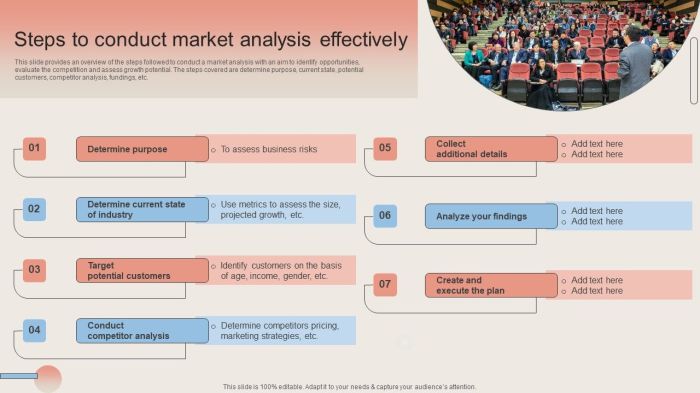
How to do a market analysis is crucial for any business aiming to thrive. This guide delves into the entire process, from defining your market scope and gathering crucial data to analyzing findings and implementing strategies. We’ll explore various types of market analysis, including industry, competitor, and consumer analyses, providing you with a practical framework to understand your target audience and the competitive landscape.
We’ll cover everything from identifying your target market and setting clear goals to collecting primary and secondary data. You’ll learn how to analyze market trends, evaluate market size and potential, and segment the market effectively. Finally, we’ll show you how to present your findings, use the results for strategic decision-making, and even explore useful tools and techniques along the way.
Defining the Scope of the Market
Market analysis is crucial for any business aiming to succeed in a competitive environment. It provides a deep understanding of the market landscape, enabling informed decisions about product development, pricing strategies, and marketing campaigns. A well-defined scope ensures that the analysis is focused and relevant, avoiding unnecessary data collection and analysis. This section delves into the various facets of defining the market scope, from identifying different analysis types to crafting a comprehensive framework for market segmentation.
Market Analysis Types
A comprehensive market analysis encompasses various perspectives. Industry analysis examines the overall trends and dynamics within a specific industry, including growth potential, technological advancements, and regulatory changes. Competitor analysis focuses on the strengths, weaknesses, and strategies of direct and indirect competitors. This provides insights into market share, pricing models, and customer preferences. Consumer analysis delves into the needs, preferences, and behaviors of the target market.
This analysis helps understand motivations behind purchasing decisions and allows businesses to tailor their offerings to specific customer segments.
A crucial part of market analysis is understanding your target audience’s online presence. This includes diving into reviews and social media chatter, which often reveals valuable insights into customer perceptions. To truly grasp the sentiment surrounding your brand, you need to leverage powerful tools like online reputation management tools. These tools allow you to monitor mentions, track keywords, and even measure the impact of your marketing efforts on brand perception.
This data is invaluable for fine-tuning your market analysis, ensuring your strategy aligns with current consumer feedback and expectations.
Identifying the Target Market
Defining the target market is a crucial step in any market analysis. It involves identifying the specific group of customers most likely to purchase a particular product or service. This process typically involves detailed demographic, psychographic, and behavioral analysis. For example, a company selling organic baby food might target parents aged 25-45, with a focus on health-conscious individuals residing in urban areas.
Figuring out market trends is key to any successful analysis. Understanding your target audience and competitor activity is crucial, but now, with ChatGPT potentially incorporating ads ( chatgpt with ads coming ), this could dramatically shift the way we gather and analyze information. Tools and resources like surveys and online forums will still be important, but this new development will need to be factored into any market analysis moving forward.
Significance of Goals and Objectives
Defining specific goals and objectives for the market analysis is essential for ensuring its effectiveness. These goals should be measurable and time-bound, guiding the analysis process and ensuring that the data collected aligns with the specific needs of the business. For instance, a goal could be to determine the market share of a new product within the first year of its launch.
This clearly defines the scope and focus of the analysis, allowing for a targeted approach.
Market Segmentation Framework, How to do a market analysis
A well-structured framework for classifying various market segments is crucial for a detailed understanding. This framework can categorize customers based on demographics (age, gender, income), psychographics (lifestyle, values, interests), and behavioral characteristics (purchase frequency, brand loyalty). This structure facilitates the targeted approach in marketing strategies. For example, a clothing retailer might segment its market into young adults, middle-aged professionals, and senior citizens, tailoring their marketing campaigns to resonate with each segment.
Examples of Market Analysis Reports
Market analysis reports can be tailored to various business contexts. For a startup launching a new mobile app, a report might focus on the competitive landscape, app store rankings, and user behavior. For an established e-commerce company, a report might analyze customer purchasing patterns, trends in product demand, and competitor pricing strategies. For a small bakery, a report might analyze local demographics, customer preferences, and potential market expansion opportunities.
| Business Context | Focus Areas |
|---|---|
| New mobile app | Competitive landscape, app store rankings, user behavior |
| E-commerce company | Customer purchasing patterns, product demand trends, competitor pricing |
| Small bakery | Local demographics, customer preferences, market expansion |
Gathering Information
Uncovering the market’s secrets involves meticulous data collection. Understanding your target audience, competitors, and market trends is paramount for strategic decision-making. This stage is crucial for forming a comprehensive picture of the market landscape and for developing informed business strategies.Gathering accurate and reliable information is vital for a successful market analysis. This includes both primary research, which involves direct interaction with potential customers, and secondary research, which leverages existing data sources.
A thorough competitor analysis is also essential for understanding the strengths and weaknesses of your rivals.
Primary Market Research Methods
Understanding your target audience directly is key to successful primary market research. This involves collecting data directly from consumers or potential customers through various methods.
- Surveys: Surveys are a common tool for gathering quantitative data, enabling you to measure attitudes, preferences, and behaviors. They can be administered online, via email, or through physical questionnaires. A well-designed survey with carefully chosen questions can provide valuable insights into customer needs and preferences. For example, a survey can reveal the importance of product features to your target market, like eco-friendly packaging or a convenient delivery option.
- Interviews: Interviews offer a deeper understanding of customer motivations and perceptions. One-on-one or focus group discussions allow for qualitative data collection, providing detailed insights into customer needs and concerns. In-depth interviews can uncover hidden motivations and reveal nuances that surveys might miss. For example, a series of in-depth interviews could reveal why customers choose your competitor’s product over yours.
- Focus Groups: Focus groups provide a platform for group discussions. A moderator guides a small group of participants to discuss a specific topic, like a new product concept or an existing brand image. These interactions help understand customer reactions to different stimuli. For instance, a focus group can identify which marketing message resonates best with your target audience.
Secondary Market Research Resources
Leveraging existing data is crucial in secondary market research. This approach saves time and resources, allowing you to analyze information collected by others.
- Government Reports: Government agencies frequently publish data on various economic sectors, demographics, and market trends. These reports can provide valuable context and background information for your analysis. For instance, government reports can offer insights into population growth, income levels, and consumer spending habits within specific regions.
- Industry Publications: Industry-specific publications, such as trade journals and magazines, often feature articles, market analysis reports, and data on industry trends. These publications provide valuable insights into the competitive landscape and future projections. For example, an industry publication could highlight emerging technologies and their potential impact on the market.
- Market Research Reports: Market research firms compile comprehensive reports on various industries and markets. These reports offer a detailed overview of market size, growth potential, and trends. They can help you identify potential opportunities and threats in your chosen market.
Competitor Analysis
Understanding your competitors is critical for developing effective strategies.
- Identifying Competitors: Competitor analysis involves identifying both direct and indirect competitors. Direct competitors offer similar products or services to yours. Indirect competitors provide alternative solutions that address the same customer need. Recognizing both types of competitors provides a more complete picture of the market landscape. For example, a direct competitor for a coffee shop might be another coffee shop in the same area.
An indirect competitor could be a tea shop or a café serving other beverages.
Competitor Profile Report Template
A well-structured competitor profile report provides a concise overview of each competitor.
| Competitor Name | Products/Services | Target Market | Strengths | Weaknesses | Market Share | Pricing Strategy | Marketing Strategies | Financial Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Example Competitor 1 | Coffee, pastries | Young professionals | Excellent coffee quality | Limited seating | 20% | Premium pricing | Social media marketing | Stable revenue |
Market Trend Analysis
Analyzing market trends is crucial for anticipating future developments.
- Predicting Future Developments: Trends can be identified by observing patterns in sales data, consumer preferences, and technological advancements. By studying these patterns, you can anticipate future developments and adjust your strategies accordingly. For instance, the rise of e-commerce has significantly altered the retail landscape, prompting many traditional businesses to adopt online sales channels.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
Once you’ve gathered your market data, the real work begins – analyzing it to extract meaningful insights. This stage involves applying various techniques to uncover patterns, trends, and potential opportunities. Effective data analysis transforms raw information into actionable intelligence, enabling informed decisions about market entry, product development, and strategic positioning.
Statistical Analysis Techniques
Statistical analysis plays a crucial role in understanding market trends and patterns. Techniques like regression analysis help determine the relationship between variables, such as pricing and sales volume. Correlation analysis identifies the degree of association between different factors, revealing potential causal links. Hypothesis testing allows you to evaluate the validity of assumptions about the market, ensuring your conclusions are statistically sound.
Knowing your target audience is key for a successful market analysis. Understanding their needs and preferences is essential, but also crucial for getting the most out of your Facebook Ads campaigns. For example, learning how to effectively target your audience and drive more clicks with get clicks facebook ads can dramatically improve your ROI. Ultimately, a thorough market analysis, including a deep dive into competitor strategies and trends, is vital for long-term success.
Furthermore, descriptive statistics, like calculating averages and standard deviations, provide a concise overview of the data, highlighting key characteristics of the target market.
Market Share Analysis
Market share analysis is fundamental to understanding a company’s position within the competitive landscape. It involves calculating the percentage of total market sales attributed to a particular company or product. This analysis helps identify market leaders, emerging competitors, and areas of potential growth. By comparing your market share to competitors, you can pinpoint strengths and weaknesses and tailor strategies accordingly.
For example, if your market share is declining, you can investigate the causes and adjust your strategies to regain market share.
Evaluating Market Size and Potential
Assessing market size and potential is essential for strategic planning. This involves analyzing the total number of potential customers and their purchasing power. Market research reports and industry data often provide estimates of market size. To evaluate potential, consider factors like growth rate, market trends, and future demand. For example, a growing market with a large customer base and increasing disposable income presents a significant potential opportunity.
Key Factors Influencing Market Demand
Several factors influence market demand, including economic conditions, consumer preferences, and competitor actions. Economic factors like inflation and recession can significantly impact consumer spending. Changes in consumer preferences, driven by trends and emerging technologies, require continuous monitoring. Competitor actions, such as new product launches or pricing strategies, directly affect market demand. A comprehensive analysis considers these factors to predict future demand and adjust strategies accordingly.
Market Segmentation
Market segmentation involves dividing the broad market into smaller, more manageable groups with shared characteristics. This allows for more targeted marketing efforts and product development. Segmentation criteria can include demographics (age, gender, income), psychographics (lifestyle, values), geographic location, and behavioral patterns (usage frequency, brand loyalty). By understanding the unique needs and preferences of each segment, you can develop tailored products and marketing campaigns.
Interpreting Findings and Drawing Conclusions
The final step in market analysis is interpreting the findings and drawing conclusions. This involves summarizing key trends, identifying potential opportunities and threats, and formulating actionable strategies. For instance, a significant increase in demand for a specific product segment could indicate a lucrative market opportunity. Conversely, declining sales figures might signal a need for strategic adjustments. By drawing clear conclusions from the analysis, you can make informed decisions that drive growth and success.
Presenting the Results
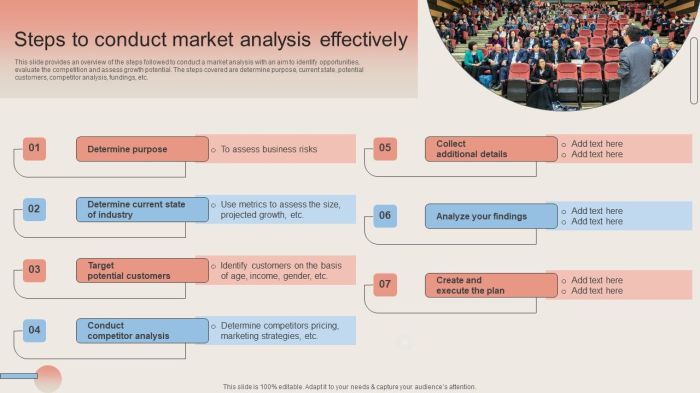
A market analysis isn’t complete without a compelling presentation of its findings. This crucial step allows stakeholders to easily grasp the key takeaways and use the insights to inform strategic decisions. Clear and concise presentation of data is essential for effective communication and actionable outcomes. A well-structured report, combined with appropriate visuals, makes the analysis impactful and memorable.
Structuring the Presentation
The structure of a market analysis report should mirror the analytical process. Begin with an executive summary that provides a concise overview. Follow this with a detailed description of the market, including demographics, trends, and competitive landscape. Subsequent sections should delve into specific segments, analyzing each in detail. Conclude with recommendations based on the analysis.
Using Tables for Clear Data Presentation
Tables are invaluable for presenting data in a structured and easily digestible format. They allow for precise comparisons and highlight key metrics.
- Comparative Analysis: A table can compare key characteristics across different market segments. For instance, a table might compare the average income, age, and purchasing habits of different customer groups.
- Data Categorization: Tables facilitate the categorization of data. Grouping sales figures by product type, region, or time period allows for quick identification of patterns and trends.
- Numerical Data Presentation: Tables are excellent for presenting numerical data. Use clear column headers and concise data entry to avoid confusion. Example: A table could present sales figures for various products over a three-year period.
Sample Executive Summary
“This market analysis examines the burgeoning market for sustainable food products in the United States. Key findings reveal a significant increase in consumer demand for organic and locally sourced food. The analysis indicates a positive correlation between consumer awareness of environmental issues and the purchase of eco-friendly alternatives. The report further identifies potential opportunities for expansion into emerging market segments, including vegan and plant-based food options.”
Visual Representations of Data
Visual aids like charts and graphs are crucial for effectively communicating complex data. They transform numerical information into easily understandable representations, enhancing comprehension and highlighting key trends.
- Bar Charts: Use bar charts to compare quantities across categories. For example, a bar chart could visualize the market share of different competing brands in a specific segment.
- Line Graphs: Line graphs are ideal for displaying trends over time. This allows for the visualization of sales growth, customer acquisition, or market penetration over a period.
- Pie Charts: Use pie charts to represent the proportion of different components within a whole. For example, a pie chart can show the distribution of consumers based on age groups.
Comparing and Contrasting Market Segments
A table format is particularly useful for comparing and contrasting different market segments. This structured approach enables a clear understanding of the similarities and differences between various groups.
| Segment | Average Income | Age Range | Purchasing Habits | Product Preferences |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Segment A | $75,000 | 25-45 | Frequent online purchases | Premium products |
| Segment B | $50,000 | 35-55 | Prefer in-store shopping | Value-oriented products |
Utilizing the Results for Strategic Decision-Making: How To Do A Market Analysis
Market analysis isn’t just about gathering data; it’s about translating those insights into actionable strategies. A well-executed analysis provides a roadmap for informed decision-making, helping businesses navigate the competitive landscape and capitalize on emerging opportunities. Understanding your target market, their needs, and their behavior is crucial for success in today’s dynamic environment. This section will delve into how to leverage market analysis results for effective strategic planning.A thorough market analysis empowers businesses to develop robust strategies tailored to specific market conditions.
This involves examining trends, competitor actions, and consumer preferences to craft marketing campaigns, product development plans, and pricing models that resonate with the target audience and drive revenue growth. This process requires careful consideration of potential risks and opportunities, allowing businesses to proactively address challenges and seize advantageous situations.
Marketing Strategy Development
Market analysis is the bedrock for crafting effective marketing strategies. By understanding consumer preferences, buying habits, and pain points, businesses can tailor their messaging and campaigns to resonate with the target audience. This involves identifying the most effective channels for reaching potential customers, developing compelling marketing materials, and optimizing campaigns for maximum impact. Understanding competitor activity, including their strengths, weaknesses, and marketing strategies, helps in differentiating your own offerings.
Effective marketing strategies are crucial for brand awareness, lead generation, and ultimately, sales.
Pricing Decisions
Market analysis provides invaluable data for informed pricing decisions. Understanding the perceived value of your product or service relative to competitors, considering factors such as production costs and market demand, allows for a data-driven approach to pricing. For example, if a market analysis reveals that customers are willing to pay a premium for a specific feature, adjusting pricing accordingly can increase profitability.
Conversely, if competitors offer similar products at lower prices, a price analysis can help determine the right pricing strategy to maintain competitiveness while maximizing revenue. Pricing decisions should consider factors like customer perception, competitor pricing, and market sensitivity to price changes.
Product Development Strategies
Product development strategies benefit greatly from market analysis insights. Analyzing market trends, customer feedback, and competitor offerings provides crucial information to identify unmet needs and develop innovative products that meet those needs. For instance, understanding emerging technologies and consumer preferences can inform the development of new products or features that align with evolving market demands. Identifying gaps in the market and focusing on those underserved areas allows for differentiation and competitive advantage.
A detailed market analysis can pinpoint emerging trends and opportunities that may not be immediately apparent.
Risk and Opportunity Identification
Market analysis is a proactive approach to identifying potential risks and opportunities. By analyzing competitor activities, economic trends, and regulatory changes, businesses can anticipate potential challenges and adapt their strategies accordingly. For example, if a market analysis predicts a decrease in consumer demand for a specific product, businesses can proactively adjust their production or explore alternative product lines to mitigate the risk.
Conversely, if a market analysis highlights a new trend or a gap in the market, businesses can capitalize on this opportunity to expand their offerings or enter new markets. Proactive risk management and opportunity identification are essential for long-term sustainability.
Tools and Techniques
Market analysis is a multifaceted process requiring a range of tools and techniques. Effective use of these tools allows for a comprehensive understanding of market dynamics, competitive landscapes, and customer behaviors. From meticulous data collection to insightful analysis and strategic decision-making, each stage benefits from employing the right methodologies and software. This section dives deep into the essential tools and techniques.
Software Tools for Market Research
Numerous software tools streamline market research, from basic data gathering to sophisticated statistical analysis. These tools facilitate data management, visualization, and interpretation, enabling researchers to make informed decisions. Specific software packages often cater to specific needs, from competitor analysis to customer relationship management (CRM).
- SurveyMonkey: A widely used platform for creating and distributing online surveys. Its user-friendly interface and diverse question types allow for data collection on various aspects of the market. Its reporting capabilities provide clear insights into respondent demographics and preferences.
- Google Analytics: A free tool offering comprehensive website analytics. It provides valuable insights into user behavior, traffic sources, and conversion rates. This information is crucial for understanding customer interactions with products or services.
- Tableau: A powerful data visualization tool that transforms raw data into compelling charts and graphs. Its interactive dashboards allow for dynamic exploration and interpretation of market trends.
- SPSS: A statistical software package used for complex data analysis. It enables users to perform advanced statistical tests and modeling to identify patterns and correlations in market data.
Market Research Methodologies
Various market research methodologies are employed to gather information and insights. The choice of methodology depends on the specific research objectives and target audience. A variety of approaches exist to achieve the desired insights, from quantitative surveys to qualitative focus groups.
- Quantitative Research: This methodology involves collecting and analyzing numerical data. Surveys and experiments are common methods used in quantitative research to determine measurable trends, statistically significant correlations, and patterns.
- Qualitative Research: This approach focuses on gathering in-depth insights and understanding through interviews, focus groups, and observations. This allows for exploring the underlying reasons behind customer behaviors and preferences.
Data Sources
Access to reliable and diverse data sources is crucial for accurate market analysis. Gathering data from various sources provides a comprehensive understanding of the market landscape. Data can come from internal sources, external databases, and industry reports.
- Government Publications: Government agencies often publish reports and statistics on economic indicators, demographics, and industry trends. These reports provide valuable insights into market dynamics.
- Industry Associations: Industry associations often provide reports, market analysis, and research on specific industries. These resources offer insights into the competitive landscape and industry trends.
- Market Research Companies: Many specialized companies conduct market research and provide reports on various sectors. These reports often offer detailed insights into consumer behavior and market trends.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is a strategic planning method used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of a business or product. It helps identify internal factors (strengths and weaknesses) and external factors (opportunities and threats) that can affect its success.
- Strengths: Identify internal capabilities and positive attributes that provide an advantage in the market.
- Weaknesses: Identify internal limitations or deficiencies that could hinder success.
- Opportunities: Identify external factors that could create a positive impact on the business or product.
- Threats: Identify external factors that could negatively affect the business or product.
Competitive Benchmarking
Competitive benchmarking is a process of comparing a company’s performance against that of its competitors. This comparison identifies areas where the company excels and areas where it needs improvement. Understanding competitors’ strengths and weaknesses helps in strategic decision-making.
- Direct Comparison: A detailed comparison of key performance indicators (KPIs) such as sales figures, market share, customer satisfaction, and product features.
- Indirect Comparison: Analyzing companies in similar industries to identify best practices and innovative strategies.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, conducting a thorough market analysis is a vital step for any business aiming for success. By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, you’ll gain a deep understanding of your target market, your competitors, and the overall market trends. This knowledge will empower you to make informed decisions, develop effective strategies, and ultimately, achieve your business objectives.
So, get ready to dive into the world of market analysis and unlock your business’s full potential!