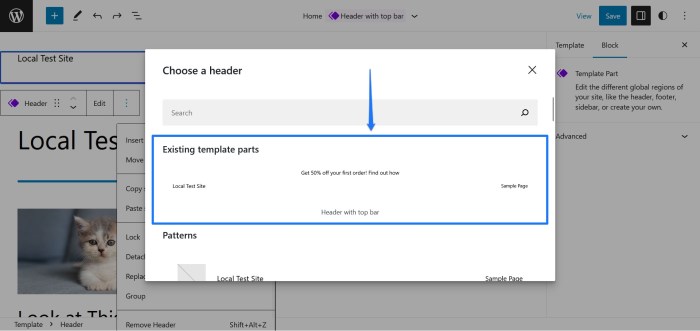
How to convert a WordPress widget into a block? This guide dives deep into transforming your trusty widgets into modern, block-based elements within your WordPress website. We’ll explore the differences between widgets and blocks, dissect the conversion process, and cover advanced techniques for complex widgets. From simple text widgets to custom creations, this comprehensive tutorial will empower you to seamlessly integrate and optimize your website’s design.
WordPress widgets have been a staple for years, but blocks are the future. This guide provides a structured approach to migrating existing widgets to the block system, ensuring your site’s functionality remains intact throughout the transition. We’ll detail the process step-by-step, offering actionable strategies for maintaining your widget’s core features and user experience.
Introduction to WordPress Widgets and Blocks
WordPress widgets and blocks are essential components for customizing the layout and functionality of websites built on the platform. They allow users to add various features and elements without needing extensive coding knowledge. Understanding their distinct characteristics and functionalities is crucial for effective website design.Widgets and blocks, while both serving the purpose of adding elements, differ significantly in their approach to content organization and integration.
Widgets are typically positioned within predefined areas on a theme, while blocks offer a more flexible and dynamic approach to content structuring. This difference in design philosophy directly impacts how you approach website development and content management.
WordPress Widgets
Widgets are pre-defined modules that can be added to specific areas of a WordPress theme. Think of them as pre-built components with specific functionalities. They’re ideal for displaying information like recent posts, social media feeds, or contact forms. WordPress themes typically offer a variety of widget areas (sidebar, footer, etc.). Placement and arrangement are dictated by the theme’s design.
Ever wanted to upgrade your WordPress site’s layout? Converting a widget into a block is a great first step, especially if you’re looking to build a unique homepage. Learning how to create a custom homepage in WordPress can be a game-changer, allowing you to tailor your site’s design to match your brand perfectly. how to create a custom home page in wordpress This often involves restructuring existing widgets into blocks for better control and flexibility.
So, while working on that custom homepage, remember the core skill of converting widgets to blocks for ultimate design control.
WordPress Blocks
Blocks represent a more modern and flexible approach to website content creation. They allow for a more granular and dynamic control over content organization. Unlike widgets, blocks are not tied to specific locations within a theme. Instead, they can be arranged freely within a post or page. This provides a more dynamic and customizable content experience.
This flexibility is a major advantage, especially in today’s complex website designs.
Widget vs. Block Advantages and Disadvantages
- Widgets offer a straightforward approach to adding pre-built functionalities to your website. They are generally easy to implement and manage, especially for basic website elements. However, they often lack the flexibility to adapt to unique design requirements.
- Blocks, on the other hand, offer unparalleled flexibility and customization. You can precisely control how each block is presented and integrated with other elements. However, this granular control can lead to a more complex implementation process, especially for users unfamiliar with the block editor.
Common Use Cases
- Widgets are frequently used for displaying sidebars, footers, and other areas with static content. Examples include author bios, recent posts, or archives. These are excellent for maintaining a consistent design and providing essential information on a website.
- Blocks are useful for creating diverse layouts and interactive elements, such as galleries, forms, or even custom content sections. They enable the development of unique and complex designs that are not easily achievable with widgets.
Widget vs. Block Comparison
| Feature | Widget | Block |
|---|---|---|
| Placement | Predefined areas (sidebar, footer) | Flexible placement within content |
| Customization | Limited customization options | High degree of customization |
| Flexibility | Less flexible | Highly flexible |
| Integration | Integration with existing theme | Integration with other blocks |
Understanding the Conversion Process
Transforming WordPress widgets into blocks is a crucial step in modernizing your website’s functionality and design. This process, while often straightforward, requires careful consideration to ensure the integrity and usability of the converted elements. Understanding the steps involved and potential challenges is key to a successful conversion.The conversion process involves more than simply changing the display method. It necessitates a deep understanding of the widget’s internal workings and a commitment to preserving its original functionality.
This is where careful planning and attention to detail become paramount.
Conversion Steps
The conversion process generally involves several key steps, each requiring careful consideration to ensure a smooth transition. These steps will vary slightly depending on the specific widget, but a common framework applies. First, analyze the widget’s code and functionality. This step is critical in determining the best approach for conversion. Next, identify the equivalent block functionality within WordPress.
This step is essential for establishing a functional parallel in the new structure. After that, construct the block, replicating the widget’s logic and design. Thorough testing is essential to ensure that the block functions correctly. Finally, integrate the block into the theme, ensuring seamless operation.
Potential Challenges
Several challenges can arise during the widget-to-block conversion process. These issues often stem from the complex nature of widget interactions and data handling within the existing theme. Compatibility issues with existing themes are common, requiring adjustments to ensure the block seamlessly integrates. Another common challenge involves preserving the original widget’s functionality and appearance. This requires a thorough understanding of the widget’s behavior and careful coding to ensure that the block replicates the widget’s logic.
Furthermore, complex interactions with other plugins or custom code may introduce unforeseen issues, necessitating careful debugging and troubleshooting.
Maintaining Functionality
Maintaining the original widget’s functionality is crucial. This includes preserving the same inputs, outputs, and overall behavior as the widget. A key element is ensuring the block handles data in the same way as the widget. For instance, if the widget handles user input, the block must perform the same validation and processing steps. This will prevent any disruption to the user experience or data integrity.
Compatibility and Backward Compatibility
Compatibility is essential. The block must seamlessly integrate with the theme and other plugins. Backward compatibility is equally important, ensuring that the converted block functions with older versions of WordPress and themes, minimizing disruptions to existing users and workflows. The block should be adaptable to future updates and modifications in the WordPress ecosystem, ensuring its longevity and reliability.
Step-by-Step Procedure
- Thorough analysis of the widget’s code and functionality. This step is critical for understanding the widget’s inner workings, input parameters, and output data. Identifying the widget’s interaction with other components of the WordPress site is equally important.
- Identification of the equivalent block functionality within WordPress. This step entails exploring available block functionalities and selecting the most suitable options. A thorough comparison of existing block features with the widget’s needs is critical.
- Careful construction of the block, meticulously replicating the widget’s logic and design. This step emphasizes precise implementation of the widget’s logic, ensuring identical input-output processes and error handling. Testing at this stage is critical.
- Integration of the block into the theme. This stage necessitates meticulous testing to ensure the block seamlessly integrates with the theme and other plugins, minimizing potential conflicts.
- Comprehensive testing to validate the block’s functionality and ensure it replicates the widget’s behavior. This step involves testing in various scenarios to catch any bugs or issues. User testing with a variety of inputs and interactions is crucial.
Techniques for Converting Widgets
Transforming WordPress widgets into blocks is a crucial step in modernizing your website’s functionality and design. This process allows for greater flexibility, enhanced customization, and a more streamlined user experience. By understanding the various techniques available, you can effectively migrate your existing widgets to the powerful block editor.Converting widgets to blocks isn’t just about swapping one component for another; it’s about leveraging the block editor’s capabilities to create a more modular and extensible system.
This involves understanding how WordPress block APIs work, how to migrate existing widget configurations, and utilizing custom code effectively. A methodical approach, including careful consideration of the conversion process, is key to success.
Ever wanted to upgrade your WordPress site’s widgets to blocks? It’s a straightforward process, but knowing how to leverage the power of a customer service cloud, like discover the power of customer service cloud , can make it even more impactful. Learning these conversion techniques unlocks more design freedom and customization options for your website, allowing you to create a seamless user experience.
So, let’s dive into the steps for converting those widgets!
Custom JavaScript Conversion
JavaScript offers a dynamic approach to widget conversion. You can use JavaScript to capture the widget’s content, attributes, and behaviors, then transform them into a corresponding block. This allows for precise control over the conversion process, enabling you to tailor the block to match the widget’s functionality. Crucially, this technique permits seamless integration of complex widget behaviors within the block system.
For instance, you can use JavaScript to manipulate the rendered output and ensure that any dynamic updates or interactions previously handled by the widget are now handled by the block.
PHP Conversion Using the Block API
Utilizing WordPress’s block API directly within PHP provides a more structured and manageable way to convert widgets to blocks. This method offers a more direct connection between the widget’s data and the block’s structure. Using PHP functions within your theme or plugin, you can retrieve widget data and create a corresponding block instance. This approach ensures that the conversion process is consistent with the core WordPress structure and minimizes potential conflicts.
This allows for clean separation of concerns between your widget’s logic and the block’s display.
Migrating Existing Widget Configurations
Migrating existing widget configurations to block settings requires careful consideration of the data being transferred. This often involves extracting the widget’s settings, converting them to a format compatible with block attributes, and then providing a user interface within the block editor to manage those settings. Tools like custom block settings and data manipulation functions within PHP are crucial for ensuring that all the widget’s functionality is accurately reflected in the block’s interface.
A clear understanding of how the widget’s data maps to block attributes is vital for a seamless migration.
Comparison of Conversion Methods
| Method | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Custom JavaScript | Widget conversion using JavaScript. | Flexible, can handle complex behaviors. | Can be more challenging to implement for complex widgets, potential for conflicts with other JavaScript code. |
| PHP Conversion using Block API | Conversion using WordPress block API within PHP. | Structured, less prone to conflicts. | Might require deeper understanding of block API for intricate conversions. |
Best Practices and Considerations: How To Convert A WordPress Widget Into A Block
Converting WordPress widgets to blocks is a powerful way to enhance your site’s flexibility and functionality. However, a thoughtful approach is crucial to avoid performance issues and ensure a seamless user experience. Understanding the best practices and potential considerations will lead to a more effective and user-friendly website.This section will explore key strategies for converting widgets, highlighting potential performance implications and outlining best practices for handling different widget types.
Converting WordPress widgets into blocks is surprisingly straightforward. You’ll find a wealth of tutorials online, and understanding the process is key to maximizing your website’s functionality. Meanwhile, the recent Google backlash against California’s privacy bill google backlash california privacy bill highlights the importance of staying updated on digital regulations. This knowledge will help you tailor your WordPress setup to comply with the evolving landscape and ensure a user-friendly, compliant experience.
Ultimately, these conversions are a great way to enhance your website’s structure and user experience.
We will also discuss how to maintain a positive user experience throughout the conversion process.
Performance Implications
Converting widgets to blocks, while generally beneficial, can have performance implications if not managed correctly. Heavy widgets, for instance, those containing complex calculations or numerous external API calls, may introduce load times on the frontend. Careful optimization of the converted block is essential to prevent these issues. Analyze your widgets thoroughly and identify those with a potential impact on site speed.
Consider pre-rendering content where possible, caching frequently accessed data, or employing lazy loading techniques to minimize the load on the browser.
Handling Different Widget Types
Various widget types present unique challenges during conversion. For example, a simple text widget is easily converted to a block with minimal modifications. However, widgets that dynamically populate content from external databases or APIs require more intricate solutions. Consider the specific requirements of each widget type. For instance, a calendar widget might require careful management of its data fetching to ensure responsiveness.
Understanding the underlying structure and functionality of each widget type is essential for a successful conversion.
Ensuring a Smooth User Experience
Maintaining a seamless user experience is paramount. Users should not notice any significant change in the way the site functions after the conversion. Consider the visual presentation of the block, ensuring it maintains the visual identity of the original widget. Furthermore, consider accessibility guidelines during the conversion. If the widget originally supported specific accessibility features, ensure these are preserved in the block equivalent.
A thorough review of the accessibility implications of the conversion is critical.
Best Practices for Conversion
Following best practices during conversion is key to maintaining a functional and user-friendly website. A well-structured approach helps prevent issues and ensure a positive user experience. The conversion should adhere to the following practices:
- Thorough Testing: Thoroughly test the converted block across various browsers and devices to ensure compatibility and identify any potential bugs.
- Prioritize Simplicity: Keep the block’s functionality simple. Overcomplicating the block will negatively impact performance and user experience.
- Maintain Existing Functionality: Ensure the converted block retains the original functionality of the widget. Any loss of functionality will negatively impact users.
- Regular Updates: Maintain and update the block after conversion to address any issues and optimize for performance.
Accessibility Considerations
Accessibility is a critical aspect to consider during the conversion process. Users with disabilities rely on accessible designs and functionalities. The converted block must adhere to accessibility guidelines, such as WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines). If the widget originally provided accessibility features, the block must retain these features, for example, alternative text for images or proper keyboard navigation.
Ensure that the converted block meets WCAG standards for accessibility.
Potential Conflicts and Resolutions
Converting widgets to blocks might introduce conflicts with existing themes or plugins. A thorough review of the theme’s structure and any relevant plugins is essential to identify potential conflicts. If conflicts are detected, addressing them promptly is crucial to ensure a smooth conversion. Solutions may include modifying the theme’s CSS or adjusting plugin settings to accommodate the new block structure.
Carefully address any identified conflicts to prevent disruptions to the website’s functionality.
Example Conversion Scenarios
Converting WordPress widgets to blocks is a powerful way to modernize your site and take advantage of the block editor’s flexibility. This section will delve into practical examples, demonstrating how to handle various widget types, from simple text widgets to complex custom widgets that interact with external APIs. We’ll examine the steps involved and highlight important considerations to ensure a smooth transition.Understanding the specific characteristics of each widget is key to a successful conversion.
Different widgets have varying functionalities and data structures, requiring different approaches. This often includes modifying existing code, creating new block components, and integrating with the block editor’s features.
Converting a “Text” Widget to a Block
The “Text” widget, a fundamental WordPress component, is a straightforward candidate for block conversion. Its primary function is displaying plain text, making it relatively easy to replicate within the block editor. The process involves creating a new block type that accepts the text content from the widget. Within the block editor, you can then modify and style this text.
The settings of the widget, including formatting options like bold, italics, and headings, need to be translated into the block editor’s interface.
Converting a Custom Widget
Custom widgets often require more in-depth conversion strategies. These widgets frequently employ custom logic and interactions. The first step involves carefully examining the widget’s PHP code to identify its functionality and data structures. This analysis will help you map the widget’s inputs and outputs to corresponding features within the block editor. You’ll need to replicate the widget’s logic within a custom block, potentially using JavaScript and React for dynamic behavior.
This often necessitates modifying existing PHP code to retrieve data and pass it to the newly created block.
Converting Widgets with Multiple Settings, How to convert a wordpress widget into a block
Widgets with numerous settings present a more complex conversion. Consider a widget with options for displaying various content types, layouts, and styles. In this scenario, you’ll need to create a block that mirrors the widget’s settings. The solution involves meticulously mapping the original widget’s settings to the block’s attributes. You will need to carefully design a user interface within the block editor that accurately represents the original widget’s options, enabling users to select various parameters.
Properly managing the data flow between the block and the backend is essential for this conversion.
Converting Widgets Using External APIs
Widgets that rely on external APIs, for example, those displaying weather data or social media feeds, pose a slightly more intricate conversion. The core challenge lies in preserving the widget’s data retrieval and display logic within the block. This involves implementing a similar API call mechanism within the block’s JavaScript component. You need to ensure that the block seamlessly fetches and renders the data from the external API, replicating the widget’s functionality.
This includes handling potential API errors and caching retrieved data for optimal performance.
Conversion Based on Widget Features
The conversion process is intrinsically tied to the widget’s specific features. For instance, a widget designed for displaying images might require different conversion steps compared to a widget handling user interactions. The widget’s purpose, its data handling mechanism, and the complexity of its interactions dictate the necessary adaptations within the block. A simple widget will require minimal changes, while a custom widget requiring data from a database or multiple API calls will demand more significant modifications.
This consideration highlights the importance of thoroughly evaluating each widget before embarking on its conversion.
Troubleshooting and Common Issues
Converting WordPress widgets to blocks can sometimes present unexpected challenges. Understanding potential pitfalls and their solutions is crucial for a smooth conversion process. This section will cover common issues, provide troubleshooting steps, and equip you with the knowledge to overcome these obstacles.
Common Conversion Errors
Several issues can arise during the conversion of a widget to a block. These errors often stem from differences in how widgets and blocks function and interact with the WordPress ecosystem. Incorrect configuration, incompatibility with the new block structure, and issues with the original widget’s code can all cause problems. Thorough examination and careful attention to detail are essential to identifying and resolving these problems.
Debugging the Conversion Process
Debugging the conversion process involves systematically identifying and resolving issues that prevent a successful conversion. This entails understanding the specific error messages, examining the block’s code for inconsistencies, and comparing it to the widget’s original code. Tools like the WordPress developer tools, which provide valuable insights into the block’s behavior and interactions, are vital during the debugging process.
Troubleshooting Scenarios
| Issue | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Block not rendering correctly | The converted block fails to display the expected content or formatting. | Verify the block’s configuration. Check for missing or incorrect attributes. Ensure the block’s CSS and JavaScript are correctly linked. Inspect the block’s HTML structure to identify any discrepancies. If necessary, revert to a backup of the previous widget configuration. |
| Widget data loss | Data from the original widget is missing or corrupted after conversion. | Carefully examine the block’s data fields to ensure the original widget’s data has been migrated correctly. Review the conversion code for potential data loss. If possible, restore the data from a backup or previous version of the widget configuration. |
| Functionality issues | The converted block doesn’t perform the expected actions. | Isolate the specific functionality that isn’t working. Compare the widget’s original functionality with the block’s behavior. Check for compatibility issues between the block and plugins or themes. Ensure the block is correctly integrated with the WordPress ecosystem. |
| Incompatibility with plugins or themes | The converted block interacts improperly with other plugins or themes. | Review the plugin and theme documentation to confirm compatibility with the block. Update plugins and themes to the latest versions. Try disabling potentially conflicting plugins temporarily to isolate the source of the issue. If necessary, contact the plugin or theme developer for assistance. |
Error Handling and Prevention
Careful planning and implementation during the conversion process are crucial for preventing errors. Thorough testing at each step, and a clear understanding of how widgets and blocks operate, will greatly reduce the likelihood of encountering problems. Maintaining detailed documentation throughout the conversion process is vital for tracking changes and resolving any issues that arise.
Advanced Conversion Techniques
Converting complex WordPress widgets to blocks requires a nuanced approach that goes beyond simple code replacements. This section delves into advanced techniques for handling custom CSS, JavaScript, external plugins, and intricate interactions, ensuring a smooth transition from the familiar widget structure to the modern block paradigm. Understanding these advanced techniques is crucial for maintaining functionality and avoiding potential compatibility issues.Often, widgets leverage custom styling and dynamic behaviors through CSS and JavaScript.
Directly translating these into block-based solutions requires careful consideration. A key strategy involves encapsulating the widget’s functionality within a custom block, allowing you to replicate the styling and logic within the block’s context.
Converting Widgets with Custom CSS
Custom CSS within widgets can often control visual elements, layouts, and interactions. To convert these widgets, identify the specific CSS rules and replicate their effect within the block’s styling. Utilize the block’s available styling options, including inline styles and CSS classes. If the CSS targets specific elements, ensure that the block’s structure mirrors the original widget’s layout.
Converting Widgets with Custom JavaScript
JavaScript in widgets often handles dynamic updates, interactions, and data manipulation. To convert JavaScript-dependent widgets, meticulously analyze the JavaScript’s behavior. Convert the widget’s JavaScript functions into a custom block’s functionality using the block’s event handlers and API. Consider how to trigger the JavaScript actions in response to block interactions, such as user input or changes to other block attributes.
Replicate the logic and behavior of the JavaScript within the block’s context.
Converting Widgets Relying on External Plugins
Some widgets depend on external plugins for their functionality. Conversion strategies for these widgets involve investigating the plugin’s interaction with the widget. If possible, integrate the plugin’s functionality directly into the custom block, either through custom components or by utilizing the plugin’s API. Alternatively, explore if the plugin offers a block-based integration. If not, consider recreating the functionality within the block or finding a similar alternative block solution.
This often requires understanding the underlying data structures and communication protocols used by the plugin.
Ensuring Seamless Transition
A seamless transition is critical for maintaining functionality. Ensure that the block’s user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) match the widget’s original design. Maintain the widget’s existing behavior and data flow. Testing the converted block thoroughly is essential. Consider A/B testing with both the original widget and the converted block to ensure equivalent functionality and user experience.
Handling Complex Interactions and Data Relationships
Widgets often involve intricate data relationships and interactions. Understanding these dependencies is crucial. Create a data model that mirrors the widget’s data structure and ensures data consistency. Employ the block’s API for managing data flow and interactions between the block and other elements. Develop methods for retrieving, updating, and manipulating data within the block’s context, ensuring compatibility with other blocks or components.
Last Recap
In conclusion, converting WordPress widgets to blocks offers significant advantages, improving site structure and maintainability. This guide provided a clear roadmap, from foundational understanding to advanced techniques. By following the detailed steps and best practices, you can confidently migrate your widgets, preserving functionality and maximizing your website’s potential. Remember, proper planning and execution are crucial for a smooth transition.