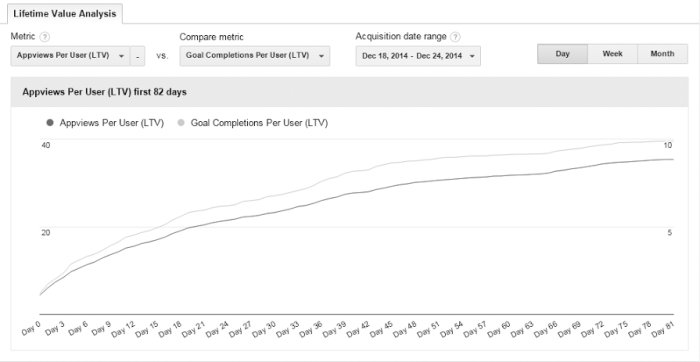
Google Analytics lifetime value sets the stage for understanding the true worth of your customers. This in-depth exploration dives into calculating customer lifetime value (LTV) within Google Analytics, revealing key components, various calculation methods, and how to leverage LTV for actionable insights and enhanced marketing strategies. We’ll uncover how to segment customers based on LTV, optimize marketing efforts, forecast revenue, and ultimately boost customer retention.
From defining LTV and its core components within the Google Analytics platform to examining the relationship between marketing spend and LTV, this comprehensive guide offers practical strategies and actionable takeaways. We’ll explore different types of LTV calculations, presenting them in a clear, easy-to-understand format. We’ll also delve into advanced considerations, such as cohort analysis and the impact of external factors on LTV.
The ultimate goal is to equip you with the knowledge to make data-driven decisions and maximize your return on investment.
Defining Lifetime Value (LTV)
Customer Lifetime Value (LTV) in Google Analytics represents the total revenue a business can reasonably expect from a single customer throughout their relationship. It’s a crucial metric for understanding the profitability of different customer segments and optimizing marketing strategies. Accurate LTV calculations empower businesses to make data-driven decisions regarding customer acquisition, retention, and product development.Understanding LTV goes beyond simply calculating the average revenue per customer.
It delves into the entire customer journey, considering factors such as the frequency and value of purchases, customer retention rates, and marketing spend. This holistic view allows businesses to allocate resources effectively and tailor strategies to maximize long-term profitability.
Customer Lifetime Value Definition
Customer Lifetime Value (LTV) is the total revenue a company anticipates a customer will generate throughout their relationship with the business. It’s a critical metric in Google Analytics, allowing businesses to understand the long-term value of individual customers and optimize strategies for maximizing revenue. LTV calculations go beyond simply looking at the initial purchase; they account for recurring purchases, customer retention, and the overall value a customer brings to the business over time.
Key Components of LTV Calculation in Google Analytics
Several factors influence LTV calculation in Google Analytics. These include the average order value (AOV), the average purchase frequency, customer retention rate, and the customer acquisition cost (CAC). These components work together to paint a complete picture of a customer’s worth to the business.
Importance of Understanding LTV
Understanding LTV is crucial for several reasons. It helps businesses prioritize customer segments that deliver the highest returns on investment (ROI). This allows for more targeted marketing campaigns, optimized pricing strategies, and improved customer retention programs. By knowing the LTV of different customer segments, businesses can allocate resources effectively to acquire and retain the most valuable customers.
Knowing your Google Analytics lifetime value is crucial, but how do you keep customers coming back? Implementing 5 psychology-based design tips to improve engagement on your website, like 5 psychology based design tips to improve engagement on your website , can significantly boost those all-important metrics. Ultimately, this leads to a higher lifetime value for each customer, which is a key performance indicator for any business.
Different Types of LTV Calculations
Various LTV calculation methods exist, each offering unique insights. These methods include simple LTV, cohort LTV, and predictive LTV. Simple LTV provides a basic understanding of average customer value, while cohort LTV reveals the value of customer groups acquired during specific periods. Predictive LTV estimates future revenue based on past behavior, allowing businesses to forecast and plan for future growth.
LTV Calculation Methods and Presentation in Google Analytics
Google Analytics doesn’t directly calculate LTV. Instead, it provides the necessary data points for businesses to perform LTV calculations using external tools or custom formulas. The data required for LTV calculation often comes from various reports within Google Analytics, including transaction data, customer acquisition data, and behavioral data. Businesses can then utilize these insights to understand their customer base and make strategic decisions.
Understanding Google Analytics lifetime value is crucial for any business. It helps you see the long-term profitability of customers. A key factor in calculating this value is the behavior at the very first step of the checkout process. Optimizing this first step of checkout can significantly influence conversion rates, which directly impacts your overall lifetime value.
So, delving deeper into this area can be a valuable exercise in Google Analytics.
Metrics Used in LTV Calculation
The table below Artikels key metrics commonly used in calculating LTV. These metrics, when combined, allow for a comprehensive understanding of the customer’s contribution to the business’s revenue over time.
| Metric | Description | Formula (if applicable) |
|---|---|---|
| Average Order Value (AOV) | The average amount spent per order. | Total Revenue / Total Number of Orders |
| Purchase Frequency | The average number of purchases made by a customer within a specific period. | Total Purchases / Total Customers |
| Customer Churn Rate | The percentage of customers who stop making purchases within a specific period. | (Number of Lost Customers / Number of Customers at Start of Period) – 100% |
| Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) | The average cost incurred to acquire a new customer. | Total Marketing Spend / Total New Customers Acquired |
| Average Customer Lifetime (CLTV) | The average time a customer remains active with the business. | Total Revenue / Total Customers |
LTV and Customer Segmentation
Understanding your customer’s lifetime value (LTV) is crucial for making informed business decisions. Knowing which customers are most valuable allows you to tailor your marketing strategies and allocate resources effectively. This is where customer segmentation based on LTV comes in. It’s not just about identifying high-value customers; it’s about understanding the unique characteristics and needs of different customer groups.Customer segmentation based on LTV allows for a more nuanced approach to marketing.
Instead of a one-size-fits-all strategy, you can craft targeted campaigns that resonate with each segment’s specific interests and pain points. This personalized approach can significantly boost customer engagement and ultimately drive higher profitability.
Customer Segmentation Strategies
Different customer segments exhibit distinct behaviors and preferences. Identifying these differences is key to developing effective marketing strategies. By understanding their LTV, you can allocate resources to maximize returns. This requires careful analysis of data points like purchase history, engagement metrics, and demographics.
Defining Customer Segments Based on LTV
Google Analytics provides valuable data for segmenting customers based on their LTV. You can filter and analyze data to identify groups with varying levels of spending, engagement, and overall value to your business. Consider these factors when segmenting:
- High LTV Customers: These are your most valuable customers, frequently making large purchases and demonstrating high engagement. They often provide a significant portion of your revenue and are key to maintaining a profitable customer base.
- Medium LTV Customers: This segment represents a significant portion of your customer base. They are valuable, but their spending and engagement are not as high as your high LTV customers. Targeting them with appropriate offers and incentives can help increase their lifetime value.
- Low LTV Customers: While these customers may not generate the same level of revenue as others, they can still be valuable. Careful analysis can reveal opportunities to increase their engagement and spending, turning them into more valuable customers.
Examples of Customer Segments and Corresponding LTV
Here are some examples of customer segments, their characteristics, and estimated LTV. These are illustrative and actual LTVs will vary depending on your business and industry.
| Customer Segment | Characteristics | Estimated LTV |
|---|---|---|
| High-Value Repeat Customers | Frequent purchases, high engagement with product/service, actively participate in loyalty programs. | $500-$1000+ |
| New Customers | First-time purchasers, potentially high potential for future purchases. | $100-$500 |
| High-Frequency, Low-Value Customers | Frequent purchases, but for low-priced items. | $100-$250 |
| Abandoned Cart Customers | Customers who have added items to their cart but haven’t completed the purchase. | Variable, depends on factors like the product and reasons for abandonment. |
Importance of Understanding Customer Segmentation and LTV
Understanding customer segmentation and LTV is critical for businesses to optimize their marketing strategies. By identifying and targeting high-value customer segments, you can allocate resources effectively and increase profitability. This targeted approach ensures that marketing efforts are focused on the segments that are most likely to generate the greatest return on investment. It also allows for more efficient resource allocation and prevents wasted spending on customers with a low LTV.
LTV and Marketing Strategies
Understanding customer lifetime value (LTV) is crucial for effective marketing. It provides a framework for making informed decisions about where to allocate resources and how to optimize campaigns for maximum return on investment (ROI). Knowing the value a customer brings over their relationship with your business allows for strategic prioritization of different customer segments and the development of targeted marketing strategies.LTV isn’t just a theoretical concept; it’s a powerful tool that can dramatically impact your bottom line.
By understanding your customers’ worth, you can refine your marketing efforts to attract high-value customers, nurture existing relationships, and ultimately, boost your overall profitability. This approach allows for a more data-driven, and less reactive, approach to marketing, resulting in more effective resource allocation.
Optimizing Marketing Campaigns with LTV
A crucial aspect of using LTV in marketing is aligning campaigns with customer segments having the highest LTV potential. This involves tailoring messaging, offers, and engagement strategies to resonate with these specific customer groups. By focusing on high-LTV segments, you can maximize the return on your marketing investments. Furthermore, it enables you to identify and prioritize areas where your marketing efforts can be most impactful.
Improving ROI Through Targeted Marketing
Marketing campaigns should be designed to directly impact LTV. Strategies should include personalized offers, loyalty programs, and exclusive content to enhance customer retention and increase their lifetime value. By providing exceptional customer experiences and creating a sense of loyalty, you can extend the customer relationship and increase the overall value derived from each customer. This is achieved by creating personalized experiences that address the unique needs and desires of individual customers.
Marketing Spend and LTV Connection
A strong correlation exists between marketing spend and LTV. Optimizing your marketing budget based on LTV projections allows for a more effective allocation of resources. By focusing your marketing efforts on segments with the highest potential for return, you can increase the overall ROI and efficiency of your marketing campaigns. For example, a company might allocate a larger portion of their budget to acquiring high-value customers, while simultaneously optimizing campaigns targeting customers with lower LTV to still yield a positive return.
Relationship Between LTV and CAC
Customer acquisition cost (CAC) is an important factor to consider when analyzing LTV. A healthy LTV-to-CAC ratio signifies that your marketing efforts are generating a positive return on investment. A higher ratio indicates a strong return, whereas a lower ratio may suggest a need to adjust your marketing strategies or target different customer segments. For example, a company with an LTV of $1,000 and a CAC of $200 is in a strong position to continue and scale their marketing efforts.
Marketing Strategies and Their Impact on LTV
Analyzing the impact of different marketing strategies on LTV provides crucial insights into campaign effectiveness. This analysis allows for a comprehensive evaluation of various strategies and the impact on customer lifetime value. The table below demonstrates the relationship between different marketing strategies and their effect on LTV.
| Strategy | Description | LTV Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Content Marketing | Creating valuable content to attract and engage customers | Increases LTV by establishing thought leadership and fostering brand loyalty |
| Social Media Marketing | Engaging with customers on social media platforms | Increases LTV through brand awareness and direct customer interaction |
| Email Marketing | Nurturing leads and customers through email communication | Increases LTV by providing personalized recommendations and exclusive offers |
| Paid Advertising | Using paid channels to reach target customers | Increases LTV by targeting high-value segments and increasing brand visibility |
LTV and Revenue Forecasting
Predicting future revenue is crucial for any business, and understanding customer lifetime value (LTV) is a powerful tool in this process. By analyzing past behavior and trends, we can develop informed projections about future revenue streams. This allows businesses to allocate resources effectively, optimize marketing campaigns, and make data-driven decisions. Forecasting revenue based on LTV provides a more nuanced understanding of the potential return on investment compared to traditional methods.
Methods for Forecasting Revenue Based on LTV in Google Analytics
Google Analytics, while not explicitly designed for LTV forecasting, provides the necessary data for creating estimations. Combining LTV calculations with other analytical tools and data sources allows for more comprehensive predictions. For example, using Google Analytics to track customer acquisition costs, marketing channel performance, and customer behavior patterns allows for more robust forecasting.
Factors Influencing Revenue Forecasting Accuracy
Several factors impact the accuracy of revenue forecasting based on LTV. Data quality is paramount. Inaccurate or incomplete data leads to unreliable projections. The reliability of the LTV calculation itself depends on the completeness and accuracy of the data used. Market trends, economic conditions, and competitor actions also play a significant role.
Unexpected events, such as a sudden shift in consumer preferences or a major industry disruption, can impact projected revenue. Furthermore, the chosen forecasting method significantly influences accuracy. Different models and approaches have varying levels of precision and suitability for specific business situations. The complexity of the business and its inherent unpredictability also contribute to the margin of error.
A detailed understanding of the specific industry and the market conditions can mitigate the impact of these uncertainties.
LTV and Revenue Projections
To illustrate the application of LTV in revenue forecasting, consider the following example. A hypothetical e-commerce company has calculated an average LTV of $500 per customer. Based on historical data and projected growth, they anticipate acquiring 100 new customers per month. This leads to a revenue projection for the coming months.
| Time Period | Estimated LTV | Projected Revenue |
|---|---|---|
| Month 1 | $500 | $50,000 |
| Month 2 | $500 | $55,000 |
| Month 3 | $500 | $60,000 |
| Month 4 | $500 | $65,000 |
| Month 5 | $500 | $70,000 |
These projections assume a consistent customer acquisition rate and average LTV. However, the actual results may vary due to unforeseen circumstances. The example demonstrates the potential of LTV in creating a revenue forecast, although the precision will always depend on the factors mentioned previously.
LTV and Customer Retention: Google Analytics Lifetime Value
Understanding customer lifetime value (LTV) is crucial for business success. However, maximizing LTV isn’t just about acquiring new customers; it’s equally important to retain existing ones. Customer retention is a key driver of long-term profitability, as repeat customers often spend more and generate higher LTV than new acquisitions. By focusing on retention, businesses can build stronger customer relationships, increase revenue streams, and create a sustainable competitive advantage.
Improving Customer Retention Rates Based on LTV Insights
Customer retention is intrinsically linked to LTV. High retention rates translate directly into higher LTV. Analyzing LTV data allows businesses to identify segments of customers who are most valuable and at risk of churning. Targeted retention strategies can then be developed to address the specific needs and pain points of these customer groups. This often involves personalized communication and offers tailored to each segment’s preferences and behaviors.
Strategies for Enhancing Customer Loyalty and Increasing LTV
Building customer loyalty is paramount for boosting LTV. Loyalty programs, exclusive discounts, and personalized recommendations can foster a sense of appreciation and encourage repeat business. Proactive customer service, including responding promptly to inquiries and resolving issues effectively, strengthens customer relationships. Providing exceptional support demonstrates value and builds trust, leading to higher retention rates and increased LTV. Furthermore, regularly soliciting feedback and actively listening to customer concerns provides invaluable insights into areas for improvement.
Understanding Google Analytics Lifetime Value (LTV) is crucial for any business. Knowing how much a customer is worth over their relationship with your company is vital for strategic decision-making. To maximize your LTV, improving email open rates is key. Strategies for improve email open rate can significantly boost customer engagement and, in turn, influence your overall LTV.
Ultimately, a strong LTV will lead to more profitable campaigns and sustainable growth.
The Connection Between Customer Churn and LTV
Customer churn, the rate at which customers discontinue their relationship with a company, significantly impacts LTV. High churn rates reduce the overall value a customer contributes over their lifetime. Every customer lost represents a lost opportunity for future revenue. Analyzing the reasons behind customer churn is crucial to implementing effective strategies for reducing it. Identifying patterns in churn allows for proactive intervention and personalized solutions, ultimately improving customer retention.
Identifying and Addressing Issues That Lead to Customer Churn
Understanding the drivers of customer churn is essential. Common reasons include poor product quality, lack of support, or dissatisfaction with pricing. In-depth customer surveys and feedback mechanisms can uncover specific issues. By listening to customer complaints and concerns, businesses can identify areas where the customer experience needs improvement. Addressing these issues directly through product enhancements, improved support systems, or revised pricing strategies can directly reduce churn.
Strategies for Reducing Customer Churn
A well-defined retention strategy is crucial for mitigating customer churn and boosting LTV. Implementing the following strategies can significantly reduce customer churn:
| Strategy | Description | Expected Impact on LTV |
|---|---|---|
| Proactive Customer Support | Providing prompt and personalized support to address customer issues before they escalate. | Reduced churn, increased customer satisfaction, higher LTV. |
| Personalized Communication | Tailoring communication channels and content to resonate with individual customer preferences. | Improved customer engagement, increased loyalty, higher LTV. |
| Incentivized Loyalty Programs | Offering rewards and exclusive benefits to loyal customers to encourage continued engagement. | Increased customer retention, higher purchase frequency, increased LTV. |
| Product/Service Improvements | Addressing customer feedback and identifying areas for product/service enhancement to meet evolving customer needs. | Improved customer satisfaction, reduced churn, higher LTV. |
| Targeted Retention Campaigns | Identifying at-risk customers and implementing targeted campaigns to address their specific needs and concerns. | Reduced churn among vulnerable customer segments, improved overall LTV. |
Advanced LTV Considerations
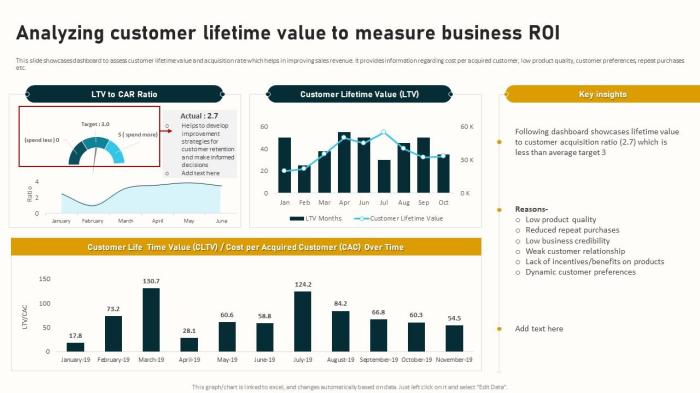
Understanding customer lifetime value (LTV) goes beyond basic calculations. Advanced techniques delve deeper into the factors influencing customer behavior and revenue streams, allowing for more accurate forecasting and targeted marketing strategies. This section explores sophisticated LTV calculations, the impact of external factors, and the importance of optimizing marketing campaigns for sustained LTV growth.Advanced LTV calculations provide a more nuanced understanding of customer value beyond simple averages.
Sophisticated models can consider various factors, like purchase frequency, average order value, and customer engagement, to predict future revenue more accurately. These models are crucial for businesses aiming to maximize return on investment (ROI) from their marketing efforts.
Cohort Analysis for Deeper LTV Insights, Google analytics lifetime value
Cohort analysis groups customers based on shared characteristics, like acquisition date or demographics. Analyzing cohorts over time allows businesses to track the revenue generated by different customer groups, identifying trends and patterns in their purchasing behavior. This granular view reveals valuable insights into customer longevity and purchasing patterns, leading to more targeted retention strategies. For example, a cohort of customers acquired during a specific marketing campaign might exhibit a higher LTV than other cohorts, suggesting the campaign’s effectiveness in attracting high-value customers.
Impact of External Factors on LTV
Several external factors influence customer lifetime value. Seasonality significantly impacts sales in many industries, with peak periods driving higher revenue and subsequent dips. Understanding these seasonal fluctuations allows businesses to adjust marketing strategies and inventory management accordingly. Promotions and discounts can also influence LTV, either positively or negatively, depending on their design and execution. For example, a poorly designed promotional offer could result in a temporary boost in sales but a long-term decrease in customer lifetime value due to reduced perceived value of the product.
Strategic promotions can improve LTV, as seen in companies like Starbucks offering loyalty programs that incentivize repeat purchases.
Optimizing Marketing Campaigns with A/B Testing
A/B testing is a critical component of optimizing marketing campaigns to improve LTV. By comparing two versions of a campaign (e.g., different headlines, call-to-actions, or landing pages), businesses can determine which performs better in terms of conversions and revenue. This iterative process allows for continuous improvement of marketing strategies, ultimately maximizing customer value. For instance, an e-commerce company might test different email subject lines to identify which generates the highest click-through rates and subsequent purchases, thereby improving the LTV of the customers engaged by those emails.
Measuring Marketing Campaign Impact on LTV
Multiple methods can measure the impact of marketing campaigns on LTV. Attribution modeling tracks the various touchpoints a customer interacts with before making a purchase, assigning value to each interaction. This approach helps determine which channels and campaigns are most effective in driving conversions and improving LTV. Another method is to analyze customer journey data to identify patterns in customer behavior.
Understanding the customer’s engagement with the brand across different touchpoints allows for a comprehensive understanding of the effectiveness of marketing campaigns in driving LTV.
Impact of Marketing Initiatives on LTV
| Initiative | Description | LTV Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Targeted Email Marketing | Personalized email campaigns based on customer segments and purchase history. | Increased LTV through higher conversion rates and repeat purchases. |
| Loyalty Programs | Incentivizing repeat purchases and brand loyalty. | Improved LTV through increased customer retention and higher average order values. |
| Content Marketing | Creating valuable content that educates and engages customers. | Enhanced LTV by fostering brand trust and driving organic traffic. |
| Paid Social Media Advertising | Targeted advertising campaigns on social media platforms. | Increased LTV through reaching specific customer segments with personalized messages. |
End of Discussion
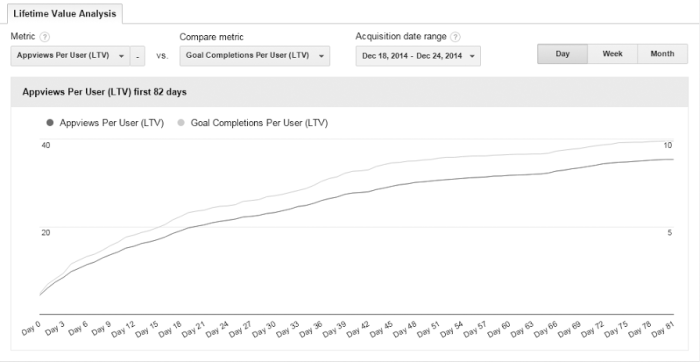
In conclusion, mastering Google Analytics lifetime value unlocks a wealth of opportunities for businesses to understand their customer base, optimize marketing campaigns, and ultimately drive revenue growth. By segmenting customers based on their LTV, businesses can tailor marketing efforts to resonate with each segment, improving customer engagement and loyalty. Forecasting revenue based on LTV insights allows for proactive planning and strategic decision-making.
Ultimately, understanding and utilizing Google Analytics LTV empowers businesses to make data-driven choices, leading to improved ROI and sustainable growth.