How to add an seo editor role in wordpress – How to add an editor role in WordPress? This guide dives deep into creating a dedicated role for managing aspects of your website. It’s crucial to have a specific role for tasks, ensuring only authorized personnel can handle sensitive elements. This approach helps maintain website security and streamline workflows, ensuring all -related activities are handled effectively and efficiently.
We’ll cover everything from setting up a custom role to integrating plugins and managing permissions, providing practical examples and troubleshooting tips.
WordPress offers various user roles, each with predefined permissions. However, a custom editor role allows for precise control over -related tasks, isolating them from other administrative functions. This approach is vital for security and workflow optimization. We’ll detail the process of creating this role, configuring plugins, and managing permissions. The outcome will be a dedicated team member empowered to optimize your website’s strategy without unnecessary access to other site elements.
Introduction to WordPress Editor Roles
WordPress, a powerful content management system, allows for granular control over user permissions. This control extends to aspects of a website, enabling administrators to manage different levels of access to optimize content for search engines. Properly assigning roles ensures that only authorized personnel can make changes impacting , maintaining data integrity and preventing unintended errors. This approach also improves workflow efficiency by clearly defining responsibilities.Assigning specific roles to users for managing aspects is crucial for maintaining website integrity and preventing unwanted modifications.
Figuring out how to add an SEO editor role in WordPress can be tricky, but it’s a crucial step for optimizing your site. Understanding the importance of online visibility is key, and exploring platforms like Google Plus can be incredibly helpful in achieving that. For instance, leveraging the benefits of Google Plus for business the benefits of google plus for business can significantly enhance your online presence.
Once you’ve grasped the nuances of Google Plus, you can return to the task of properly configuring the SEO editor role in WordPress for a more comprehensive approach to online marketing.
-related tasks, such as research, meta-description optimization, and content strategy, can have a significant impact on a website’s search engine rankings. Restricting access to these tasks to designated personnel helps to prevent accidental changes that could negatively affect a website’s visibility in search results. It also helps maintain a clear chain of responsibility for activities.
WordPress User Roles and Default Permissions
WordPress offers various user roles with varying levels of access to website functionalities. These roles are pre-defined and provide a framework for controlling user permissions. Understanding the default permissions of each role is essential for effectively managing responsibilities.
- Administrator: The administrator role possesses full control over all aspects of the website, including . They can modify website settings, create and edit content, manage users, and access all plugins and themes. They are the ultimate decision-makers for strategy and implementation.
- Editor: Editors can create and edit content, manage comments, and customize posts and pages. They have a limited role in , often focused on content creation and optimization according to guidelines set by the administrator.
- Author: Authors can create and edit their own content, manage comments related to their posts, and have limited involvement.
- Contributor: Contributors can create and edit content, but their access is restricted to their own content, with very limited capabilities.
- Subscriber: Subscribers have the most limited access, primarily for reading content.
Comparison of User Roles and Permissions
The table below provides a comparison of different user roles and their corresponding permissions and other functionalities. This breakdown allows for a clear understanding of the access levels granted to each role.
| User Role | Permissions | Other Permissions | Level of Access |
|---|---|---|---|
| Administrator | Full access: research, meta tag editing, content optimization, site-wide settings | Full access to all website functionalities | Highest |
| Editor | Can edit elements on posts and pages (meta descriptions, title tags), manage categories and tags, and implement best practices as instructed | Create and edit content, manage comments, and access the media library | High |
| Author | Limited access to settings, mainly for their own content | Create and edit content, manage comments related to their posts | Medium |
| Contributor | Limited capabilities, restricted to their own content | Create and edit content | Low |
| Subscriber | No permissions | Read content | Lowest |
Integrating Plugins with the Role
Choosing and configuring plugins tailored to your WordPress editor role is crucial for maximizing efficiency and effectiveness. This involves selecting compatible plugins, properly configuring them, and customizing settings to optimize performance for your specific needs. A well-integrated plugin empowers your editors to focus on content quality while ensuring it’s optimized for search engines.Integrating plugins with your custom WordPress editor role isn’t a one-size-fits-all process.
Each plugin will have its own set of features and configuration options. Understanding these nuances and tailoring the plugin settings to the specific needs of the role is key to avoiding conflicts and ensuring smooth operation. This approach also allows for targeted optimization, maximizing the impact of the editor role within your site’s structure.
Selecting Compatible Plugins
Selecting the right plugin is the first step towards effective integration. Consider factors like ease of use, comprehensive features, and compatibility with your WordPress theme and existing plugins. A well-researched selection ensures a seamless integration experience.
Installing and Activating Plugins
The installation process for most WordPress plugins is straightforward. Locate the plugin in the WordPress plugin directory, download and install it, and then activate it. Follow the plugin’s instructions carefully for optimal results. Activating the plugin completes the initial setup phase, paving the way for configuration and customization.
Configuring Plugins for the Editor Role
Plugin configuration is crucial for aligning the editor role with specific tasks. Most plugins offer options for managing content settings and -related features. Understanding the plugin’s settings is essential for optimizing the workflow for the role. Tailoring these settings allows you to fine-tune the plugin’s functionality for the editor’s specific responsibilities.
Adding an SEO editor role in WordPress is a great way to manage content creation and optimization. However, a common pitfall is accidentally creating duplicate content, which can seriously harm your SEO. To avoid this, understanding how to prevent duplicate content is crucial, and the duplicate content issues the complete guide on how to solve will help you identify and fix potential problems.
Once you’ve mastered this, you can confidently assign the SEO editor role, knowing you’re setting your site up for success.
Popular Plugins and Custom Role Compatibility
Many popular plugins are compatible with custom roles, allowing you to assign specific permissions and features to the editor. The level of compatibility can vary, and checking documentation is crucial. Consult the plugin’s documentation for detailed information on how it interacts with different WordPress roles.
- Yoast : Widely regarded as one of the most popular plugins, Yoast typically offers extensive customization options for different roles. Detailed instructions are available within the plugin’s documentation.
- All in One Pack: This plugin offers a range of features and is known for its user-friendly interface. The plugin’s documentation will detail how to adjust permissions for custom roles.
- Rank Math : This plugin provides a comprehensive suite of tools. Its documentation should guide you on how to manage different roles’ access to plugin settings.
Tailoring Plugin Settings for the Editor Role
Tailoring plugin settings to match the editor role’s responsibilities is vital. Restricting access to certain features and permissions, like bulk editing or site-wide settings, can prevent accidental changes or misuse. This prevents any unwanted alterations to critical site elements. This meticulous configuration ensures that the editor role is performing its intended function without impacting the site’s functionality.
Managing Editor Permissions
Fine-tuning the editor role in WordPress involves careful management of permissions to ensure they align with the editor’s responsibilities and prevent unintended actions. This section details how to modify the role’s permissions, granting or revoking specific access levels, and maintaining oversight of their activities.Precise control over the editor’s capabilities is crucial for maintaining site security and integrity.
This control ensures that the editor’s actions are confined to their designated tasks, preventing potential damage or misuse of administrative privileges.
Modifying the Editor Role
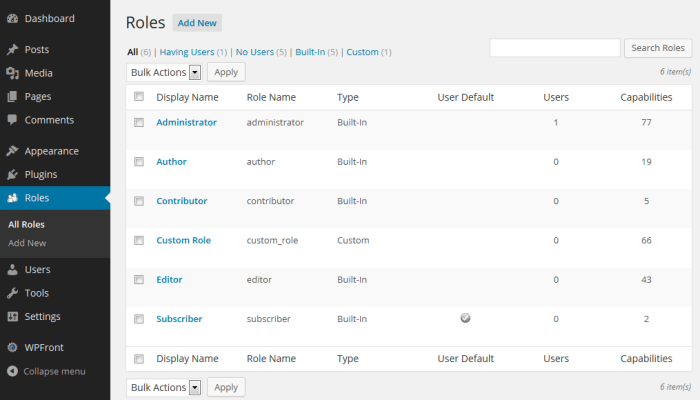
WordPress’s user role management system allows for granular control over what tasks an editor can perform. To modify the editor role, navigate to the Users > Roles screen in your WordPress dashboard. Here, you can customize the permissions for the editor role. Look for the ” Editor” role, and edit the permissions as needed. This involves checking or unchecking the boxes corresponding to different actions.
Granting Specific Permissions
Granting specific permissions to the editor role is critical for effective management. This enables a focused approach, allowing the editor to execute tasks without unnecessary access to other functionalities. Examples include granting permission to edit specific post types or pages, allowing access to specific menus, or restricting their access to sensitive administrative areas.
Revoking Permissions
Revoking permissions from the editor role is equally important. This protects the site from unauthorized actions. If an editor needs access revoked for any reason, administrators can selectively remove permissions to specific areas, thus maintaining a secure and controlled environment.
Monitoring and Auditing Editor Activities
Monitoring and auditing editor activities is essential for maintaining a secure and transparent WordPress environment. Tools and plugins can provide detailed logs of actions taken by the editor. These logs track edits, page views, and other actions, allowing for a review of their activities. This helps identify potential issues or unusual patterns. By analyzing these logs, administrators can promptly address any concerns and maintain site security.
Example Scenario: Restricting Access to Theme Customization
To restrict access to theme customization for the editor, locate the “Theme Options” permission in the user role management panel. Unchecking this option will prevent the editor from accessing or modifying theme settings. This is a straightforward way to limit the editor’s ability to affect the site’s visual appearance.
Security Considerations for Editor Roles

Assigning editor roles in WordPress opens up potential security vulnerabilities if not handled carefully. Compromised editor accounts can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive website data, configuration changes, and even complete site takeover. Therefore, robust security measures are crucial for safeguarding your WordPress site.Careful consideration of security protocols is paramount when implementing editor roles. This involves more than just assigning permissions; it necessitates a proactive approach to protecting sensitive data and configurations, as well as educating editors on best practices.
Protecting Sensitive Data and Configurations
Restricting access to sensitive files and directories is critical. WordPress core files and themes, plugins, and database credentials should be shielded from unauthorized access. This can be achieved through the use of appropriate file permissions and directory restrictions. Using the WordPress file system to protect sensitive files is a best practice. It’s essential to understand that the WordPress file system’s permissions directly impact the security of your site.
Importance of Strong Passwords and Access Controls
Strong passwords are the first line of defense against unauthorized access. Enforce a password policy that mandates a minimum length, complexity (including numbers and symbols), and regular password changes. Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) as an additional layer of security for added protection. The use of strong passwords and access controls prevents unauthorized individuals from gaining access to sensitive information and configurations.
Using a password manager can significantly enhance the strength and management of passwords.
Implementing Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security to account logins. When a user attempts to log in, they’ll need to verify their identity through a secondary method, like a text message or authenticator app. This makes it significantly harder for attackers to gain access, even if they have a compromised password. Implementing 2FA for all users, including editors, is a fundamental step in enhancing security.
Practical Examples of Editor Roles
Defining specific editor roles within a WordPress website is crucial for efficient workflow and accountability. These roles ensure that tasks are handled effectively and responsibilities are clearly Artikeld, which is vital for any team, especially as it grows. This approach streamlines content creation and optimization processes, ultimately enhancing the website’s search engine visibility.Different types of websites require tailored editor roles.
A blog will need a different structure than an e-commerce site, for example. Adapting the roles to match the unique needs of the business and its workflow is essential for success.
E-commerce Website Editor Roles
A well-structured editor role system for an e-commerce website should reflect the varied nature of tasks involved. Different levels of editors can manage specific aspects of the site’s , from product page optimization to overall site architecture.
- Product Page Optimizer: This editor focuses on optimizing individual product pages. Their responsibilities include research, meta description writing, image alt tag optimization, and ensuring product descriptions are compelling and -rich. This role is critical for boosting product visibility in search results and driving targeted traffic to specific products.
- Category Manager: This editor manages the of product categories. Their duties include research for category pages, ensuring accurate category descriptions, and optimizing meta tags to improve visibility for broader product sets. This position is crucial for overall category performance and search engine understanding of the website’s product offerings.
- Site Structure Specialist: This role focuses on the broader site structure, ensuring proper internal linking and navigation. They work on optimizing site architecture to facilitate better search engine crawling and indexing. This is key for enhancing overall site visibility and user experience.
Blog Website Editor Roles
For a blog, the roles often revolve around content creation and optimization.
Figuring out how to add an SEO editor role in WordPress can be tricky, but it’s a crucial step for managing content effectively. Once you’ve got that sorted, consider integrating push notifications to boost engagement on your site. Push notifications to boost engagement are a fantastic way to keep visitors coming back for more, and that, in turn, helps your SEO efforts.
Ultimately, mastering WordPress roles is key to optimizing your site for success.
- Content Strategist: This editor researches s, identifies content gaps, and plans blog posts that address audience needs. They also create editorial calendars and ensure content consistency. This position ensures the blog remains focused on relevant topics and attracts targeted readers.
- Writer: This role is focused on writing blog posts that are both engaging and optimized for search engines. They incorporate s naturally, write compelling meta descriptions, and optimize images and headings. This role is key to producing high-quality content that ranks well in search results.
- Link Builder: This editor focuses on acquiring backlinks from reputable websites. Their responsibilities include outreach to relevant websites, guest blogging, and building relationships with influencers to enhance the blog’s authority and visibility in search results.
Scaling Editor Roles
As a team grows, editor roles can be scaled to accommodate additional responsibilities and expertise. For example, a junior editor might focus on basic research and meta descriptions, while a senior editor takes on more complex tasks like site audits and content strategy. This tiered approach ensures that responsibilities are appropriately distributed, fostering team growth and efficiency.
Clear definitions of roles, responsibilities, and reporting structures are crucial for managing the expanded team effectively.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Adding an editor role in WordPress can sometimes present challenges. Understanding potential pitfalls and how to resolve them is crucial for smooth implementation and effective management. This section details common problems and their solutions, ensuring a robust and functional editor role.Troubleshooting involves methodical steps and a clear understanding of WordPress’s structure, plugin interactions, and user permissions.
Identifying the source of the problem is often the first step toward a resolution. Careful examination of error messages, plugin logs, and user permissions can pinpoint the cause of any issues.
Identifying Plugin Conflicts
Plugin conflicts are a frequent cause of issues with custom roles, especially when integrating plugins. Different plugins may have conflicting functionalities or incompatible code. This can lead to unexpected behavior, including the editor role not functioning as expected.
- Carefully review the plugin compatibility documentation. Most reputable plugins provide details on compatibility with other plugins and WordPress versions.
- Deactivate plugins one by one to isolate the conflicting plugin. This methodical approach allows you to determine which plugin is causing the problem.
- Check plugin update logs for any error messages that might indicate incompatibility issues. Plugins often include logs that detail any errors encountered during operation.
- If the conflict persists, contact the plugin developer for support or investigate the plugin code for potential conflicts.
Managing Permissions Issues
Incorrect permissions for the editor role can lead to various problems. The editor might lack the necessary access to crucial functionalities or have excessive permissions, potentially compromising security.
- Double-check the permissions assigned to the editor role. Ensure that the role has the necessary capabilities to perform tasks, such as editing content metadata, managing s, and using plugins.
- Review the documentation for the plugins you are using. This documentation often Artikels the specific permissions required for the plugin to function correctly.
- Use the WordPress user management panel to meticulously adjust the editor role permissions. This allows precise control over the editor’s capabilities.
- If the permissions are set correctly but the issue persists, consider checking for other roles or users with conflicting permissions that might be interfering with the editor’s operations.
Debugging with the WordPress Debug Log, How to add an seo editor role in wordpress
Activating the WordPress debug log can provide valuable insights into errors or issues. The debug log records information about plugin interactions, user actions, and other relevant events, helping to pinpoint the root cause of problems.
- Enable the WordPress debug log in your `wp-config.php` file. This involves adding a specific line of code to the file.
- Observe the debug log for any error messages or warnings related to the editor role or the plugins. This step helps you understand what went wrong and why.
- Check the error messages carefully for clues about the nature of the issue. Many error messages provide specific details about the problem, including file paths and plugin names.
- Thoroughly examine the debug log entries to identify the point of failure. A comprehensive understanding of the log can guide you toward the appropriate solution.
Custom Role Conflicts
Custom roles, when improperly implemented, can lead to conflicts with plugins or other WordPress functionalities. Ensure the custom roles are designed and configured to avoid conflicts with existing roles and plugins.
- Carefully review the custom role’s capabilities. Verify that the custom role has the appropriate permissions for interacting with the plugins and that it doesn’t conflict with existing roles.
- Test the custom role with a non-critical website or environment before deploying it to a production site. Testing the custom role in a staging or development environment ensures the role’s functionality and compatibility with other components.
- Examine the codebase of the custom role for potential conflicts. Ensure there are no errors or inconsistencies in the code that could interfere with the plugins.
- Consider using the WordPress role management tools for troubleshooting. These tools allow you to check for potential conflicts between roles and other WordPress elements.
Conclusive Thoughts: How To Add An Seo Editor Role In WordPress
In conclusion, creating a dedicated editor role in WordPress is a strategic move for better website management. It empowers authorized personnel to handle tasks effectively while safeguarding your website’s security. We’ve covered the entire process, from role creation to plugin integration and security considerations. By following these steps, you’ll be well-equipped to enhance your website’s performance and streamline your workflow.
Remember to tailor the role to your specific needs and regularly review permissions to maintain optimal security and efficiency.