Google on search console noindex detected errors – Google Search Console noindex detected errors can significantly impact your website’s visibility. Understanding these errors, their causes, and how to fix them is crucial for success. This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of noindex errors, exploring various types, troubleshooting techniques, and preventative measures to keep your site ranking high.
We’ll dissect common causes like problematic robots.txt files, incorrect meta tags, and server-side issues. Learn how to identify these errors within Google Search Console and implement effective solutions. From basic troubleshooting to advanced techniques, this guide covers everything you need to understand and address noindex errors on your website.
Understanding the Issue
Noindex detected errors in Google Search Console signal a problem with how your website is telling Google which pages to include or exclude from search results. These errors, often stemming from incorrect robots.txt directives or meta tags, can significantly impact your website’s visibility and search engine optimization () performance. Understanding these errors and how to fix them is crucial for maintaining a healthy online presence.These errors essentially tell Google’s crawlers not to index specific pages, which means those pages won’t appear in search results.
This can lead to a decrease in organic traffic, missed opportunities for lead generation, and a negative impact on your overall website performance. Identifying and rectifying these errors is a critical step in ensuring your website is discoverable and accessible to potential customers.
Noindex Detected Errors in Google Search Console
Noindex errors in Google Search Console arise when Google’s crawlers encounter directives instructing them not to index specific pages. This could be due to various reasons, including improper meta tags, incorrect robots.txt rules, or even issues with the website’s server configuration.
Types of Noindex Detected Errors
Various types of noindex directives can lead to errors reported in Google Search Console. These can include:
- Incorrectly placed or formatted
<meta name="robots" content="noindex">tags within the HTML of a page. This tag explicitly tells Google not to index that specific page. - Conflicting or overlapping directives in the robots.txt file. This could result in Google’s crawlers receiving contradictory instructions about indexing.
- Issues with server-side responses. If the server sends a 404 (page not found) error or a similar non-200 status code, Google might interpret this as a directive to not index the page.
- Problems with dynamically generated pages. If a website generates pages on the fly, there might be issues with how these pages are structured and whether they’re being correctly indicated as indexable.
Impact on Website Visibility
Noindex errors directly impact a website’s visibility in search results. Pages marked with noindex directives are excluded from Google’s index, meaning they are not considered for ranking and are thus invisible to searchers. This can result in a significant reduction in organic traffic, as users are unable to find these pages via search.
Common Reasons for Noindex Errors
Common reasons for these errors often include:
- Incorrect Robots.txt Configuration: A robots.txt file that blocks access to critical pages can lead to noindex errors. It’s crucial to ensure that the robots.txt file doesn’t inadvertently block pages that should be indexed.
- Incorrect Meta Tags: Incorrect or missing meta tags (specifically the robots meta tag) can cause Google to misinterpret the page’s intended visibility.
- Server Errors: Server-side issues, such as returning 404 errors, can result in Google interpreting the pages as not indexable.
- Dynamic Content Issues: Dynamically generated pages that don’t correctly indicate their status (indexable or not) can also cause indexing problems.
Effect on Performance
Noindex errors negatively impact performance by limiting the amount of content Google can index. This reduces the total number of pages available to be ranked, thus lowering the website’s overall search visibility and organic traffic. Consequently, lower rankings and fewer clicks result from decreased exposure in search engine results pages (SERPs).
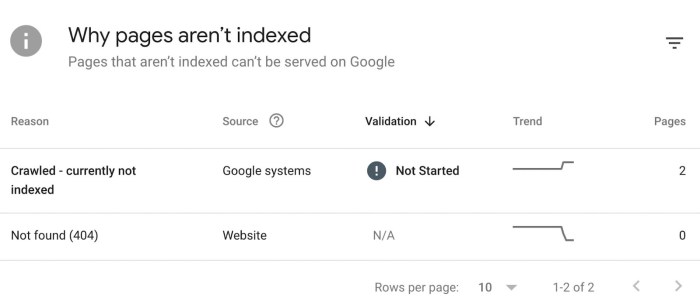
Locating Noindex Errors in Google Search Console
Google Search Console provides tools to identify noindex errors. By analyzing crawl data and index coverage reports, you can pinpoint specific pages that have been excluded from indexing due to noindex directives.
Troubleshooting Techniques
Unveiling the mysteries behind “noindex detected” errors in Google Search Console requires a systematic approach. These errors often stem from misconfigurations in your website’s code or server settings. By understanding the potential causes and employing the right troubleshooting steps, you can effectively address these issues and restore your site’s proper indexing.Addressing “noindex detected” errors is crucial for maintaining a healthy website presence.
Seeing “noindex detected” errors on Google Search Console can be a pain, right? It means Google can’t index certain pages on your site, potentially impacting your search rankings. One possible reason for this is that you might be using content personalization, like showing different content to different users based on their preferences. If you’re not properly handling this personalization, it could lead to duplicate content issues, which Google might flag as “noindex.” Understanding how content personalization works is key to fixing these errors; you can learn more about it here: content personalization what is it.
Ultimately, thorough configuration and testing are essential to ensure your personalized content is indexed correctly and avoids these noindex issues on Search Console.
These errors signal that Googlebot, the search engine crawler, is instructed not to index specific pages or your entire site. This can severely impact your search engine rankings, visibility, and ultimately, your online success. Proactive troubleshooting helps ensure Google can correctly crawl and index your content.
Potential Solutions for Noindex Errors
Understanding the different types of “noindex detected” errors is vital for pinpointing the root cause and applying the right corrective measures. The table below provides a comprehensive overview of potential causes and corresponding troubleshooting steps.
| Error Type | Possible Cause | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|---|
| robots.txt issue | Incorrect or missing directives in your robots.txt file, which controls how search engines crawl your site. | Review and update the robots.txt file to ensure it doesn’t block essential pages. Verify that the file is correctly uploaded to your server’s root directory. |
| meta tag errors | Incorrect or missing “noindex” meta tags in the HTML source code, which are used to prevent indexing. | Inspect the HTML source code of the affected pages for any incorrect or missing meta tags. Ensure that noindex directives are used correctly. Consider the presence of other conflicting meta tags. |
| server-side issues | Problems with your server configuration or incorrect server responses, preventing proper crawling. | Verify your server’s configuration settings. Check server access logs for error messages that might indicate issues during crawling. Ensure that your server is responding correctly to Googlebot’s requests. |
Importance of Server Logs
Examining server logs is a critical step in diagnosing server-side issues. Error messages in these logs often reveal the root cause of indexing problems, such as issues with file permissions, database queries, or other server-side problems.
Inspecting HTML with Developer Tools
Utilizing developer tools within your web browser provides a powerful way to inspect the HTML structure and identify potential meta tag errors. These tools allow you to view the source code of a webpage, enabling the identification of incorrect or missing meta tags, and ensure proper use of noindex directives.
Reviewing and Updating robots.txt
Reviewing and updating your robots.txt file is essential for managing how search engine crawlers interact with your website. This file instructs crawlers which parts of your site to crawl and index. An improperly configured robots.txt file can prevent Googlebot from accessing critical pages, leading to indexing issues. Carefully review the file’s directives, ensuring that essential pages are not blocked.
Content Recommendations
Correctly implementing noindex directives is crucial for managing search engine visibility. Ignoring these directives can lead to unwanted indexing of pages you want excluded, impacting crawl budget and potentially hindering your strategy. Understanding the nuances of noindex implementation ensures your site’s optimal visibility and avoids penalties.Proper noindex implementation, including the correct use of meta tags, robots.txt, and HTTP headers, is vital for maintaining a well-organized and efficient website from a search engine perspective.
This approach helps you maintain control over which pages are indexed and which are not, allowing you to prioritize important content and avoid indexing irrelevant or outdated material.
Correct Noindex Implementation Examples
Noindex directives can be implemented in various ways, each serving a specific purpose. The proper implementation of noindex directives is essential for preventing unwanted pages from appearing in search engine results.
- Using the robots meta tag: This is the most common method. The `meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”` tag tells search engines not to index the page. You can combine it with `nofollow` to prevent link follow. For example, ` ` effectively prevents indexing and the propagation of links from that page.
- Robots.txt Implementation: The robots.txt file is used to instruct search engine crawlers about which parts of your website to crawl and which to avoid. A robots.txt file that excludes specific pages from crawling prevents them from being indexed. For example, to prevent indexing of pages under `/category/old-products/`, add the following rule to your robots.txt file:
“`
User-agent:
–
Disallow: /category/old-products/
“`
This rule instructs all search engine crawlers (indicated by `*`) to not crawl any URLs that begin with `/category/old-products/`. - Using HTTP Headers: HTTP headers provide a more granular control over how search engines treat your pages. A `X-Robots-Tag: noindex` header in the HTTP response of a page explicitly tells search engines not to index that page. This method offers fine-grained control over indexing.
Importance of Correct HTTP Headers
Using the correct HTTP headers for noindex directives is crucial for precise control over how search engines treat your pages. The correct use of HTTP headers is paramount to ensuring that search engines understand and respect your instructions regarding indexing. Incorrect or missing headers can lead to unexpected indexing behavior.
HTML Meta Tags for Noindex
The `meta` tag is a fundamental HTML element for controlling how search engines interact with your pages.
| Meta Tag | Description | Example Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Exclude page from search engine indexes | ||
| Exclude page from search engine indexes and prevent search engines from following links on the page. |
Using Google Search Console for Testing
Google Search Console provides a powerful tool for verifying the effectiveness of your noindex directives. Use the “Fetch as Google” tool to simulate how Googlebot crawls your site and check whether the noindex directives are correctly applied. This allows you to identify and fix any discrepancies between your implementation and how Googlebot interprets it.
So, you’ve got those pesky “noindex detected” errors popping up in Google Search Console? Frustrating, right? A good way to improve your email deliverability and engagement is by A/B testing your email campaigns. By experimenting with different subject lines, calls to action, and even email layouts, you can see which variations perform best. This crucial data informs your future email strategies, ultimately leading to a better user experience and a more successful outcome for your SEO efforts, thus resolving those pesky “noindex detected” errors.
Want to learn more about A/B testing your email campaigns? Check out this helpful guide: ab testing email campaigns.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing “noindex detected” errors is crucial for maintaining optimal search engine visibility. These errors, often stemming from misconfigurations or overlooked details, can significantly impact your website’s ranking and organic traffic. Proactive measures are key to ensuring your site remains discoverable by search engines.A robust preventative approach combines meticulous website audits, strategic tool utilization, and adherence to best practices in sitemap and robots.txt management.
By understanding potential pitfalls and implementing appropriate safeguards, you can mitigate the risk of “noindex” errors and maintain a strong online presence.
Best Practices for Preventing Noindex Errors
Implementing best practices is vital to avoiding “noindex” errors. These errors can arise from various sources, including improper meta tags, faulty robots.txt directives, and issues with sitemap structure. By adhering to these recommendations, you can proactively prevent these errors.
Google Search Console is showing noindex detected errors, which can be a real pain. Often, these errors are related to poor website structure or overlooked technical SEO. This is where effectively managing a sales team can actually help – the same analytical thinking used to boost sales performance can be applied to identify and resolve these issues.
Addressing the root causes of these errors, whether it’s updating robots.txt or fixing broken links, will ultimately improve your search engine rankings.
- Regular Website Audits: Regular website audits are essential for identifying potential issues before they negatively impact search visibility. A comprehensive audit should encompass the site’s technical aspects, including server responses, meta tags, robots.txt files, and sitemaps. This proactive approach ensures that any indexing problems are detected and addressed promptly, minimizing the risk of lost traffic.
- Utilizing Indexing Tools: Employing tools specifically designed for website indexing analysis can help pinpoint potential problems early. These tools often provide detailed reports on crawling issues, including any directives that might prevent indexing. By proactively identifying these issues, you can take corrective measures before they impact your search ranking.
- Implementing Correct Sitemaps: A well-structured sitemap is crucial for guiding search engine crawlers through your website. It should accurately reflect the hierarchy of your content and ensure that all important pages are accessible. A clear and well-maintained sitemap enhances indexing efficiency, significantly reducing the likelihood of noindex errors.
- Avoiding Errors in Robots.txt: The robots.txt file acts as a guide for search engine crawlers, specifying which pages or directories should be excluded from indexing. Carefully reviewing and testing the robots.txt file is vital. Ensure it accurately reflects your desired indexing strategy to avoid inadvertently blocking crucial content.
- Using Correct HTTP Headers: Proper HTTP headers are critical for conveying instructions to search engines about how to treat each page. Implementing correct headers like `X-Robots-Tag` can explicitly instruct crawlers on whether to index a page or not. Consistent use of these headers minimizes the risk of unintended indexing limitations.
Importance of Regular Website Audits
Website audits are crucial for proactively identifying and addressing potential issues before they significantly affect search engine visibility. A regular audit process helps maintain a healthy and optimized website.Regular audits provide valuable insights into your website’s technical health. They allow you to address indexing problems early, minimizing the potential for noindex errors and ensuring your content is readily available to search engines.
Regular assessments identify areas needing improvement, leading to optimized website performance and search visibility.
Using Tools for Identifying Potential Issues
Tools dedicated to website indexing analysis provide valuable data for preventing “noindex” errors. Utilizing these tools proactively can identify problems before they impact search visibility.These tools offer detailed reports on crawling issues, including directives that might hinder indexing. By identifying these issues early, you can take corrective measures and prevent negative consequences on your website’s ranking. The insights gained from these tools can significantly contribute to optimizing your website’s search performance.
Advanced Considerations: Google On Search Console Noindex Detected Errors
Tackling complex “noindex detected” errors in Google Search Console requires a deeper dive beyond basic troubleshooting. These issues often stem from intricate interactions between your website’s code, third-party integrations, and Google’s crawling mechanisms. Understanding the nuances of these interactions is key to resolving these persistent problems.Resolving complex “noindex” errors necessitates a multifaceted approach, encompassing scrutiny of third-party plugins, caching configurations, dynamic content generation, redirect structures, and the utilization of the Search Console API.
This detailed exploration provides strategies to identify and rectify these often-subtle issues.
Third-Party Plugin/Extension Issues
Third-party plugins and extensions can sometimes inadvertently introduce “noindex” directives. These directives, often unintentional, can prevent search engines from indexing specific pages or entire sections of your website. Careful review of plugin documentation is crucial. Identifying and disabling potentially problematic plugins is a common approach to pinpoint the source of the error.
- Verify plugin compatibility with your website’s theme and other plugins.
- Review plugin settings for any conflicting “noindex” directives.
- Consider disabling plugins temporarily to isolate the cause of the issue.
Caching Mechanism Debugging
Caching mechanisms, while designed to improve website performance, can sometimes interfere with Google’s indexing process. Incorrect caching configurations can lead to outdated or incomplete content being presented to search engine crawlers. Diagnosing caching problems often involves scrutinizing the server-side caching configurations and ensuring proper cache invalidation.
- Check caching headers to ensure proper directives are set for Googlebot.
- Use developer tools to inspect the caching behavior of specific pages.
- Implement robust cache invalidation strategies to ensure fresh content is always available.
Dynamic Content Generation Troubleshooting, Google on search console noindex detected errors
Dynamically generated content, while offering flexibility, can present indexing challenges. Googlebot may not correctly interpret dynamic parameters or fail to render the content as intended. Carefully crafted robots.txt rules and proper use of canonical tags are crucial in such scenarios.
- Use canonical tags to specify the definitive version of dynamic content.
- Ensure that dynamic parameters do not lead to duplicate content issues.
- Employ robots.txt to guide Googlebot to specific sections of dynamic content.
Redirect Management and Indexing Impact
Redirects, while necessary for website maintenance and user experience, can disrupt indexing if not implemented correctly. Temporary redirects, especially when used for long periods, can confuse search engines and lead to errors. Careful implementation of permanent redirects and accurate 301 redirects is essential.
- Use 301 redirects for permanent relocations.
- Avoid unnecessary or prolonged use of temporary redirects.
- Ensure redirects are working as expected using a web browser’s developer tools.
Google Search Console API Automation
The Google Search Console API allows for automated detection and resolution of indexing errors. This automated approach is particularly useful for large websites or those experiencing frequent changes. Implementing scripts to monitor and respond to errors in real time can be extremely effective. This allows for proactive problem-solving.
- Utilize the API to fetch data on indexing issues.
- Develop scripts to automatically address identified errors.
- Implement regular monitoring of your website’s indexing status using the API.
Final Summary
In conclusion, navigating Google Search Console noindex errors requires a multifaceted approach. By understanding the various types of errors, their potential causes, and implementing the troubleshooting techniques Artikeld, you can effectively address these issues and improve your website’s search visibility. Regular website audits, proactive error prevention, and a thorough understanding of proper implementation of noindex directives are key to long-term success.