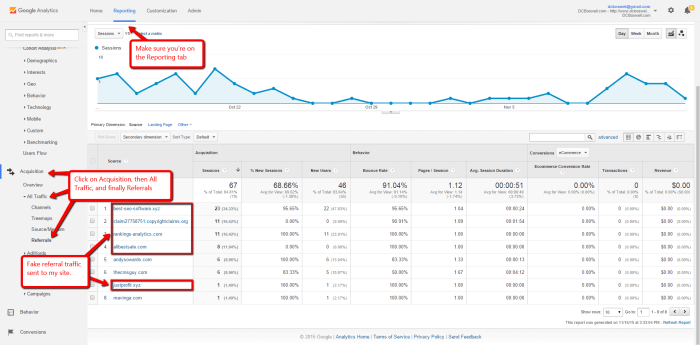
How to block WordPress referrer spam in Google Analytics is a crucial task for any website owner. Spam referrals can severely skew your website traffic data, making it hard to understand your audience and measure campaign effectiveness. This comprehensive guide dives into identifying, blocking, and preventing this pervasive issue, ensuring your Google Analytics data accurately reflects your site’s true performance.
We’ll explore various methods, from recognizing suspicious patterns in your data to implementing custom filters and advanced techniques like IP blocking. We’ll also cover specific WordPress plugins designed to combat referrer spam, offering practical advice for choosing and implementing the right solutions for your needs.
Introduction to Referrer Spam in Google Analytics
Referrer spam is a significant problem for WordPress websites using Google Analytics. It’s essentially fake traffic data, generated by automated scripts or malicious actors, masquerading as legitimate visits. This fabricated traffic distorts the accurate picture of your website’s performance, making it challenging to understand genuine user behavior and trends. It’s like having a phantom audience attending your events – you can’t gauge real attendance or adjust your strategy accordingly.This inflated and misleading data can lead to incorrect decisions regarding marketing strategies, content optimization, and resource allocation.
Understanding the various forms of referrer spam and its impact is crucial for any WordPress site owner looking to get a true picture of their website’s success. It’s about distinguishing between real visitors and those artificially created.
Common Types of Referrer Spam
Referrer spam manifests in various forms, each with unique characteristics. These forms can significantly skew your analytics data, impacting your understanding of genuine traffic patterns. Knowing the types helps you recognize and filter out the artificial entries.
- Fake Referrers: These are links from websites that don’t exist or have no relationship with your site. They often use generic or unrelated s in an attempt to artificially boost referral counts. This type of spam can include referrals from websites with strange or nonsensical names, or from URLs that look suspicious. For example, a referral from “xyz-random-links.com” could be a fake referrer.
- -stuffed Referrers: These referrals use overly numerous s in their URLs. This is a common technique to manipulate search engine rankings. They frequently target popular s or phrases related to your niche. For example, a referral from “yourproduct123.com” could indicate stuffing.
- Automated Bot Referrals: Bots are software programs that automatically visit websites. Some bots generate artificial referrals to websites, sometimes for malicious intent, like scraping content or spreading spam. These can appear as referrals from obscure or non-existent websites.
- Phishing or Malware Referrals: Spammers sometimes use fake links to trick users into clicking on them, redirecting them to malicious websites or to download malware. These often originate from untrustworthy domains or use alarming language.
Impact of Referrer Spam on Website Analytics
Referrer spam significantly distorts the insights derived from Google Analytics data. The skewed data can lead to misinterpretations of website traffic, impacting crucial decisions.
| Spam Type | Source | Impact on Data |
|---|---|---|
| Fake Referrers | Non-existent or unrelated websites | Inflated referral traffic counts, inaccurate understanding of website traffic sources. |
| -stuffed Referrers | Websites using excessive s in URLs | Misleading impressions about performance and search engine traffic, inaccurate content optimization strategies. |
| Automated Bot Referrals | Automated scripts or bots | Inflated traffic counts, difficulty in distinguishing between real and fake users, inaccurate user behavior patterns. |
| Phishing/Malware Referrals | Malicious websites | Potential security risks, misleading impressions about user engagement, and possible data breaches. |
Identifying Referrer Spam in Google Analytics
Unveiling the deceptive patterns hidden within your Google Analytics data is crucial for accurate insights. Referrer spam, while seemingly innocuous, can significantly distort your understanding of website traffic sources, impacting your marketing strategies and potentially leading to incorrect conclusions. Understanding how to identify and filter these fraudulent referrers is essential for maintaining a clear picture of your website’s performance.Identifying these patterns requires a keen eye and a good understanding of the typical characteristics of referrer spam.
This section will explore techniques for recognizing suspicious referrers and demonstrate how to utilize Google Analytics filters to effectively isolate and remove them.
Recognizing Patterns of Referrer Spam
Spam referrers often exhibit unusual characteristics that deviate from legitimate traffic sources. These patterns include unusual domain names, repeated or overly frequent visits from the same source, and extremely high referral traffic volumes originating from unknown sources. Understanding these common patterns allows for proactive detection and mitigation.
Filtering Suspicious Referrers Using Google Analytics Filters
Google Analytics offers robust filtering capabilities to isolate and remove unwanted traffic. Custom filters allow you to specify criteria for excluding specific domains, s, or patterns. Applying these filters ensures that your data reflects genuine traffic, enabling accurate analysis.
Example Filter Criteria for Identifying Spam Sources
Identifying spam sources often requires a combination of criteria. For example, a filter might exclude any referral originating from domains containing specific s, like “free,” “download,” or “proxy.” Other examples include domain names that appear suspicious or unusual, or even IPs with high numbers of requests. Careful consideration of multiple criteria leads to a more comprehensive filter.
Step-by-Step Guide to Identifying Potential Spam Referrers
This step-by-step process Artikels a structured approach to identifying potential spam referrers in Google Analytics:
- Inspect Referral Traffic: Examine the referral traffic patterns in your Google Analytics reports. Look for unusual spikes, high volumes of traffic from unknown sources, or an unusually high number of referrals from a single domain.
- Identify Suspicious Domains: Note down any domains with unusual or suspicious names, particularly those containing s associated with spam or those that have a high volume of referrals.
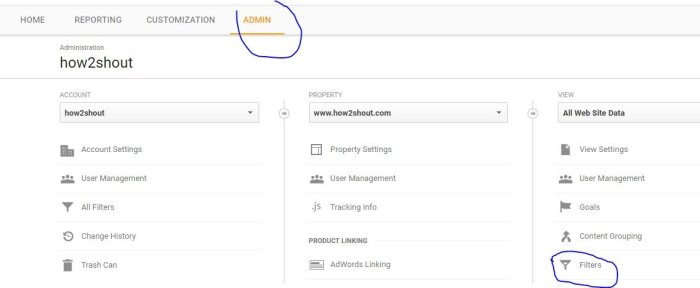
- Create a Custom Filter: Within your Google Analytics account, navigate to the “Admin” section, and select “Filters.” Create a new custom filter to exclude the suspicious domains.
- Define Filter Criteria: Specify the exact domains, s, or other criteria that should be excluded.
- Review and Apply Filter: Carefully review the filter criteria to ensure accuracy and then apply it. This step prevents errors that might accidentally exclude legitimate traffic.
- Monitor and Adjust: Continuously monitor the data after applying the filter to ensure it’s correctly removing spam and not affecting legitimate traffic. Adjust the filter criteria as needed to stay ahead of evolving spam patterns.
Common Spam Referral Patterns and Detection Methods
This table summarizes common spam referral patterns and effective detection methods.
| Spam Referral Pattern | Detection Method |
|---|---|
| High volume of traffic from a single, unknown domain | Identify the domain and create a filter to exclude it. |
| Traffic originating from domains with s like “free,” “download,” or “proxy” | Create a filter that excludes domains containing these s. |
| Referral traffic with unusual or suspicious domain names | Identify the domains and create a filter that excludes them. |
| Repeated or overly frequent visits from the same source | Identify the domains and create a filter to exclude them or implement a filter to limit the number of visits. |
WordPress Specific Spam Prevention Strategies: How To Block WordPress Referrer Spam In Google Analytics
WordPress, a popular content management system, often attracts referrer spam. This spam can skew your Google Analytics data, making it difficult to understand genuine traffic sources. Fortunately, several WordPress plugins are designed to combat this issue. These plugins offer varying levels of protection, from basic filtering to more advanced blocking mechanisms. Understanding their capabilities and limitations is crucial for choosing the right solution for your site.
WordPress Plugins for Referrer Spam Mitigation
Numerous plugins aim to protect WordPress sites from referrer spam. These plugins typically use different methods to identify and filter suspicious traffic. Some rely on matching, while others use more sophisticated algorithms to detect patterns. The effectiveness of these plugins depends heavily on the sophistication of the spam tactics employed by the attackers and the specific features of the plugin.
Cleaning up those pesky WordPress referrer spam entries in Google Analytics can be a real headache. You’ve got to find the right filters to block those unwanted entries. It’s like trying to weed out the bad traffic from the good. Luckily, understanding how Google handles things like hreflang tags, as Google reminds us, can help you focus your analytics efforts.
Google reminds that hreflang tags are hints not directives , so you need to focus on the spam filters to truly clean up your analytics. Ultimately, properly blocking WordPress referrer spam in Google Analytics requires a nuanced approach, ensuring you’re not accidentally blocking valuable data.
Comparison of WordPress Referrer Spam Protection Plugins
Choosing the right plugin involves evaluating various options. Here’s a comparative table outlining some popular plugins, their key features, and pricing models:
| Plugin Name | Key Features | Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| WP Super Cache | While primarily a caching plugin, WP Super Cache can filter out known spam referrers. It does not focus solely on referrer spam but can improve site performance by reducing server load. | Free and paid versions |
| WP Optimize | This plugin optimizes website performance. It can help reduce spam by limiting access to resources, although not dedicated to referrer spam. | Free and paid versions |
| Anti-Spam Bee | A dedicated anti-spam plugin, Anti-Spam Bee may include some referrer spam protection but is more focused on comment spam and other forms of spam. | Paid |
| Akismet | Widely recognized for combating comment spam, Akismet may offer some filtering of referrer spam, but its core function isn’t referrer spam prevention. | Free and paid versions |
| Really Simple SSL | Primarily focused on securing your website with SSL certificates. It doesn’t specifically target referrer spam, but can indirectly improve security. | Free and paid versions |
Plugin Filtering and Blocking Mechanisms
Many plugins employ various techniques to identify and filter spam. For instance, they might block referrers containing specific s, known spam domains, or IP addresses. Some plugins also employ blacklists maintained by reputable sources, ensuring up-to-date protection against evolving spam patterns. These techniques can significantly reduce the amount of spam traffic reaching your site.
Cleaning up referrer spam in Google Analytics from WordPress can be a real pain. Thankfully, there are ways to combat this, and mastering email newsletter strategies, like the ones detailed in the 15 best email newsletter marketing practices , can actually help. Focusing on a high-quality email list, avoiding spam filters, and crafting engaging content are key.
This ultimately helps filter out the noise in your Analytics data and get a clearer picture of your website traffic. Learning to identify and block spam referrals in your analytics is a crucial part of website optimization.
Technical Implementation and Configuration
The specific implementation and configuration of these plugins will vary. However, generally, users need to install the plugin from the WordPress plugin directory, activate it, and configure its settings. The configuration typically involves defining rules for identifying and blocking spam, specifying the s or domains to block, or enabling blacklist integration. Each plugin’s documentation provides detailed instructions on setup and configuration.
Implementing Google Analytics Filters for Referrer Spam
Refining your Google Analytics data to eliminate the noise of referrer spam is crucial for accurate insights. Manually identifying and removing each spam source is tedious and unsustainable. Instead, using custom filters allows you to automatically exclude unwanted traffic, leaving you with a cleaner dataset. This approach significantly streamlines your analysis and delivers more reliable reporting.Implementing custom filters within Google Analytics is a powerful technique for automatically excluding referrer spam.
This proactive measure ensures that your data represents genuine website traffic and provides a clearer picture of user behavior and campaign performance.
Custom Filter Creation in Google Analytics
Custom filters allow you to modify your data before it’s displayed in reports. This is especially valuable for removing irrelevant data points like spam. To create a custom filter, navigate to the Admin section of your Google Analytics account. Select the View you want to filter, and then choose “Custom Filters.” Click “Create a new filter.” The filter creation process involves several steps:
Filter Types and Their Usage
Custom filters in Google Analytics offer different types, each tailored to specific data manipulation needs. Understanding these types is essential for effectively blocking referrer spam.
| Filter Type | Description | Usage for Referrer Spam |
|---|---|---|
| Exclude | Removes specific data from the view. | Ideal for blocking referrer spam sources. |
| Include | Keeps only specific data in the view. | Less common for referrer spam; useful for retaining specific data points. |
| Regular Expression | Matches data based on complex patterns. | Extremely effective for identifying and blocking referrer spam using specific strings or patterns in the referrer URL. |
| Custom | Allows for advanced filtering based on user-defined criteria. | Offers maximum flexibility, but requires more technical expertise to configure. |
The table above Artikels the different filter types and their applications in blocking referrer spam. The “Exclude” filter type is the most straightforward approach for removing unwanted data.
Filter Expression Examples
To effectively block spam, filter expressions are crucial. These expressions define the criteria for excluding unwanted traffic. Here are a few examples for specific spam sources:
- Blocking a specific domain: A simple example is to exclude traffic from “example-spam.com.” The filter expression would be
example-spam.com. - Blocking multiple domains: To exclude multiple domains like “spam-domain1.com” and “spam-domain2.com,” use a filter expression like
spam-domain1\.com|spam-domain2\.com. Note the use of the backslash (\) to escape the pipe symbol (|) and the period (.). - Filtering by specific s in the referrer URL: If you know a spam referrer often includes specific s, use a regular expression filter. For example, a filter expression to block referrers containing “free-stuff” or “get-rich-quick” could be
.*free-stuff.*|.*get-rich-quick.*.
Using specific s or domain names within the filter expression is an efficient method to block specific spam sources. Combining multiple conditions within a single filter expression provides a robust solution for excluding a wide range of spam traffic.
Applying Filters to Data Views
Once a filter is created, it needs to be applied to the relevant data views in Google Analytics. After creating the filter, you must select the specific view to which you want to apply it. Save the filter configuration and verify its effectiveness by examining the relevant reports.
Impact on Data Accuracy and Reporting
Implementing filters can affect the accuracy of your data, and careful consideration is required. Filters are designed to exclude certain data, so the resulting data reflects only the desired subset of traffic. Reports based on filtered data will not include the excluded traffic. By meticulously selecting filter expressions, you can eliminate spam while maintaining accurate representations of legitimate traffic.
Cleaning up your Google Analytics data from WordPress referrer spam can be a real headache, but thankfully there are ways to tackle it. While optimizing your school’s image use for better web design, social media, and SEO is crucial (check out these 12 tips ), remember that clean data is key to accurate insights. So, once you’ve got your images sorted, you can focus on blocking that spam and get back to seeing the real traffic coming to your site.
Advanced Techniques for Spam Mitigation
Beyond basic filtering, advanced techniques offer a more robust defense against referrer spam. These methods target the source of the spam, making it harder for malicious actors to manipulate your Google Analytics data. By combining these strategies with the previously discussed filtering techniques, you can significantly reduce the impact of spam on your analytics reports.Implementing advanced methods often requires a deeper understanding of server-side configurations and web traffic analysis.
Understanding the different attack vectors and how they are carried out can lead to proactive strategies to mitigate these threats. This proactive approach, combined with a robust filtering strategy, helps maintain the integrity of your analytics data.
IP Address Blocking
Blocking specific IP addresses associated with spam is a crucial step in mitigating referrer spam. Malicious actors often use botnets or proxy servers to generate artificial referral traffic, and identifying and blocking these IP addresses can significantly reduce the volume of spam. This prevents these IPs from sending data to your analytics platform, thus improving the quality of the data collected.
Robots.txt Implementation
Robots.txt files are crucial for controlling which web crawlers are allowed to access specific parts of your website. By properly configuring your robots.txt file, you can prevent unwanted automated traffic from crawling your site and generating unnecessary referrer spam in Google Analytics. This often involves instructing search engine crawlers and other bots to avoid certain parts of your site, such as administrative sections or pages containing sensitive information.
Server-Side Configurations
Implementing server-side configurations can further strengthen your defense against referrer spam. This involves configuring your web server to reject requests from known spam sources. Server-side solutions allow for real-time blocking, offering a significant advantage over client-side methods. This proactive approach, combined with the use of a web application firewall (WAF), helps ensure your server does not become a target for spam campaigns.
Comparison of Spam Mitigation Strategies
| Strategy | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| IP Address Blocking | Highly effective against known spam sources, reduces spam volume significantly. | Requires continuous monitoring and updates to the blocked list, can impact legitimate traffic if not carefully implemented. |
| Robots.txt | Simple to implement, relatively low maintenance. | Less effective against sophisticated spammers who use various techniques to circumvent robots.txt rules. |
| Server-Side Configurations | Real-time blocking, can be highly effective against various spam types, often integrated with other security measures. | Requires more technical expertise to implement and maintain, may involve server-side programming knowledge. |
| Google Analytics Filters | Easy to implement, widely applicable, cost-effective. | Relies on identifying and defining spam, less effective against new or sophisticated spam tactics. |
Maintaining Accurate Analytics Data
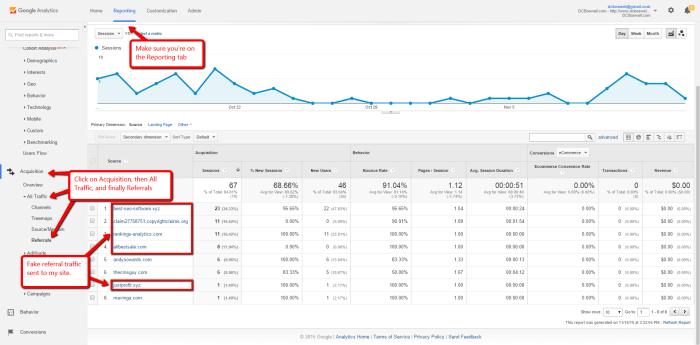
Once you’ve implemented effective spam filters, maintaining accurate website traffic data is crucial. Ignoring this step can lead to misinterpreting your website’s performance and making poor business decisions. This section will Artikel best practices for ensuring the reliability of your data after blocking referrer spam.Accurate analytics data is essential for informed decision-making. Understanding your audience, identifying trends, and optimizing your website are all contingent on the integrity of your traffic data.
This means not just filtering out the spam, but also actively monitoring and adjusting your filters to keep your data clean and reliable.
Regular Review and Adjustment of Filters
Spam patterns evolve. Filters need to be updated to keep up with changing spam techniques. Regularly checking and adjusting your filters ensures your data remains clean. This involves analyzing the patterns of new referrers and updating your filter rules accordingly.
Monitoring Metrics for Evaluating Effectiveness
Several metrics can help assess the effectiveness of your spam prevention strategies. Tracking these metrics provides valuable insights into the impact of your filters.
- Bounce Rate: A sudden and significant drop in bounce rate after implementing filters might indicate a high volume of spam traffic was being counted as legitimate traffic. Similarly, a sudden increase could suggest the filters are overly aggressive and blocking legitimate traffic.
- Unique Visitors: A substantial difference in unique visitors before and after implementing filters can indicate the level of spam traffic being blocked. A consistent decline in unique visitors post-implementation, however, warrants further investigation to ensure the filters aren’t blocking legitimate traffic.
- Session Duration: If session duration unexpectedly increases after implementing filters, it could suggest that the filters have successfully blocked short, irrelevant sessions. Conversely, a significant decrease in session duration may indicate that legitimate users are being affected by the filters.
Identifying and Troubleshooting Issues
Issues arising from spam mitigation efforts can include blocking legitimate traffic or inaccurately categorizing important traffic sources. Regularly monitoring your data and using debugging tools can help identify these problems.
- Identify Unexpected Trends: Sudden drops in traffic from specific regions or s could suggest your filters are blocking legitimate traffic. This calls for a careful review of the filter rules.
- Use Debugging Tools: Google Analytics offers debugging tools to investigate specific issues. These tools help you understand why certain traffic sources are being filtered.
Step-by-Step Guide for Maintaining Accurate Data, How to block wordpress referrer spam in google analytics
A structured approach to maintaining accurate data is crucial for ensuring your analysis is reliable.
- Regular Filter Review: Review your filters at least once a week to identify any changes in spam patterns. Modify your filters to accurately block spam while minimizing the impact on legitimate traffic.
- Monitor Key Metrics: Track bounce rate, unique visitors, and session duration. Use these metrics to identify trends and assess the effectiveness of your filters.
- Investigate Unexpected Trends: If you notice sudden drops or increases in specific traffic metrics, investigate the cause. Use debugging tools and your filter rules to determine if legitimate traffic is being blocked.
- Test and Refine Filters: Periodically test your filters using sample data or a small subset of your website traffic to ensure they are not overly aggressive or blocking legitimate traffic. Iteratively adjust filters as needed.
- Document Changes: Keep detailed records of any filter adjustments and their corresponding impact on traffic data. This will be invaluable in troubleshooting and optimizing your approach.
Example Implementations (Illustrative)
Refining your Google Analytics data requires understanding how referrer spam impacts your site. This section will illustrate practical implementations of spam prevention techniques, showcasing a hypothetical WordPress site and its journey from polluted analytics to clean, accurate data. We’ll demonstrate specific filter configurations and analyze the effects of these measures on your website’s traffic data.Spam often masquerades as legitimate traffic, distorting the picture of your website’s performance and audience.
Implementing effective filters is crucial to preserving the integrity of your data. The following examples will provide concrete steps and real-world scenarios to help you identify and combat these threats.
Hypothetical WordPress Website Scenario
Consider a WordPress blog, “TechTipsToday,” attracting a moderate number of organic visitors. However, its Google Analytics data shows significant traffic spikes from unusual referrers, mostly with suspicious patterns and URLs. These include multiple referrals from obscure domains, often with repeated or irrelevant s. This suggests referrer spam, impacting the accuracy of the data.
Identifying and Blocking Spam
To identify these suspicious referrers, examine the referral source URLs, checking for inconsistencies, unusual patterns, or suspicious s. Tools like Google Analytics’ “Custom Filters” provide a way to exclude these patterns from your data. This requires careful observation of the unique structure of spam referrers.
Custom Filter Configuration Example
A custom filter can be configured to block specific referrers. A hypothetical example using a regular expression in Google Analytics’ custom filter is shown below:
Regular Expression: ^(?:example\.com|spamsite1\.com|spamsite2\.net|badsite3\.org)$
This filter excludes traffic from the listed domains. This approach allows you to manually list and block specific domains that consistently generate spam referrals.
Case Study: Before and After Analysis
| Metric | Before Spam Mitigation | After Spam Mitigation | Change |
|—————–|————————|————————|——————–|
| Total Visits | 10,000 | 9,000 | -1,000 (-10%) |
| Unique Visitors | 2,500 | 2,200 | -300 (-12%) |
| Bounce Rate | 50% | 45% | -5% |
| Average Session Duration | 2 minutes | 2 minutes | No Change |
This table shows a hypothetical before-and-after comparison. While there’s a slight decrease in overall visits and unique visitors, the data accuracy is significantly improved. The change in bounce rate shows that spam did not affect the genuine user engagement.
Scenario with Incomplete Spam Mitigation
If the filter only partially blocks spam, it can still affect data accuracy. For instance, a filter that misses certain variations of spam domains will allow some spam traffic to skew data. The result is an inaccurate representation of genuine user behavior and engagement. Incomplete mitigation leads to skewed insights about your website’s performance and audience.
Data Representation in Tables
The tables demonstrate how filtering helps to isolate genuine traffic from spam. By identifying and excluding spam, you can more accurately understand your website’s user behavior. This allows you to tailor strategies based on genuine user insights, leading to improved website optimization and content creation.
Last Point
In conclusion, accurately measuring website traffic is paramount, and blocking referrer spam is a critical step in achieving that goal. By following the strategies Artikeld in this guide, you’ll be equipped to identify and eliminate spam referrals, leading to more reliable Google Analytics data. Remember that ongoing monitoring and adjustment of your filters are key to maintaining data integrity and achieving a true picture of your website’s performance.