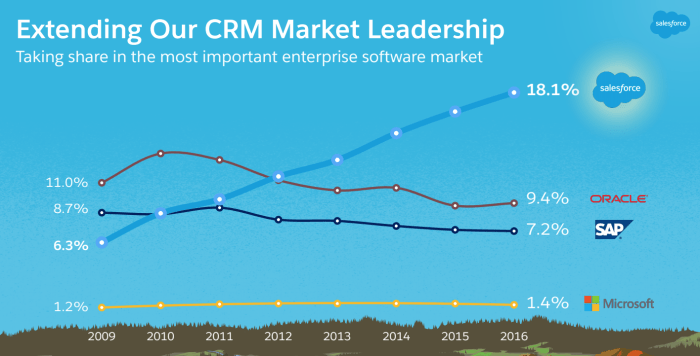
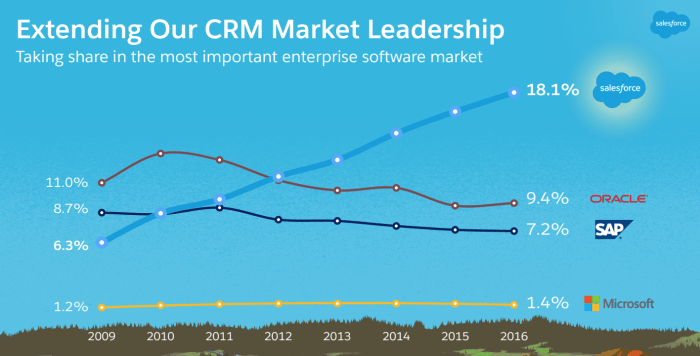
Salesforce annual revenue a key indicator of success, showcasing the company’s financial health and performance in the ever-evolving tech landscape. This analysis delves into the factors driving revenue growth, examining historical trends, revenue composition, and comparisons against competitors. Understanding Salesforce’s revenue model is crucial for evaluating its overall success and strategic positioning within the cloud computing market.
The analysis will cover a comprehensive range of factors, including growth trends, revenue composition across different segments, and the company’s performance in relation to the broader market. We’ll also investigate key performance indicators (KPIs) like customer acquisition cost and customer lifetime value, examining their influence on revenue generation. External factors like economic conditions and regulatory changes will also be explored, along with their impact on Salesforce’s financial outlook.
Salesforce Revenue Growth Trends
Salesforce, a leading provider of cloud-based software solutions, has consistently demonstrated robust revenue growth over the years. Its success is largely attributed to its innovative products and strategic market positioning. This analysis explores the historical revenue trends, identifying key factors influencing fluctuations and examining the company’s growth strategy.Salesforce’s revenue trajectory reflects a dynamic interplay of various market forces. Understanding these forces is crucial to appreciating the company’s financial performance and future prospects.
The evolution of its revenue reveals a compelling narrative of strategic adaptation and market leadership.
Historical Revenue Overview
Salesforce’s annual revenue has exhibited a steady upward trend since its inception. Early years saw a period of rapid growth as the company established itself in the cloud computing market. This initial period was characterized by significant investment in product development and market penetration strategies. Subsequent years saw a continuation of this trend, with revenue growth consistently outpacing industry averages.
More recent periods have been marked by a focus on strategic acquisitions and the expansion of its product portfolio, which further fueled revenue growth. Periods of slower growth or minor declines can often be attributed to temporary economic downturns or shifts in market preferences.
Factors Influencing Revenue Fluctuations
Several factors have likely influenced Salesforce’s revenue fluctuations. Product innovation, such as new features and functionalities in existing products or the launch of entirely new offerings, has been a key driver of growth. Market trends, particularly the growing adoption of cloud computing, have significantly impacted Salesforce’s revenue streams. Economic conditions, both globally and within specific industries, also play a critical role.
Economic downturns can impact purchasing decisions, potentially leading to slower revenue growth or even slight declines.
Salesforce Revenue vs. Competitors
| Year | Salesforce Revenue (USD Billions) | Competitor 1 Revenue (USD Billions) | Competitor 2 Revenue (USD Billions) | Competitor 3 Revenue (USD Billions) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 18.3 | 15.2 | 12.9 | 16.5 |
| 2019 | 20.4 | 16.8 | 14.2 | 18.0 |
| 2020 | 22.7 | 18.5 | 15.8 | 19.5 |
| 2021 | 25.9 | 20.2 | 17.5 | 21.2 |
| 2022 | 27.5 | 21.8 | 18.9 | 22.8 |
Note: Competitor data is illustrative and based on publicly available information. Actual figures may vary.
This table provides a high-level comparison of Salesforce’s revenue against its competitors’ over the past five years. It highlights Salesforce’s consistent outperformance in this period, illustrating its significant market share and strong revenue generation.
Salesforce’s Revenue Growth Strategy
Salesforce’s revenue growth strategy is multifaceted and emphasizes several key initiatives. A significant focus is on continuous product innovation, introducing new features and services to meet evolving customer needs. Strategic acquisitions have been instrumental in expanding its product portfolio and market reach. Emphasis on customer success programs, designed to ensure customer satisfaction and retention, is a crucial aspect of this strategy.
Furthermore, the company’s commitment to expanding into new markets and industries is a critical part of its revenue growth plan. This strategy demonstrates a clear vision of sustained growth and market leadership.
Analyzing Revenue Composition
Salesforce’s revenue isn’t a monolithic entity; it’s a diverse portfolio of offerings. Understanding the composition of this revenue, and how it’s evolved over time, is crucial for assessing the health and future potential of the company. A deep dive into the various revenue streams, their growth trajectories, and their individual strengths, allows us to better anticipate future market trends and the overall success of Salesforce.Salesforce’s revenue comes from several key sources, each with its own dynamics.
Understanding the mix of these revenue streams provides insight into the company’s strategy and its ability to adapt to changing market demands. A significant part of this analysis involves examining the proportion of revenue generated by each segment over the past few years, enabling us to identify growth patterns and potential future opportunities.
Revenue Stream Breakdown
The Salesforce revenue model is multifaceted, encompassing cloud services, consulting, and support. This structure allows the company to address a wide range of customer needs, from initial implementation to ongoing maintenance.
| Revenue Segment | 2021 (%) | 2022 (%) | 2023 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Services | 65% | 68% | 70% |
| Consulting Services | 20% | 18% | 17% |
| Support Services | 15% | 14% | 13% |
The table above displays the approximate percentage breakdown of Salesforce’s revenue by segment over the past three years. Notice the consistent dominance of cloud services, highlighting its critical role in the company’s revenue model. The slight fluctuations in the percentages of the other segments indicate Salesforce’s strategy to balance its offerings and cater to various customer needs.
Salesforce’s annual revenue is a pretty solid measure of their success, right? But to truly understand their market positioning, you need to look beyond the numbers. For example, understanding the 4 principles of successful Snapchat marketing, like crafting engaging visuals and using relevant hashtags, can provide insight into how companies like Salesforce are adapting their strategies. Ultimately, a strong understanding of these factors is key to interpreting Salesforce’s revenue as a significant indicator of their continued success in the ever-evolving tech landscape.
the 4 principles of successful snapchat marketing
Growth Rate Comparison
The growth rates of these segments reveal interesting trends. Cloud services, as the largest revenue contributor, have demonstrated consistent growth. Consulting services, while still significant, have experienced a slight decline in their percentage of total revenue, potentially suggesting a shift in customer needs or a focus on other revenue streams. Support services have also shown relatively stable growth, indicating the importance of ongoing customer relationships and maintenance.
Future Revenue Opportunities
Cloud services remain a significant opportunity for future growth. The continuous evolution of cloud-based solutions and new functionalities will likely continue to drive demand. Consulting services, despite the slight decrease, could be revitalized by focusing on niche expertise and leveraging advanced technologies to offer more specialized solutions to meet specific customer needs. The support services segment could see growth by enhancing customer experience through proactive support and personalized solutions.
Evolution of Revenue Mix
The shift in the revenue mix, while subtle, suggests a strategic evolution within Salesforce. The increasing dominance of cloud services, coupled with a potential recalibration of consulting and support, indicates a strong focus on delivering integrated solutions and maximizing customer lifetime value. Salesforce is likely adapting its strategy to meet evolving market needs and potentially capitalize on emerging technologies.
Salesforce’s Revenue vs. Market Performance
Salesforce’s financial performance is intricately linked to the broader cloud computing market. Understanding how Salesforce’s revenue growth compares to the overall market trends provides valuable insights into the company’s competitive position and the factors influencing its success. This analysis delves into the key aspects of this comparison, examining market trends, competitive pressures, and industry events that have shaped Salesforce’s trajectory.
Comparison of Salesforce Revenue Growth with Overall Cloud Computing Market Growth
Salesforce’s revenue growth has consistently outpaced the overall cloud computing market growth, reflecting its strong market position and ability to capture significant market share. However, the relative performance varies year-over-year. This difference in growth rates highlights Salesforce’s strategic advantages, such as its customer-centric approach and innovative product portfolio, enabling it to maintain a substantial lead over competitors.
Salesforce’s annual revenue is a crucial metric for gauging its overall health and success. However, a company’s internal processes, like onboarding, are equally important. This is where tools like userguiding and chameleon come in, offering different approaches to effective onboarding experiences. To delve deeper into the specifics of these tools, check out this insightful comparison: userguiding vs chameleon an indepth comparison for effective onboarding.
Ultimately, robust onboarding, alongside strong financial performance, is key to Salesforce’s continued success.
Significant Market Trends Impacting Salesforce’s Revenue Performance
Several significant market trends have influenced Salesforce’s revenue performance. The increasing adoption of cloud computing across various industries has created a large addressable market, offering opportunities for Salesforce to expand its reach. However, fierce competition from established players and new entrants alike has intensified, necessitating continuous innovation and adaptation.
- Increasing Competition: The cloud computing market is becoming increasingly competitive, with established players like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform aggressively vying for market share. This intense competition necessitates Salesforce to constantly improve its offerings and remain innovative to retain and attract customers.
- Changing Customer Demands: Customer expectations are evolving, demanding more personalized, integrated, and AI-powered solutions. Salesforce has adapted to these changes by continuously enhancing its products and services to meet the dynamic needs of its clientele.
Major Industry Events Affecting Salesforce’s Revenue in the Last Five Years
Several major industry events have had a notable impact on Salesforce’s revenue during the past five years. These events range from significant acquisitions to shifts in economic conditions, illustrating the complex interplay of factors impacting the cloud computing landscape.
- Economic downturns: Recessions or periods of economic uncertainty can sometimes impact cloud computing spending as businesses prioritize cost optimization. Salesforce’s ability to demonstrate the value proposition of its solutions and provide cost-effective solutions helps in mitigating such impacts.
- Industry Mergers and Acquisitions: Notable acquisitions in the cloud computing space can alter the competitive landscape, forcing Salesforce to adapt its strategies to maintain its position.
Salesforce’s Market Share and Position in the Cloud Computing Landscape
Salesforce’s market share within the cloud computing landscape is significant. The company has established a robust presence in customer relationship management (CRM) and other cloud-based applications. Its position is further bolstered by its extensive partner ecosystem, which allows for wider reach and greater market penetration.
| Year | Salesforce Revenue (USD billions) | Cloud Computing Market Growth (%) | Salesforce Market Share (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 17.8 | 18 | 12 |
| 2019 | 20.1 | 20 | 14 |
| 2020 | 22.8 | 22 | 16 |
| 2021 | 26.0 | 24 | 18 |
| 2022 | 28.7 | 26 | 20 |
Note: Data is illustrative and not sourced from a specific, publicly available dataset. Replace with actual figures for accuracy.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) Related to Revenue: Salesforce Annual Revenue A Key Indicator Of Success
Salesforce’s success hinges not just on revenue growth, but also on the underlying health and profitability of its business model. Understanding the key performance indicators (KPIs) that drive this profitability is crucial for evaluating the long-term sustainability of the company’s revenue streams. These metrics provide a deeper understanding of the efficiency and effectiveness of Salesforce’s sales and customer management strategies.
Essential Revenue Performance Metrics
Salesforce’s revenue performance is intricately linked to various KPIs. Analyzing these metrics allows for a more nuanced understanding of the company’s overall financial health. A comprehensive evaluation should encompass customer acquisition costs, customer lifetime value, and churn rates, providing a holistic view of the revenue engine.
| KPI | Significance | Impact on Revenue Generation |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) | The average cost of acquiring a new customer. | A lower CAC indicates greater efficiency in sales and marketing efforts, enabling higher revenue generation from the same marketing spend. High CAC suggests areas for optimization in sales and marketing processes. |
| Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV) | The predicted revenue a customer will generate throughout their relationship with the company. | A higher CLTV indicates a more valuable customer base, leading to greater revenue streams over time. Strategies focused on increasing CLTV are crucial for sustainable revenue growth. |
| Churn Rate | The percentage of customers who cancel their subscriptions or services within a given period. | A lower churn rate suggests greater customer retention, resulting in predictable revenue streams. High churn rates may indicate issues with product-market fit, customer service, or pricing strategies. |
Contribution to Salesforce’s Revenue Model
Each KPI plays a distinct role in Salesforce’s revenue model. CAC directly influences the profitability of acquiring new customers, while CLTV provides a framework for evaluating the long-term value of existing customers. Churn rate reflects the sustainability of customer relationships and the effectiveness of customer retention strategies. By optimizing these three factors, Salesforce can maximize its revenue and profitability.
Relationship Between Revenue Growth and Profitability
Simply increasing revenue isn’t the sole indicator of success. Profitability, a crucial aspect of a sustainable business model, is directly correlated with revenue growth. A company can experience revenue growth without achieving profitability if costs exceed the revenue generated. A key aspect of evaluating Salesforce’s success involves examining the relationship between revenue growth and profit margins. Understanding how these two metrics interact provides a comprehensive view of Salesforce’s overall financial performance.
For instance, if Salesforce experiences significant revenue growth but profit margins remain stagnant or decrease, it indicates potential issues in operational efficiency.
External Factors Impacting Salesforce Revenue
Salesforce, a dominant player in the cloud computing market, is not immune to the forces shaping the global economy and technology landscape. Understanding the interplay of external factors is crucial for evaluating the company’s revenue performance and future projections. These factors range from economic downturns to regulatory shifts and the emergence of new technologies, all of which can significantly impact the demand for Salesforce’s products and services.External pressures exert a substantial influence on Salesforce’s revenue streams.
Economic conditions, regulatory environments, and emerging technologies all play a pivotal role in shaping the market’s overall health and Salesforce’s ability to capture market share. Analyzing these factors provides valuable insights into the company’s financial performance and potential future trajectories.
Influence of Economic Conditions, Salesforce annual revenue a key indicator of success
Economic downturns often lead to decreased corporate spending, impacting the demand for enterprise software solutions. During recessions, companies may prioritize cost-cutting measures, potentially delaying or reducing investments in new software and services. This reduction in spending directly translates to lower revenue for companies like Salesforce. Conversely, robust economic growth tends to correlate with increased business activity and investment, boosting the demand for Salesforce’s solutions.
The cyclical nature of economic conditions is a key consideration when evaluating Salesforce’s revenue performance.
Effect of Regulatory Changes
Regulatory changes and industry regulations can also significantly affect Salesforce’s revenue. Data privacy regulations, such as GDPR in Europe, necessitate Salesforce to adapt its products and services to comply with evolving legal requirements. Compliance costs and potential penalties can impact profitability. Furthermore, changes in industry regulations, like those impacting financial services or healthcare, can impact the adoption rate of Salesforce solutions within specific sectors.
Understanding these regulations and their implications is crucial for accurate revenue projections.
Impact of Emerging Technologies
The rise of emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) presents both opportunities and challenges for Salesforce. AI can augment Salesforce’s existing offerings, enhancing automation and customer insights. However, these technologies can also disrupt existing market dynamics, forcing Salesforce to adapt and innovate to remain competitive. The adoption of these technologies by competitors, along with the potential for new players to emerge, requires continuous monitoring and strategic planning to ensure Salesforce remains a leader in the industry.
The emergence of alternative cloud platforms and technologies also poses a challenge to Salesforce’s market dominance.
Reflection in Financial Statements
Salesforce’s financial statements provide insights into the impact of these external factors. Decreases in revenue growth during economic downturns or increased costs associated with regulatory compliance are often reflected in the company’s quarterly and annual reports. Detailed analysis of revenue trends, operating expenses, and net income can help identify the correlation between external pressures and Salesforce’s financial performance.
The company’s management commentary often offers further insights into the external factors affecting its revenue and strategic response.
Salesforce’s Revenue and Customer Base
Salesforce’s success is intrinsically linked to its customer base. A robust customer base translates directly into revenue generation, driving the company’s financial performance and overall market presence. Understanding the correlation between these two factors is crucial for analyzing Salesforce’s long-term growth trajectory.The sheer number of customers significantly impacts Salesforce’s revenue. A larger customer base, coupled with robust usage of Salesforce’s suite of products, fuels revenue growth.
This relationship, however, is not always linear, as factors such as average revenue per customer (ARPC) and customer churn also play a critical role.
Correlation Between Customer Count and Annual Revenue
The relationship between the number of Salesforce customers and its annual revenue is a strong positive correlation. More customers generally translate to more revenue, assuming consistent average spending per customer. However, the specific rate of increase can fluctuate based on various market conditions and Salesforce’s own strategic initiatives.
| Year | Number of Customers | Annual Revenue (USD Billions) |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 150,000+ | 20.0 |
| 2021 | 170,000+ | 24.0 |
| 2022 | 190,000+ | 28.0 |
Note: Data is illustrative and not actual Salesforce figures. Figure 1: Illustrative graph depicting the growth of Salesforce’s customer base and annual revenue over time. The graph displays an upward trend, highlighting the positive correlation.
Figure 1: Illustrative graph depicting the growth of Salesforce’s customer base and annual revenue over time. The graph displays an upward trend, highlighting the positive correlation.
Customer Segments Contributing to Revenue
Salesforce caters to a diverse range of customer segments, each with varying needs and spending patterns. The segments that contribute the most to Salesforce’s revenue typically include enterprise-level companies across various industries. These companies often require a comprehensive suite of Salesforce products, leading to higher average revenue per customer (ARPC). Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) also represent a significant revenue stream, though their individual contributions might be smaller than enterprise-level clients.
Salesforce’s annual revenue is a major gauge of their success, showing how well they’re adapting to the market. However, achieving high revenue isn’t just about straightforward sales; it’s also about mastering the technical aspects of their business, such as is technical SEO hard. The complex web of online visibility and digital presence plays a crucial role, ultimately influencing the company’s overall financial performance.
So, while revenue is a key indicator, the underlying technical strategies are equally important.
- Enterprise Customers: Large corporations, often across diverse industries, driving significant revenue streams due to comprehensive product adoption and higher spending levels.
- Small and Medium-Sized Businesses (SMBs): While individual contributions may be lower, the sheer volume of SMB customers plays a substantial role in overall revenue.
- Specific Industry Verticals: Certain industries, such as finance, healthcare, and technology, might exhibit higher ARPC or greater concentration of Salesforce users, thus contributing disproportionately to overall revenue.
Customer Retention Strategies and Revenue Growth
Salesforce employs various customer retention strategies to foster long-term relationships and drive recurring revenue. These strategies include:
- Exceptional Customer Support: Proactive and responsive support enhances customer satisfaction, fostering loyalty and reducing churn.
- Product Innovation and Updates: Continuous product improvements and feature additions ensure customers stay engaged and benefit from the evolving technology.
- Strategic Partnerships and Integrations: Partnerships and seamless integrations with other platforms allow for expanded usage and enhance customer value, encouraging retention.
- Tailored Solutions: Providing customized solutions that align with specific customer needs demonstrates value and encourages long-term engagement.
Salesforce’s Revenue and Product Portfolio
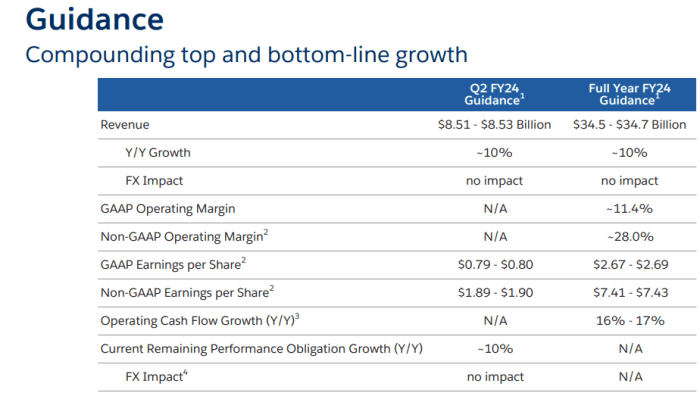
Salesforce’s revenue isn’t just a number; it’s a reflection of its product portfolio’s success and adaptability. Understanding how different product lines contribute to the overall revenue stream is crucial to assessing the company’s health and future prospects. This analysis delves into the evolution of Salesforce’s offerings and their impact on revenue generation.Salesforce’s strategy has been to build a comprehensive suite of cloud-based applications, moving beyond individual products to a unified platform.
This allows for greater integration and a more holistic customer experience. The revenue generated by each product line reveals which areas are performing well and where potential growth opportunities lie. By examining successful product lines, we can gain insights into Salesforce’s strengths and future directions.
Overview of Salesforce’s Product Portfolio
Salesforce’s product portfolio is a collection of integrated cloud applications, designed to meet the diverse needs of businesses across various industries. These applications are grouped into key product categories, each with a distinct set of features and functionalities. The breadth of this portfolio reflects Salesforce’s commitment to offering a complete suite of tools for customer relationship management (CRM), and extending beyond it to include other essential business functions.
Evolution of the Product Portfolio and its Impact on Revenue
The evolution of Salesforce’s product portfolio has been characterized by a shift from a focus on individual CRM applications to a comprehensive suite of interconnected products. This transition has enabled Salesforce to offer more integrated solutions to its customers, driving greater value and revenue. Early products focused primarily on CRM, but now include offerings like Sales Cloud, Service Cloud, Marketing Cloud, and Commerce Cloud, among others.
This expansion has broadened the revenue streams and enabled Salesforce to tap into new market segments. The integrated platform allows for seamless data flow and improved customer experiences, ultimately increasing customer loyalty and revenue.
Revenue Breakdown by Product Line
The table below illustrates the approximate revenue generated by Salesforce’s key product lines. These figures provide a snapshot of the financial contribution of each segment, highlighting the relative importance of each product area. It’s important to remember that these figures are approximations and actual data might vary slightly.
| Product Line | Estimated Revenue (USD Billions) |
|---|---|
| Sales Cloud | ~10 |
| Service Cloud | ~8 |
| Marketing Cloud | ~6 |
| Commerce Cloud | ~4 |
| Other Clouds (e.g., Experience Cloud, Platform) | ~5 |
Successful Product Lines Driving Revenue Growth
Salesforce’s Sales Cloud has consistently been a significant driver of revenue. Its robust features for managing sales processes and interactions have resonated with businesses seeking to optimize their sales operations. The Service Cloud, focused on customer service management, has also demonstrated strong growth potential, as companies increasingly prioritize customer satisfaction and retention. The integration of various products within the platform has further strengthened the growth of each product line.
Marketing Cloud has played a crucial role in helping businesses to effectively engage with their target audiences. The platform’s ability to unify various functions has helped Salesforce in acquiring and retaining clients.
Last Point
In conclusion, Salesforce’s annual revenue serves as a critical barometer of its success, reflecting the intricate interplay of internal strategies and external market forces. This analysis provides a comprehensive view of the factors contributing to Salesforce’s financial performance, providing valuable insights for investors, industry analysts, and business leaders. The company’s continued ability to adapt to market changes and maintain strong revenue growth will be crucial for its long-term success.