didn’t treat the message map as a static document. They continuously monitored customer feedback and adjusted the messaging based on data insights. This ensured the map remained relevant and effective.
Challenges Encountered and Overcoming Them
- Data Collection and Analysis: Gathering and interpreting large amounts of customer data required significant investment in tools and resources. They addressed this by using a combination of survey tools and website analytics dashboards, ensuring data was readily accessible to all relevant teams.
- Alignment across Teams: Initially, there were communication gaps between departments, leading to inconsistent messaging. This was resolved through regular team meetings and workshops focused on understanding the message map and its application across the business.
Lessons Learned
- Customer-centricity is an ongoing process: Regular customer feedback analysis and iterative improvements are essential for maintaining a customer-centric approach. This ensures the message map remains relevant.
- Collaboration is paramount: Effective message mapping requires cross-functional alignment to ensure consistent brand messaging and customer experience across all channels.
Examples Across Industries
| Industry | Example of Customer-Centric Message Map |
|---|---|
| Finance | A bank focused on simplifying the application process for small business loans. The message map highlighted the ease and speed of the application process, tailored to the specific needs of small business owners. |
| Healthcare | A clinic aimed at reassuring patients about the safety and effectiveness of new treatments. The message map highlighted the safety protocols and positive outcomes of the new treatment in a reassuring manner. |
| E-commerce | A clothing retailer using customer feedback to address concerns about sizing and fit. The message map was updated to include detailed size charts and customer reviews to increase customer confidence. |
Visualizing Customer Journeys
Unveiling the customer journey is crucial for crafting effective marketing strategies and delivering exceptional experiences. Visual representations transform abstract customer interactions into tangible insights, allowing businesses to understand pain points, identify opportunities, and optimize their offerings. A well-defined customer journey map is an invaluable asset in understanding how customers interact with your brand, and this understanding fuels data-driven decisions that enhance customer satisfaction.Customer journey visualization is not merely a pretty picture; it’s a powerful tool for understanding the customer experience.
By mapping out the various touchpoints, businesses can gain a holistic view of how customers interact with their products or services, identifying bottlenecks and opportunities for improvement. This holistic understanding is fundamental for developing customer-centric message maps that resonate with the customer at every stage of their journey.
Methods for Visualizing Customer Journeys
Different methods exist for visualizing customer journeys, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right method depends on the specific needs and resources of the business. These methods range from simple flowcharts to complex interactive prototypes, catering to various levels of detail and complexity. The key is to select a method that effectively captures the essence of the customer experience without overwhelming the process.
- Flowcharts: These diagrams depict the sequence of events in a customer’s journey. They are straightforward and easily understandable, ideal for outlining the basic steps of a process. Flowcharts are particularly useful for identifying potential bottlenecks or inefficiencies in the customer journey.
- Customer Journey Maps: These maps visually represent the customer’s emotional and behavioral journey. They go beyond simple steps, considering customer emotions, motivations, and pain points at each touchpoint. Journey maps often incorporate qualitative data like customer feedback and interviews to paint a richer picture of the experience.
- Interactive Prototypes: For a more immersive experience, interactive prototypes allow stakeholders to simulate the customer journey, experiencing it firsthand. This can help identify areas for improvement and provide a more intuitive understanding of the customer’s perspective.
- User Persona Profiles: Creating user persona profiles is a crucial step for customer journey visualization. These profiles embody the key characteristics of different customer segments. By identifying these segments, businesses can tailor their strategies to the unique needs and motivations of each persona.
Example Customer Journey Map for a SaaS Product
Imagine a typical customer journey for a software-as-a-service (SaaS) product aimed at small businesses. The customer, let’s call them “Sarah,” needs a solution for inventory management.
- Awareness: Sarah researches inventory management software online. She stumbles upon our SaaS product through a targeted advertisement.
- Consideration: Sarah explores our website, comparing features and pricing with competitors. She reads reviews and testimonials to gauge the reliability and customer support.
- Decision: Sarah decides to try a free trial of our software. She is impressed with the user-friendliness and ease of use. The trial period allows her to assess the product’s practical value and integration with her business processes.
- Action: Sarah purchases the software, prompted by its efficiency and value. She then sets up her account and begins to use the product.
- Retention: Sarah enjoys the ease of use and efficiency gained through our product. She uses customer support frequently and effectively to overcome challenges, fostering positive engagement.
Comparison of Visualization Tools
| Tool | Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flowchart Software (e.g., Lucidchart) | Simple visual representation of steps, conditional logic | Easy to create, inexpensive, widely available | Limited in depicting emotions and motivations, cannot show complex journeys |
| Customer Journey Mapping Software (e.g., Typeform) | Visual representation of customer experience, incorporating emotions and touchpoints | Rich insights into customer experience, data-driven | Can be complex to implement, may require more resources |
| Interactive Prototyping Tools (e.g., Figma) | Allows users to simulate the journey | Immersive experience, allows for user feedback | Requires more technical skills, can be expensive |
Integrating Customer Journey Maps into Message Maps
Integrating customer journey maps into message maps involves aligning messaging with each stage of the customer’s journey. This ensures that the messaging is relevant and resonates with the customer at each touchpoint. For instance, awareness-stage messaging should focus on highlighting the problem the product solves, while decision-stage messaging should emphasize the product’s unique value proposition. This strategic alignment is critical for creating a cohesive and impactful customer experience.
Importance of Visual Communication
Visual communication is vital for effective customer journey communication. Visuals make complex information easily understandable and memorable. They provide a clear and concise representation of the customer’s experience, facilitating communication and collaboration among team members. By using visual aids, businesses can effectively communicate the customer’s journey and ensure that everyone involved in the process understands the customer’s perspective.
Engaging customers through customer-centric message maps is key in today’s digital landscape. Understanding your audience and crafting messages tailored to their needs is crucial, but the importance of digital marketing today, especially in the Twitter age, especially in the Twitter age , cannot be overstated. Effective communication strategies built on these maps are vital to success, no matter the platform.
Adapting to Changing Customer Needs
Staying ahead of the curve in today’s dynamic market requires a deep understanding of your customers and their evolving needs. A customer-centric message map is a living document, not a static one. Businesses that fail to adapt their communication strategies to reflect these shifts risk losing touch with their target audience. Successfully adapting requires a proactive approach, focusing on continuous feedback, predictive analysis, and a willingness to experiment.Customer preferences are constantly changing, influenced by factors like technological advancements, social trends, and economic shifts.
A message map that accurately reflects these shifts is critical for maintaining a strong connection with your audience. A static message map will quickly become outdated and ineffective, leading to disengagement and lost opportunities. Proactive adaptation is key to maintaining relevance and fostering lasting customer relationships.
Continuous Monitoring and Feedback Collection
Monitoring customer interactions across all channels is essential for identifying shifts in preferences and pain points. This includes analyzing website traffic, social media engagement, customer service interactions, and survey responses. Regularly collecting feedback through various channels provides crucial insights into customer sentiment and expectations. By actively listening to customer feedback, companies can understand evolving needs and tailor their messaging accordingly.
Incorporating Customer Feedback into Message Map Updates
Feedback mechanisms should be integrated into the message map update process. This can be achieved through dedicated feedback forms, surveys, or social media monitoring tools. Categorize and analyze the feedback, identifying recurring themes and trends. Use this data to refine existing messages and develop new ones that directly address customer concerns and desires. The feedback should be used to validate and adjust assumptions about customer needs and motivations.
Predicting Future Customer Needs and Trends
Staying ahead of the curve requires a degree of foresight. Analyzing industry trends, competitor strategies, and technological advancements allows for informed predictions about future customer needs. Market research, competitor analysis, and social media listening tools can provide valuable insights into emerging trends. For example, if a new technology is gaining traction, consider how that might influence customer needs and adapt your messaging to address them proactively.
By predicting potential shifts, companies can preemptively adjust their message maps and maintain a competitive edge.
Example of Adapting to a Changing Market
Consider a company selling athletic apparel. Initially, their message map focused on performance-enhancing features. However, as the market shifted towards sustainability and ethical sourcing, they recognized a change in customer priorities. The company integrated feedback from surveys and social media engagement into their message map updates, emphasizing eco-friendly materials and ethical production practices. By anticipating and adapting to this change, the company maintained customer loyalty and attracted new customers aligned with the evolving values of the market.
They shifted their messaging to address the concerns of customers focused on sustainable practices, while still highlighting performance benefits. This example demonstrates how a proactive approach to adapting message maps can successfully navigate changing market landscapes.
Last Word
In conclusion, engaging customers effectively requires a deep understanding of their needs and preferences. By implementing customer-centric message maps, businesses can cultivate stronger relationships, drive customer loyalty, and ultimately, achieve sustainable growth. This guide provides a roadmap to building and optimizing these maps for lasting success. Remember to continuously adapt and refine your approach based on evolving customer needs and market trends.