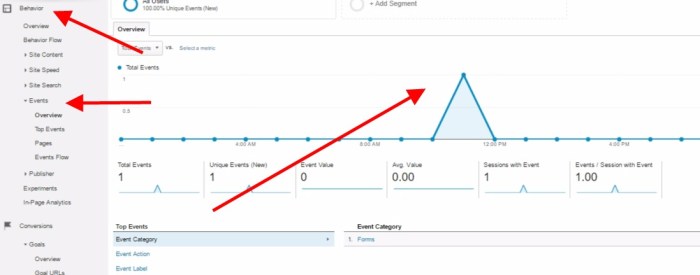
Events in Google Tag Manager are the key to unlocking website activity insights. They act as triggers, allowing you to track everything from simple page views to complex user interactions. Understanding these events is crucial for optimizing your website and campaigns.
This guide will delve into the fundamentals of Google Tag Manager events, exploring their types, implementation, and advanced techniques. We’ll also cover best practices and practical use cases for different scenarios, including A/B testing and lead generation.
Introduction to Google Tag Manager Events
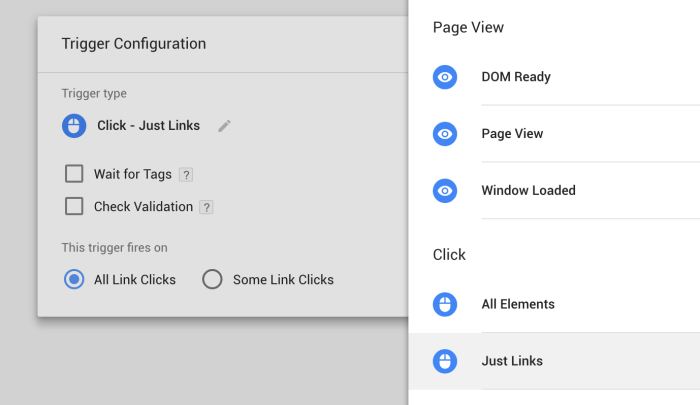
Google Tag Manager (GTM) events are actions that occur on a website, such as a user clicking a button or navigating to a new page. They are fundamental to tracking website activity and understanding user behavior. Events provide valuable insights into how users interact with your website, enabling you to optimize your site’s design and functionality to improve conversions and engagement.Understanding these events allows marketers and web analysts to gain a deep dive into user journeys, pinpointing areas for improvement and tailoring campaigns for better results.
This data-driven approach to website management leads to a more effective and efficient online presence.
Understanding Website Events
Events in GTM are crucial for tracking user interactions on your website. They are the building blocks for gathering data about user behavior, providing a detailed picture of how visitors navigate your site and engage with its content. Common website events include page views, button clicks, form submissions, and video plays. Tracking these actions provides invaluable insights into user engagement and allows you to make informed decisions about your website’s design and content.
Understanding events in Google Tag Manager is crucial for tracking user interactions. A key aspect of this is choosing the right approach for your A/B testing, which often involves comparing different versions of a page element. This decision hinges on whether to employ a single A/B test or a more complex multiple variant approach. The intricacies of ab testing vs multiple variant are explored in more detail here ab testing vs multiple variant.
Regardless of the method, robust event tracking in GTM ensures you get accurate data on which version resonates best with your audience.
Types of Google Tag Manager Events
Different types of events capture various user interactions, each offering unique insights. These event types are used to trigger tags, enabling the collection of data for analysis and optimization.
- Page View: This event occurs when a user navigates to a new page on your website. It’s essential for tracking page visits, understanding user flow, and analyzing which pages are most popular.
- Button Click: This event captures when a user clicks a button on your website. Button clicks are valuable for identifying popular actions, analyzing user engagement, and understanding how users interact with interactive elements.
- Form Submission: This event records when a user completes a form on your website. Form submissions are crucial for tracking lead generation, understanding conversion rates, and improving form usability.
- Video Play: This event occurs when a user starts playing a video on your website. Tracking video plays is important for measuring engagement with video content and understanding which videos are most popular.
Event Types and Use Cases
The following table Artikels various event types and their corresponding use cases, along with implementation considerations.
Triggering Tags with Events
Events in GTM serve as triggers for tags. When a specific event occurs, the corresponding tag is activated, enabling the collection of data for analysis. For example, when a user clicks a button, a tag can be triggered to record the click and send data to a marketing platform. This allows for more precise and targeted marketing campaigns.
Implementing Event Tracking
Diving deeper into Google Tag Manager, understanding how to implement event tracking is crucial for accurate data collection and insightful analysis. Event tracking allows you to monitor specific user interactions on your website, providing valuable data on user behavior and enabling targeted optimization. This section will walk you through the steps of setting up event tracking in GTM, creating custom events, and utilizing triggers to effectively capture these events.Event tracking in Google Tag Manager is not just about collecting data; it’s about leveraging that data to understand your users’ journey.
By meticulously tracking events, you can pinpoint specific actions, measure engagement levels, and ultimately improve the overall performance of your website or application.
Setting Up Event Tracking in Google Tag Manager
Setting up event tracking in Google Tag Manager involves a multi-step process, starting with defining the specific user interactions you want to monitor. This could include button clicks, form submissions, video plays, or product additions to a cart. Once you’ve identified the events, you can then configure the necessary tags and triggers to record these interactions and feed the data into your analytics platform.
Creating Custom Events
Custom events are fundamental to tracking specific actions that aren’t already covered by standard GTM events. They enable you to track unique user behaviors tailored to your website’s specific functionality. For instance, you might want to track a user clicking a “Learn More” button, completing a complex form, or adding a product to a wish list. Custom events offer granular control over what data you capture.
The Role of Triggers in Event Tracking
Triggers in GTM are the gatekeepers of event firing. They determine when a tag should be activated based on specific conditions. These conditions are usually linked to user actions, such as a click, a scroll, or a page load. Properly configured triggers ensure that tags fire only when the intended event occurs, preventing unnecessary data collection and ensuring accuracy.
Different Trigger Types
Various trigger types are available in GTM, each suited to different event scenarios. “On Page Load” triggers fire when a page loads, while “On Click” triggers respond to user clicks on specific elements. “Custom Event” triggers, as the name suggests, activate when a predefined custom event occurs. “View” triggers fire when a specific page is viewed, while “Form Submit” triggers fire when a form is submitted.
Implementing an Event for Adding a Product to a Cart
This detailed procedure guides you through tracking product additions to a shopping cart using GTM.
| Step | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Create a new event. | Event name: ‘Product Added to Cart’ |
| 2 | Define the trigger. | Trigger type: ‘Custom Event’ Event name: ‘Product Added to Cart’ |
| 3 | Create a tag to fire on the event. | Tag type: ‘Custom Tag’ Data Layer Variable: the data layer variable containing product information. |
This structured approach ensures the product information is sent to Google Analytics and other relevant platforms. This allows for detailed tracking and analysis of product additions, helping you understand user behavior and optimize your e-commerce strategy.
Event Structure and Attributes: Events In Google Tag Manager
Understanding the structure and attributes of events in Google Tag Manager is crucial for effectively tracking user interactions on your website. This allows for detailed analysis of user behavior, enabling data-driven decisions for optimizing your website and marketing campaigns. A well-defined event structure, coupled with meaningful attributes, provides a rich dataset that helps you gain valuable insights.Events are the fundamental building blocks of tracking in Google Tag Manager.
They represent significant user actions, such as button clicks, form submissions, or product purchases. The structure of an event, encompassing its name, category, and various parameters, dictates how the event is identified and categorized within your data. This structure enables comprehensive reporting and provides actionable insights.
Event Structure
Events in Google Tag Manager are defined by a combination of attributes and parameters. The core of an event lies in its name, which uniquely identifies the action. This name serves as a primary identifier, allowing you to differentiate between various user interactions. Furthermore, categorizing events through event categories helps you group similar actions for analysis. The category attribute provides context, allowing you to analyze user behavior across different areas of your website.
Event Attributes
Event attributes provide crucial context and detail about the event. They allow you to drill down into specific user actions and tailor your analysis to different aspects of your website’s functionality. The significance of these attributes lies in their ability to refine your tracking, leading to more targeted insights.
Event Parameters
Event parameters provide further detail and customization beyond the basic attributes. Parameters are key-value pairs that offer granular data about the event. For example, you can include product details, such as the product ID, price, or category, in a “Product Purchase” event. These parameters enrich the data, providing a more comprehensive understanding of the user interactions.
Custom Parameters in Events
Custom parameters empower you to add unique and relevant information to your events. You can create custom parameters for any attribute relevant to your website’s functionality. This allows for the tracking of specific details, such as user demographics or campaign information. For example, you can include a custom parameter for the campaign name that triggered a specific event.
Methods to Access and Utilize Event Attributes
Event attributes can be accessed and utilized in various ways within Google Tag Manager. Using the built-in variables and custom JavaScript variables, you can extract specific attribute values to create more nuanced reports and trigger specific actions. For example, using a variable that extracts the event name allows you to trigger different tags based on the type of event.
Understanding events in Google Tag Manager is crucial for tracking user interactions. For example, if a brand wants to track when someone clicks on an ad on Snapchat, they need to set up specific events in GTM. This allows them to measure the effectiveness of their Snapchat campaigns. Learning how brands can use Snapchat effectively, like utilizing interactive lenses or engaging filters, can be directly tied back to your Google Tag Manager setup.
A good resource on this is how brands can use snapchat , which offers a deeper dive into the potential of this platform. Ultimately, the right event tracking in GTM is key to understanding your Snapchat strategy’s impact.
The ability to use variables greatly increases the flexibility of event tracking.
Table of Event Attributes
Advanced Event Tracking Techniques
Diving deeper into event tracking in Google Tag Manager allows for more nuanced insights into user behavior. Moving beyond basic page views and clicks, advanced techniques enable the capture of complex interactions, ultimately providing a richer understanding of your website’s performance. This involves tracking not just
- what* users do, but
- how* they do it, leading to more targeted and effective optimization strategies.
Complex Event Tracking
Tracking complex user actions, such as form submissions with specific field values, requires more granular event definitions. For instance, consider a contact form. Instead of simply tracking a form submission, you can track submissions where a user entered their email address and selected a specific product category. This level of specificity empowers you to segment your data and identify user preferences, allowing for more targeted marketing campaigns.
By defining specific criteria within your event tags, you can achieve a detailed understanding of user actions.
Real-time Tracking with Event Listeners, Events in google tag manager
Event listeners in Google Tag Manager allow for real-time tracking of user interactions. This capability is particularly valuable for dynamic elements or complex interactions where a single event is not enough to capture the whole picture. For example, a live chat widget might require tracking user interactions as they happen. This approach offers immediate feedback on user behavior, facilitating quick adjustments to optimize the user experience.
Best Practices for Event Tracking
Maintaining consistency and accuracy is key to effective event tracking. Descriptive event names improve data analysis and interpretation. Using a standardized naming convention across all events ensures consistency and prevents ambiguity. This approach is critical for the long-term effectiveness of your tracking system.
Understanding events in Google Tag Manager is crucial for tracking user interactions. A key part of this is building a strong partner network, which can help you expand your reach and knowledge base. By having a solid build a partner network , you can gain access to valuable insights and resources, improving your event tracking and ultimately your overall Google Tag Manager strategy.
This will help you better understand how your users are interacting with your website.
Optimizing Event Tracking
To ensure your event tracking system operates efficiently, consider these optimization methods:
- Regularly review and update your event definitions: Outdated event definitions can lead to inaccurate data representation, rendering your analytics less reliable. Regularly review and update your event definitions to reflect current website functionality.
- Use descriptive event names: Descriptive event names are crucial for data analysis. Instead of “buttonClick,” use “productAddButton” to understand the specific action taken by the user.
- Ensure proper implementation of triggers: Inaccurate triggers lead to missing or inaccurate data. Verify that triggers are properly configured to accurately capture events, and troubleshoot any issues with their implementation.
Handling Multiple Concurrent Events
Multiple events occurring simultaneously can complicate tracking. Strategies to manage this situation include using event attributes to distinguish between concurrent events. For instance, in a shopping cart scenario, you could track both “add to cart” and “update quantity” events. Using unique identifiers or timestamps in event attributes allows for clear identification of each event within a specific time frame.
This is important because it avoids ambiguity and confusion when analyzing data.
Identifying and Fixing Event Tracking Issues
Regular checks and troubleshooting are necessary for a robust event tracking system.
- Regular audits: Regularly audit your event tags to ensure they are correctly configured and working as intended. This proactive approach helps identify and resolve potential issues before they impact data accuracy.
- Data validation: Validate the data collected by your event tags to identify any inconsistencies or anomalies. This step is critical for maintaining the reliability of your analytics data.
Improving Event Tracking Efficiency
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Regularly review and update your event definitions | Helps avoid outdated data, ensuring that your event definitions remain relevant to the current site structure and functionality. |
| Use descriptive event names | Facilitates analysis by providing clear context to the recorded events. |
| Ensure proper implementation of triggers | Avoids inaccurate data by ensuring that events are correctly associated with user actions. |
Event Tracking for Specific Use Cases
Event tracking in Google Tag Manager isn’t just about counting clicks; it’s a powerful tool for understanding user behavior and tailoring experiences. This section delves into how to use events for various business objectives, from optimizing marketing campaigns to driving lead generation. We’ll explore practical examples and show how events can be customized to track specific interactions, ultimately leading to more personalized and effective marketing strategies.Event tracking, when implemented correctly, provides granular insights into user actions.
This detailed data empowers marketers to make informed decisions, optimizing campaigns and enhancing user engagement. By understanding specific user interactions, you can refine strategies and deliver tailored experiences that resonate with individual needs and preferences.
A/B Testing
A/B testing allows businesses to compare different versions of a webpage or marketing campaign to determine which performs better. Event tracking is crucial for this process. By tracking specific events like button clicks or form submissions for different variations, you can quantify the impact of each iteration and identify the most effective design.
- Tracking different button variants: Implement separate event tags for each button variant. When a user clicks a button, the corresponding event is triggered. This allows for precise measurement of which button design yields the highest conversion rate.
- Analyzing form field interactions: Track events for specific form field interactions, like field changes, form submissions, and error handling. This reveals user behavior within the forms, identifying bottlenecks or areas for improvement.
Lead Generation
Lead generation involves capturing user information to nurture potential customers. Event tracking can be a critical component of this process. Tracking events related to form submissions, contact requests, or other engagement activities helps you understand how users interact with your lead capture forms.
- Form submission tracking: Implement an event that fires when a user submits a form. Collect data from the submitted form fields, such as name, email, and company, in the event parameters. This data is invaluable for lead nurturing and qualification.
- Contact request tracking: Track events for specific contact forms or email submissions. This enables you to measure the effectiveness of different contact methods and identify areas where user engagement can be improved.
E-commerce
E-commerce platforms benefit significantly from event tracking, enabling detailed analysis of user behavior during the purchase journey. Tracking these events allows you to understand which product pages are most viewed, which items are added to carts, and ultimately, which items are purchased.
- Product page views: Track events when users visit specific product pages. This allows for analysis of product popularity and identification of potential product gaps.
- Add to cart events: Track events when users add products to their cart. This enables you to monitor the effectiveness of product recommendations and promotions.
- Checkout completion events: Track events when users complete the checkout process. Collect data on the specific items purchased, payment methods, and shipping information for comprehensive analysis.
Personalization
Personalization involves tailoring user experiences based on individual preferences and behaviors. Event tracking plays a vital role in enabling this. By tracking user interactions with personalized content, you can gather insights into which elements resonate most effectively with specific segments.
- Personalized product recommendations: Track events when users interact with personalized product recommendations. This data helps to optimize recommendation algorithms and improve conversion rates.
- Customized content delivery: Track events when users interact with personalized content. This data allows you to gauge the effectiveness of personalized content and identify areas for improvement.
Dynamic Marketing Campaigns
Dynamic marketing campaigns adapt in real-time based on user behavior. Event tracking is a key element in enabling this. By tracking user actions within the campaign, you can dynamically adjust the content and messaging displayed to maximize engagement and conversion.
- Dynamically adjust ad copy: Track user engagement with ad copy variations. Use the data to optimize ad copy in real-time and improve campaign performance.
- Personalized promotions: Track events associated with promotions. Use data to trigger personalized promotions and offers based on user behavior.
Integration with Analytics Platforms
Integrating event tracking with analytics platforms like Google Analytics provides comprehensive insights into user behavior. The data collected through events can be used to create custom reports and visualizations. This helps in better understanding trends, user journeys, and campaign performance.
- Custom reports: Use the data collected from events to create custom reports in Google Analytics, revealing detailed insights into user behavior and campaign performance.
- Data visualization: Create visualizations of event data in Google Data Studio, or other tools, to understand key trends and make data-driven decisions.
Event Tracking Strategies Table
| Use Case | Event Example | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| A/B Testing | Button Click (different button variants) | Track click events for each variant |
| Lead Generation | Form Submission | Track form submissions with specific data |
| E-commerce | Product Page View, Add to Cart, Checkout Completion | Track events throughout the purchase journey |
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, mastering events in Google Tag Manager empowers you to gather valuable data, gain actionable insights, and personalize user experiences. By implementing the strategies discussed here, you can unlock the full potential of your website and drive remarkable results.