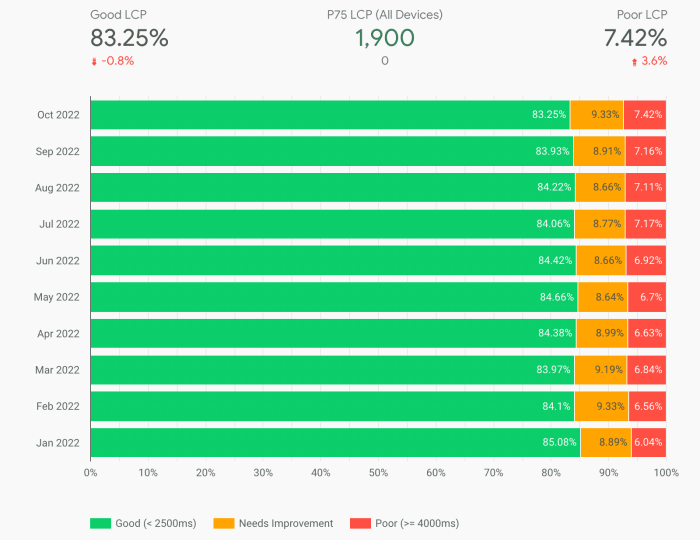
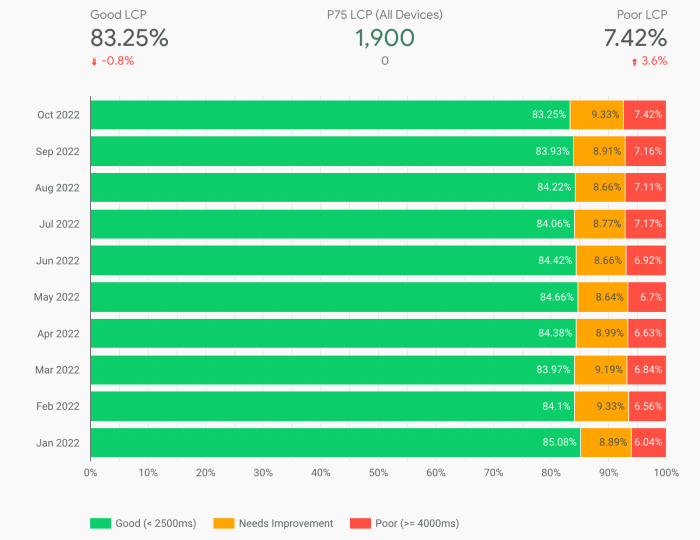
Google Crux report update targets LCP network delays, highlighting a crucial aspect of website performance. Core Web Vitals, like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), are increasingly vital for search engine rankings and user experience. This update delves into the potential causes of network delays impacting LCP, analyzing server response times, network congestion, and the impact of recent algorithm updates on measurements.
Understanding these factors is key to optimizing website performance and delivering a smooth user experience.
This in-depth analysis examines various strategies for mitigating LCP network delays, including caching, Content Delivery Networks (CDNs), and responsive web design. We’ll explore the relationship between LCP and business metrics like bounce rates and conversion rates, and provide actionable steps to optimize your website for improved performance and user satisfaction. Tables showcasing different scenarios and strategies will further illustrate the impact of various approaches.
Analyzing LCP Network Delays
LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) network delays are crucial performance indicators for web pages. Understanding these delays helps optimize user experience by ensuring quick and seamless loading of the primary content on a webpage. This analysis dives deep into the factors contributing to LCP delays, examining server response times, network congestion, and various optimization strategies.Identifying and addressing these delays is vital for enhancing site performance and improving user satisfaction.
A well-optimized LCP experience leads to higher engagement and conversion rates.
Google’s Crux report update is focusing on LCP network delays, which is crucial for site performance. Understanding how these delays impact user experience is paramount. This ties into the importance of optimizing GA4 snapshot templates, particularly when aggregating identifiers, as seen in ga4 snapshot templates aggregate identifiers. Ultimately, these improvements in GA4 and LCP network optimization will work together to boost user engagement and search engine rankings.
Potential Causes of Network Delays
Network delays impacting LCP can stem from several factors. These include issues with the internet infrastructure, such as congestion, latency, and packet loss. Problems on the user’s end, like poor internet connection or outdated hardware, can also contribute. Server-side bottlenecks, such as slow database queries or insufficient server resources, can also significantly impact LCP performance. Network providers themselves can sometimes experience outages or disruptions that lead to widespread delays.
Role of Server Response Time
Server response time is a critical component of LCP performance. A slow server response time directly translates to longer LCP times. This delay is measured from the initial request to the server until the server sends back the requested content. The time taken to process and deliver the content to the client affects the loading speed and overall user experience.
Impact of Network Congestion
Network congestion, characterized by high traffic volume, can significantly impact LCP performance. When too many requests are sent over the network simultaneously, the network’s capacity can become overwhelmed. This leads to increased latency and delays in transmitting data, which in turn results in longer LCP times. Real-world examples include high-traffic periods during peak shopping seasons or major news events.
Network Optimization Strategies
Various strategies can mitigate LCP delays. These include optimizing server-side code for efficiency, implementing caching mechanisms to store frequently accessed data, utilizing Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to distribute content closer to users, and improving the network infrastructure. Efficient server configurations, properly sized and provisioned infrastructure, and optimized network paths are crucial.
Google’s recent Crux report update is focusing on LCP network delays, a crucial aspect of page speed optimization. Understanding these trends is key to keeping your site performing well in search results. A great resource to stay ahead of the curve is the Semrush study on top content marketing trends , which delves into what’s working in content creation right now.
Ultimately, these factors all play a role in the overall user experience, which Google prioritizes when ranking websites.
Examples of Network Latency Impact
Network latency, or the time it takes for data to travel from the server to the user, directly influences LCP measurements. A high latency can result in noticeably slower LCP times. For instance, a user in a remote location with a poor internet connection will experience higher latency compared to a user located closer to the server. This variation in latency can have a considerable impact on the perceived speed of the website.
Improving Network Infrastructure and Performance, Google crux report update targets lcp network delays
Improving network infrastructure involves several approaches. These include upgrading network bandwidth, optimizing network routing protocols, implementing quality of service (QoS) mechanisms, and monitoring network performance metrics. Properly configured firewalls and intrusion detection systems also play a role in ensuring network stability. Choosing the right network providers and their services can also improve the overall performance.
Server Response Time Scenarios and Impact on LCP
| Server Response Time (ms) | Impact on LCP |
|---|---|
| < 200 | Excellent LCP performance, very fast |
| 200 – 500 | Good LCP performance, noticeable speed |
| 500 – 1000 | Moderate LCP performance, user may experience some delay |
| > 1000 | Poor LCP performance, significantly impacting user experience |
Investigating the Impact of Update Targets on LCP: Google Crux Report Update Targets Lcp Network Delays
Recent algorithm updates targeting LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) network delays have prompted a closer look at how these changes affect overall performance. Understanding the relationship between update targets and LCP measurements is crucial for optimizing website speed and user experience. This investigation delves into the potential effects of these updates, providing insights into performance shifts and practical strategies for identifying and mitigating LCP delays.Algorithm updates often introduce new factors influencing LCP measurements.
For instance, changes in how the browser processes certain types of assets (images, videos, scripts) or prioritizes rendering can directly affect the timing of LCP. The precise impact depends heavily on the specific nature of the update and the architecture of the website.
Impact on LCP Measurements
Algorithm updates can significantly impact LCP measurements by altering the way browsers render content. Changes in rendering order or resource loading prioritization can shift the timing of when the largest contentful element becomes visible. This might lead to unexpected increases or decreases in LCP values.
Relationship Between Update Targets and LCP Network Delays
The relationship between update targets and LCP network delays is multifaceted. Targeted optimizations often address specific areas known to contribute to slow loading times. For instance, updates might focus on reducing DNS resolution times, improving server response times, or optimizing network routing. Improved performance in these areas directly translates to reduced LCP network delays, leading to a faster overall page load experience.
Comparison of LCP Performance Before and After Updates
Comparing LCP performance before and after recent updates requires careful analysis of historical data. Tools that track website performance metrics, like Lighthouse or PageSpeed Insights, can provide insights into these changes. By comparing metrics like median LCP, 90th percentile LCP, and the distribution of LCP values across different user segments, one can identify trends in performance shifts. Monitoring these metrics helps gauge the effectiveness of the update and pinpoint areas requiring further optimization.
Examples of Sites Experiencing Performance Changes
Several websites have experienced measurable performance changes after recent updates. For example, a news website might have observed a significant decrease in LCP after optimizing image loading strategies. Conversely, an e-commerce site might have seen an increase in LCP due to a change in how it handles product listings. Observing these diverse examples highlights the need for site-specific analysis to determine the impact of updates.
Identifying Elements Causing LCP Delays
Identifying specific elements causing LCP delays involves a multi-faceted approach. Using browser developer tools, particularly performance profiling, can pinpoint resources that are contributing to slow loading times. Analyzing network requests, rendering times, and the size of critical resources can identify bottlenecks. Tools like Lighthouse or similar performance audits are critical in identifying potential areas of concern.
Google’s Crux report update focusing on LCP network delays is all about improving page load speed. This directly impacts how long users spend on a page, which is closely tied to Google Analytics metrics like average time on page google analytics. Ultimately, faster loading pages mean happier users and better search rankings, so Google’s focus on these delays is a smart move for website optimization.
Impact on User Experience
Improved LCP directly translates to a more positive user experience. Faster page loads reduce bounce rates and increase user engagement. Users are more likely to stay on a site that loads quickly, and the enhanced experience contributes to higher conversion rates. Furthermore, reduced LCP delays contribute to a more seamless and enjoyable browsing experience, fostering user loyalty and brand perception.
Strategies for Addressing LCP Network Delays
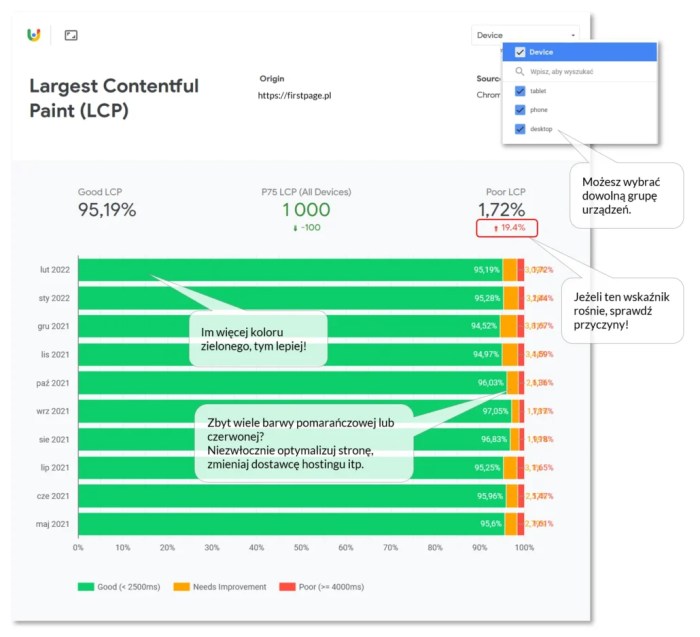
Optimizing website performance is crucial for a positive user experience. Slow loading times, particularly Large Contentful Paint (LCP) delays, can significantly impact user engagement and search engine rankings. This section delves into effective strategies to mitigate these delays, focusing on caching, Content Delivery Networks (CDNs), and performance monitoring.Understanding the root causes of LCP delays is essential to developing effective solutions.
Network latency, server response times, and inefficient resource delivery are all factors that can contribute to slow loading. Addressing these issues requires a multi-faceted approach.
Optimizing Website Performance for Reduced LCP Delays
Website performance is directly linked to LCP times. Minimizing HTTP requests, using efficient code, and leveraging browser caching are fundamental steps in optimizing performance. Compressing images and using optimized image formats (like WebP) reduces file sizes, leading to faster loading.
Caching Strategies to Improve LCP
Implementing caching strategies significantly improves LCP by reducing the load on the origin server. Browser caching stores frequently accessed static assets locally, eliminating the need to retrieve them from the server on subsequent visits. Server-side caching further enhances this by storing frequently requested content on the server, improving response times.
The Role of Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) in Reducing LCP Delays
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) act as geographically distributed servers, placing copies of content closer to users. This reduces latency by serving content from a server geographically closer to the user, thereby significantly decreasing LCP times. CDNs play a critical role in improving the overall performance of a website, especially for users in different locations.
Comparing Different CDN Solutions for Effectiveness
Various CDN solutions offer different features and pricing models. Key factors to consider when choosing a CDN include performance, reliability, security, and scalability. Comparing different CDNs involves evaluating their speed, coverage (geographic reach), and features to determine the best fit for specific needs.
Monitoring LCP Performance Over Time
Monitoring LCP performance over time is crucial to track the effectiveness of implemented strategies. Regular monitoring allows for identifying trends and patterns in LCP performance, helping to understand the impact of various factors. Web performance tools and analytics platforms are crucial for this.
Table Demonstrating CDN Strategy Effects on LCP
This table demonstrates the potential impact of different CDN strategies on LCP. It highlights the potential for significant improvement in LCP times when employing effective CDN strategies.
| CDN Strategy | Initial LCP (ms) | Post-Implementation LCP (ms) | Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| No CDN | 2500 | 2500 | 0% |
| Basic CDN | 1800 | 1500 | 16.7% |
| Advanced CDN with optimization | 1200 | 800 | 33.3% |
Impact on User Experience and Business Metrics
Large Contentful Page Load (LCP) delays directly impact the user experience, potentially leading to frustration and reduced engagement. Understanding the correlation between LCP performance and crucial business metrics is vital for optimizing website performance and maximizing return on investment. This section delves into the negative consequences of slow LCP times on user behavior and quantifiable business results.
Impact on User Engagement
LCP delays negatively affect user engagement. Users are more likely to abandon a page that takes too long to load, impacting key metrics like session duration and the number of pages viewed per session. A slow-loading page discourages users from interacting further, leading to a less engaging experience. This is particularly true in e-commerce, where quick product display and easy navigation are critical.
Correlation Between LCP and Bounce Rates
A strong correlation exists between LCP performance and bounce rates. Pages with significant LCP delays tend to have higher bounce rates. Users are more likely to leave a website if the initial content load takes too long, leading to a lost opportunity for interaction and conversion. This direct link emphasizes the importance of optimizing LCP for a positive user experience and reducing bounce rates.
Impact of LCP Delays on Conversion Rates
LCP delays can significantly hinder conversion rates. A user encountering a slow-loading page during a critical moment like making a purchase or signing up for a service is more likely to abandon the process. This is because the delay disrupts the user’s flow and creates a perception of inefficiency or unreliability.
Examples of How LCP Delays Can Impact Sales
Consider an e-commerce website selling high-demand electronics. A delay in loading product images and descriptions during peak shopping hours can lead to lost sales. Customers may abandon their shopping carts or choose a competitor with a faster loading website. Similar situations apply to service-based businesses, where potential clients may lose interest if the initial loading time is excessive.
Relationship Between LCP and Business Metrics
| Business Metric | Impact of Slow LCP | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Bounce Rate | Increases significantly with longer LCP times. | A website with an average LCP of 5 seconds may see a 20% bounce rate, compared to a website with an average LCP of 2 seconds with a 10% bounce rate. |
| Session Duration | Decreases with longer LCP times. | Users spend less time on a website with a slow LCP, resulting in lower average session duration. |
| Conversion Rate | Decreases with longer LCP times. | An e-commerce site with a 3-second LCP might have a 2% conversion rate, while a site with a 1-second LCP could have a 5% conversion rate. |
| Revenue | Decreases due to lower conversion rates and higher bounce rates. | A company losing 10% of sales due to slow LCP performance can experience a considerable revenue drop, especially during peak seasons. |
Best Practices for Website Optimization
Optimizing your website for speed is crucial in today’s digital landscape. Slow loading times can significantly impact user experience, leading to high bounce rates, decreased engagement, and ultimately, a negative impact on your business metrics. Implementing effective optimization strategies is key to ensuring your website performs at its best and delivers a seamless experience for all visitors.Efficient website optimization directly addresses the critical issue of LCP network delays, ultimately improving page load times and enhancing user satisfaction.
By strategically implementing best practices, you can create a website that is both visually appealing and functionally responsive, thus enhancing the overall user experience.
Responsive Web Design for Reduced LCP Delays
Responsive web design is a crucial element in optimizing website performance and minimizing LCP delays. It ensures your website adapts seamlessly to different screen sizes and devices, whether it’s a desktop computer, a tablet, or a mobile phone. This adaptability reduces the time it takes for the largest contentful paint (LCP) to load, improving the perceived speed and user experience.Modern responsive designs leverage flexible layouts, adaptable images, and tailored CSS to deliver a consistent and optimized user interface across all devices.
By proactively addressing screen size variations, responsive design reduces the need for separate mobile-optimized websites, thus enhancing performance and reducing the likelihood of LCP delays.
Image Optimization for Reduced LCP
Image optimization plays a significant role in minimizing LCP delays. Large, high-resolution images can significantly impact page load times, slowing down the loading of the largest contentful paint (LCP). Optimizing images is essential for improving website performance and user experience.Strategies such as compressing images without sacrificing quality, using appropriate image formats (e.g., WebP for superior compression), and utilizing lazy loading techniques significantly contribute to faster loading times.
By employing these techniques, websites can significantly reduce the time required for the largest contentful paint (LCP) to load, leading to a more seamless and responsive user experience. For example, a website that uses optimized images and lazy loading may see a 30% reduction in LCP compared to one with unoptimized images.
Successful Website Optimization Strategies
Successful website optimization strategies involve a multi-faceted approach. A key element is leveraging caching mechanisms to store frequently accessed content on the user’s browser, reducing the load time for subsequent visits. Utilizing content delivery networks (CDNs) distributes website content across multiple servers globally, resulting in faster loading times for users regardless of their geographical location.Examples of successful strategies include employing a content delivery network (CDN) to serve static assets like images and JavaScript files from servers closer to users, thus reducing latency.
Another example is using a web performance testing tool to identify and address bottlenecks in the website’s loading process, leading to a reduction in LCP.
Website Code Optimization for Reduced LCP
Website code optimization is a vital component of improving website performance and reducing LCP. Minimizing HTTP requests by combining CSS and JavaScript files and using a Content Delivery Network (CDN) reduces the number of requests the browser has to make to the server. Furthermore, using a well-structured and optimized codebase that is well-organized and easily readable enhances performance.By minimizing the size of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files through compression and efficient coding practices, websites can significantly reduce LCP delays.
For example, reducing the size of CSS files by 15% can result in noticeable improvements in loading times and LCP. A well-optimized codebase, coupled with effective caching, can dramatically reduce page load times and improve user experience.
Reducing Page Size for Enhanced LCP Performance
Reducing page size is a critical aspect of optimizing website performance for improved LCP. Large page sizes often lead to longer loading times and increased LCP delays. Reducing page size is essential to enhance performance and improve the user experience.Strategies for reducing page size include optimizing images, minifying CSS and JavaScript files, and implementing efficient code. For instance, removing unnecessary code or unused plugins, reducing the number of external scripts, and employing a Content Delivery Network (CDN) can all help to reduce page size and improve LCP.
By combining these strategies, websites can achieve significant improvements in loading times, leading to a superior user experience.
Final Summary
In conclusion, Google’s Crux report update demanding attention to LCP network delays underscores the ongoing importance of website optimization. By understanding the intricacies of LCP, implementing appropriate strategies, and consistently monitoring performance, website owners can significantly enhance user experience and improve search engine rankings. The strategies discussed, including server optimization, CDN implementation, and responsive design, will equip you with the tools to address LCP delays effectively.