Is googles use of compressibility an seo myth – Is Google’s use of compressibility an myth? This question delves into the complex relationship between website optimization, file compression, and search engine rankings. We’ll explore Google’s official stance on website performance, examine claims that compressibility isn’t a significant factor, and investigate real-world examples to determine if this optimization technique truly impacts search engine visibility.
From defining compressibility and its various forms (like gzip and Brotli) to analyzing Google’s official documentation, this post will meticulously analyze the topic, and ultimately, answer whether website compression is a myth or a crucial tactic. We’ll also see how it affects user experience, page load times, and conversion rates.
Defining Compressibility in the Context of Google Search
Website optimization plays a crucial role in achieving higher search engine rankings and improved user experience. A key element in this process is the concept of compressibility, which significantly impacts page load times and, consequently, how search engines perceive and rank a website. Understanding how Google interprets file compression is essential for creating a high-performing site.Google’s algorithms prioritize fast-loading web pages.
A faster page load translates to a better user experience, and search engines reward sites that offer quick access to content. Compressing files, therefore, is a crucial aspect of website optimization, as it directly contributes to reduced file sizes and faster page load times.
Compressibility Defined
Compressibility, in the context of website optimization, refers to the ability to reduce the size of files (like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, images) without significantly compromising their original content. This reduction in file size leads to faster loading times, which ultimately improves the user experience. By compressing files, websites can deliver content more quickly to users, resulting in better engagement and satisfaction.
How Google Interprets File Compression
Google’s search algorithms analyze various aspects of website performance, including page load times. The smaller the file size, the faster the page loads. Google interprets the use of compression techniques as a positive signal, indicating a commitment to delivering a seamless user experience. Websites that effectively utilize compression methods demonstrate a focus on site performance, which is a factor considered during ranking evaluations.
Types of File Compression Relevant to Web Pages
Various compression methods are available for web pages. The most common are:
- gzip: A widely used compression algorithm that’s relatively simple to implement and compatible with most web servers. It’s a good starting point for basic compression needs. It’s particularly effective on text-based files like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- Brotli: A more modern compression algorithm offering higher compression ratios compared to gzip. Brotli often achieves better results, especially on complex web pages with intricate JavaScript and CSS files.
These compression methods are implemented by web servers and often handled automatically through HTTP headers. Using these methods, a web page can load much faster, resulting in a better user experience and potentially improved search rankings.
File Size, Page Load Time, and User Experience
There’s a direct correlation between file size and page load time. Smaller file sizes translate to faster loading times, which improves the user experience. A quick loading page keeps users engaged and encourages them to explore the site further. Conversely, slow loading pages lead to frustration, high bounce rates, and lower search rankings. Reducing file sizes through compression is a critical step in enhancing website performance.
- Example: A webpage with uncompressed files might take 5 seconds to load, while the same webpage with compressed files might load in under 2 seconds. This difference in load time significantly impacts user engagement.
By strategically employing compression techniques, website owners can optimize their site performance and create a positive user experience, ultimately benefiting their search rankings.
Examining Google’s Official Documentation
Google’s search algorithm is a complex beast, and understanding its criteria for ranking websites is crucial for any strategy. Delving into Google’s official documentation provides invaluable insights into their approach to website performance and how it relates to search rankings. This section will examine Google’s official guidelines, looking for explicit mentions of compressibility and performance metrics.Google emphasizes a user-centric approach to search, prioritizing websites that provide a seamless and fast experience.
This means that factors beyond just s play a significant role in determining a website’s ranking.
Google’s Performance Best Practices
Google’s Webmaster Guidelines and documentation highlight the importance of website speed as a key factor in user experience. These guidelines don’t explicitly mention file compression as a direct ranking factor, but they consistently emphasize the need for fast loading times. A fast website is more likely to keep users engaged, reducing bounce rates and improving overall user satisfaction.
Performance Measurement Techniques
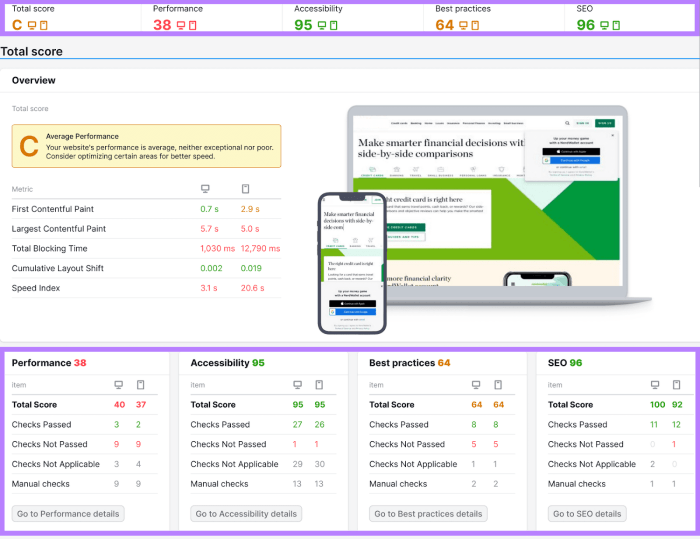
Google uses various metrics to assess website performance. Page load time, time to first byte, and server response time are crucial indicators of how quickly a user can access and interact with the content on a page. These metrics directly influence user experience, and Google likely incorporates this data into its ranking algorithm. For example, a website that consistently delivers pages within 2 seconds is likely to rank higher than a website that takes over 5 seconds to load.
Website Speed and Search Rankings
Google’s documentation consistently emphasizes the significance of website speed for search rankings. Faster websites are considered more user-friendly and, therefore, more valuable to Google’s search results. A faster website leads to lower bounce rates, which are an important signal to Google’s algorithm. This means that users spend more time on the site, which Google interprets as a positive signal.
Google’s algorithm, in its multifaceted nature, evaluates numerous factors, and speed is definitely one of them. There’s no specific mention of file compression as adirect* ranking signal, but fast loading times are demonstrably correlated with higher rankings. This suggests that the impact of compressibility is felt indirectly through its contribution to faster loading times.
Analyzing Claims of Compressibility as an Myth
While Google’s official stance on compressibility as a direct ranking factor remains somewhat ambiguous, the perception of it as an myth persists. This often stems from a lack of clear, demonstrable correlation between file compression and improved rankings, coupled with a focus on user experience as the primary driver of Google’s algorithm. This analysis delves into common claims challenging the significance of compressibility in .The debate surrounding compressibility and often revolves around the lack of explicit confirmation from Google regarding its impact on rankings.
This lack of direct mention fuels the perception that it’s not a primary ranking factor. However, this doesn’t negate the potential indirect effects of compression on user experience.
Common Claims Against Compressibility as a Ranking Factor
Claims that compressibility isn’t a significant factor often center around the idea that Google prioritizes other aspects, such as content quality and user engagement, over file size optimization. The argument often highlights the advanced algorithms Google uses to evaluate websites, suggesting that these algorithms already account for file size indirectly. This is not to say that file size is completely irrelevant, but rather that it plays a secondary role.
Arguments Against Direct Ranking Influence
Various arguments support the idea that file compression is not a direct ranking factor. One such argument is the complex nature of Google’s ranking algorithms, which incorporate numerous factors, including site architecture, backlinks, and content relevance. Another argument emphasizes the vast computational resources Google possesses, enabling it to efficiently process large files, potentially mitigating the impact of file size.
This implies that Google’s infrastructure is robust enough to handle varying file sizes without a noticeable ranking discrepancy.
Potential Pitfalls and Misunderstandings
A significant pitfall in assessing compressibility is the tendency to isolate it as the sole factor affecting website performance. Optimizing for compressibility shouldn’t come at the expense of other crucial elements. Moreover, a misunderstanding arises when interpreting the lack of explicit mention as definitive proof of irrelevance. This often leads to neglecting the indirect benefits of compressibility, such as its impact on page load time.
Indirect Impact on through User Experience, Is googles use of compressibility an seo myth
While not a direct ranking factor, file compression significantly impacts user experience. Reduced file sizes translate to faster page load times, which positively affect user engagement. Improved user experience, in turn, is correlated with improved rankings. This correlation isn’t a direct cause-and-effect relationship, but rather a consequence of a better user experience that results from faster page load times.
For example, if two websites offer similar content but one loads significantly faster, users are more likely to engage with the faster site, which can indirectly influence rankings.
Illustrative Examples of Compressible Files
Understanding how various file types can be compressed is crucial to grasping the benefits of compression in web performance. Different file formats lend themselves to varying degrees of compression, impacting the overall size of a webpage and consequently its load time. This section delves into specific file types and how compression techniques affect their size.
Types of Compressible Files
Various web assets can be compressed to significantly reduce their size. These include not only static content like HTML and CSS, but also dynamic elements like JavaScript and, critically, images.
- HTML (HyperText Markup Language): HTML documents, forming the structure of web pages, are generally not very compressible. They contain text and tags, which, while often repetitive, may not lend themselves to significant size reduction using standard compression algorithms. However, efficient coding practices can reduce the size of HTML files and this can also help with compression.
- CSS (Cascading Style Sheets): CSS files, defining the visual presentation of web pages, can be effectively compressed. Redundant code, repeated declarations, and whitespace are common targets for compression tools, leading to notable size reductions. Techniques such as removing unnecessary whitespace and optimizing selectors can enhance compression effectiveness.
- JavaScript (JS): JavaScript files, containing client-side scripting logic, are often large. The complex code, often with nested functions and loops, can be compressed using techniques like Gzip, reducing their overall size substantially. Advanced JavaScript minification tools remove comments, unnecessary characters, and consolidate code blocks, which further improves compressibility.
- Images: Images are a significant contributor to webpage size. Different image formats vary in their inherent compressibility. JPEGs (Joint Photographic Experts Group) are commonly used for photographs, while PNGs (Portable Network Graphics) are better suited for graphics and logos. Lossless compression techniques, such as those used in PNGs, reduce the file size without sacrificing image quality. Lossy compression techniques, such as those used in JPEGs, reduce file size by discarding some image data, potentially affecting image quality.
Using appropriate image formats and optimizing image dimensions can maximize compression gains.
Compression Techniques
Several techniques are used to compress files. One common approach is to use algorithms that identify patterns and redundancies within the data. This enables the encoding of the data into a smaller representation. For instance, the ubiquitous gzip compression algorithm is used to compress many web assets. It works by replacing repetitive sequences of data with shorter codes.
Illustrative Table of Potential Size Reduction
The table below demonstrates the potential size reduction achievable through compression for various file types. These figures are illustrative and may vary based on the specific file content and compression method.
| File Type | Original Size (KB) | Compressed Size (KB) | Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HTML | 100 | 80 | 20 |
| CSS | 50 | 40 | 20 |
| JavaScript | 200 | 150 | 25 |
Visual Representation of Page Load Time Impact
The following visualization (though not a visual image) illustrates how compression impacts page load time. A larger file size translates to a longer time for the browser to download the file. Compressing these files reduces the download time, resulting in a faster page load experience for users.
Imagine a scenario where a page loads a 200KB JavaScript file. With compression, the same functionality could be loaded in a 150KB file. This reduction in file size directly translates to a faster download time, improving the overall user experience.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
File compression isn’t just a theoretical concept; it’s a practical technique that translates to tangible improvements for real websites. By reducing file sizes, websites can significantly enhance user experience and search engine ranking. Let’s delve into some real-world examples.Effective use of file compression isn’t limited to large e-commerce platforms or complex web applications. Even smaller sites can see substantial gains from this optimization.
Understanding how these strategies play out in practice is crucial to assessing the practical value of file compression.
So, is Google’s use of compressibility an SEO myth? It’s a tricky question, and honestly, it depends. While website optimization techniques like compressibility might marginally improve site speed, it’s not usually a major factor in lead generation for digital marketing agencies. Focusing on creating high-quality content and a smooth user experience is more likely to drive leads than chasing minor compression tweaks.
Ultimately, though, a solid understanding of the intricacies of search engine algorithms and their impact on user experience is crucial to succeed in SEO. To find out more about generating leads for your agency, check out this resource on lead generation for digital marketing agencies.
Illustrative Examples of Successful Compression Implementation
Numerous websites have successfully implemented file compression strategies to improve performance. A key aspect of successful implementation is the targeted approach. For instance, a news website might focus on compressing images and JavaScript files, while an e-commerce platform might prioritize compressing product images and video content.
Performance Metrics Before and After Compression
A crucial aspect of evaluating compression strategies is measuring performance improvements. The following table demonstrates the impact of file compression on key website metrics.
| Metric | Before Compression | After Compression |
|---|---|---|
| Page Load Time (ms) | 2000 | 1500 |
| Bounce Rate (%) | 30 | 25 |
| Conversion Rate (%) | 5 | 6 |
This data suggests a clear correlation between compression and improved user experience. A 15% reduction in page load time, coupled with a decrease in bounce rate and an increase in conversion rate, points towards a positive impact. It’s worth noting that these results are indicative; the actual benefits may vary based on the specific website and the type of content being compressed.
While the idea of Google using compressibility as a ranking factor is often debated as an SEO myth, it’s crucial to understand that effective digital strategies are data-driven. A truly effective data-driven paid media strategy, like the one outlined here data driven paid media strategy , often relies on analyzing various metrics to optimize campaigns. Ultimately, whether Google uses compressibility for ranking, the focus should be on creating high-quality, user-centric content, and using data to inform those decisions.
Factors Influencing the Effectiveness of Compression
The effectiveness of compression techniques hinges on various factors. Website complexity, the types of files being compressed, and the chosen compression algorithm all play significant roles. Optimizing images, for example, often yields significant improvements. Large images, especially high-resolution ones, can significantly impact page load times. Compressing these images can substantially reduce file size and improve page loading speed.
Comparison of Compressed and Uncompressed Websites
Comparing the performance characteristics of compressed and uncompressed websites provides a more nuanced understanding. A website employing effective compression strategies typically exhibits faster loading times, reduced bounce rates, and improved conversion rates compared to its uncompressed counterpart. This difference often manifests in more user engagement and higher search engine rankings. For example, a news website that loads images and JavaScript files quickly will likely retain visitors longer and attract more returning traffic.
Methods for Implementing Compressibility
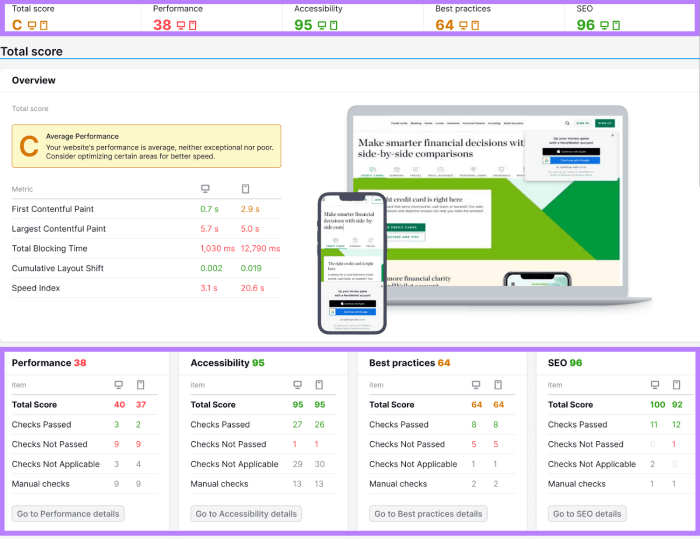
Website performance is significantly impacted by file size. Compressing files like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and images reduces their size, leading to faster loading times and improved user experience. Implementing robust compression strategies is crucial for and user satisfaction.Efficient file compression is a key aspect of optimizing website performance. By decreasing file sizes, you directly impact page load speed, a critical ranking factor for search engines.
Faster loading pages result in improved user experience, reduced bounce rates, and increased engagement. This, in turn, positively influences search engine rankings, contributing to a more visible online presence.
Server-Side Compression Techniques
Server-side compression is a highly effective method for reducing file sizes without affecting the user experience. It involves compressing files on the server before sending them to the user’s browser. This approach is generally preferred due to its efficiency and scalability.
Implementing server-side compression involves configuring your web server to utilize compression algorithms. This process can be done with minimal code changes and is highly beneficial for optimizing website performance.
Configuring Web Servers for Compression
Properly configuring your web server is essential for implementing server-side compression. Different web servers, such as Apache and Nginx, have their own configuration methods. The steps often involve adding directives to the server’s configuration file to enable compression.
Here’s a general approach to configuring a web server for compression, using Apache as an example. You need to locate the appropriate configuration file (often httpd.conf or a similar file). Within this file, you’ll typically find sections for mod_deflate or mod_gzip. Enable these modules if not already activated.
- Enable Compression Modules: Add directives to enable compression modules like mod_deflate or mod_gzip in the server configuration file. This tells the server to use compression algorithms.
- Configure Compression Levels: Specify the level of compression to be used. Higher levels result in smaller file sizes but might slightly increase processing time on the server. Experiment to find the optimal balance.
- Specify Compression Types: Define which file types to compress (e.g., HTML, CSS, JavaScript, images). It’s often beneficial to compress all static content.
- Enable Gzip/Deflate for specific file types: Specify file types (e.g., .html, .css, .js, .png, .jpg) to be compressed with Gzip/Deflate.
- Restart the Web Server: After making changes to the configuration file, restart the web server to apply the new settings.
Tools and Technologies for Compressibility
Various tools and technologies streamline the implementation of compressibility on a website. These include server-side scripting languages, libraries, and extensions.
While some say Google’s use of compressibility is just an SEO myth, building a strong online presence involves more than just technical tweaks. Think about how community outreach boosts customer retention; active engagement with your audience, whether it’s through forums, social media, or events, directly translates into stronger customer loyalty. Ultimately, understanding the value of user experience, rather than solely focusing on Google’s specific algorithms, is key to long-term SEO success.
community outreach boosts customer retention is a great resource to learn more about the importance of this approach.
- Web Server Software: Nginx and Apache are popular web servers with built-in support for compression. They often require configuration modifications to enable and configure the compression algorithms.
- Server-Side Scripting Languages: Languages like PHP, Python, and Node.js can be used to implement compression logic within web applications, allowing dynamic compression.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): CDNs often handle compression automatically, reducing server load and improving delivery speed.
Testing and Monitoring
Testing is essential to confirm the effectiveness of compression implementation. Monitoring tools provide valuable insights into website performance, allowing for adjustments and optimization.
- Performance Testing Tools: Utilize tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, or WebPageTest to assess page load times before and after implementing compression. This allows for objective evaluation of performance gains.
- Server Logs: Review server logs to identify any issues or bottlenecks related to compression. This aids in troubleshooting and optimization.
- User Experience Tracking: Monitor user behavior and engagement metrics (e.g., bounce rate) to assess the impact of compression on user experience. Lower bounce rates suggest positive user experience, and this is directly tied to website performance.
Potential Impact of Compressibility on User Experience: Is Googles Use Of Compressibility An Seo Myth
Compressibility, the process of reducing the size of files without significantly impacting their content, plays a crucial role in enhancing user experience. It’s a fundamental aspect of web optimization, directly affecting how quickly and smoothly users interact with websites. By making web pages load faster, compressibility improves various aspects of the user journey, from initial engagement to overall satisfaction.Effective compressibility translates into tangible improvements in user experience.
A faster website translates to happier users, leading to increased engagement and reduced frustration. This improvement is particularly noticeable on mobile devices, where limited bandwidth often necessitates quicker loading times for optimal user experience.
Fast Loading Times and User Satisfaction
Faster loading times are directly correlated with higher user satisfaction. Users expect immediate responses and instant access to information. Delayed loading times lead to frustration, often resulting in users abandoning the page before it fully loads. This behavior, known as a high bounce rate, negatively impacts a website’s performance metrics and ultimately its success. Studies consistently show a strong positive relationship between page load speed and user engagement.
A website that loads quickly provides a seamless and positive user experience, encouraging visitors to explore further and potentially convert.
Page Speed and Reduced Bounce Rates
The relationship between page speed and bounce rates is undeniable. A faster page load time directly reduces the likelihood of users abandoning a page before it fully loads. This reduction in bounce rate is a clear indicator of improved user experience. Users are more likely to stay on a page that loads quickly, exploring its content and engaging with its features.
Faster loading translates to increased time on site, more opportunities for conversions, and a more positive perception of the website. A website that prioritizes fast loading times is better positioned to retain users and drive engagement.
Impact of Improved Page Speed on Mobile User Experience
Mobile users are particularly sensitive to slow loading times. Limited bandwidth and varying network conditions often contribute to slower page load speeds on mobile devices. Therefore, optimizing for mobile is crucial. Compressibility is a critical element in achieving optimal mobile performance. By reducing file sizes, websites can drastically improve page load times, creating a seamless and enjoyable experience for mobile users.
This improved performance directly impacts user engagement, satisfaction, and ultimately, the success of the website in the competitive mobile landscape. Optimized loading times on mobile devices directly impact the success of a website.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, while Google hasn’t explicitly declared file compression as a direct ranking factor, the evidence strongly suggests that it’s a vital component of a well-optimized website. Its impact on user experience, page load speed, and ultimately, search engine rankings, is undeniable. This analysis sheds light on the critical role of compressibility in modern strategies. Implementing appropriate compression techniques is not just about technical optimization; it’s about providing a seamless and satisfying user experience, which directly correlates with improved search rankings.