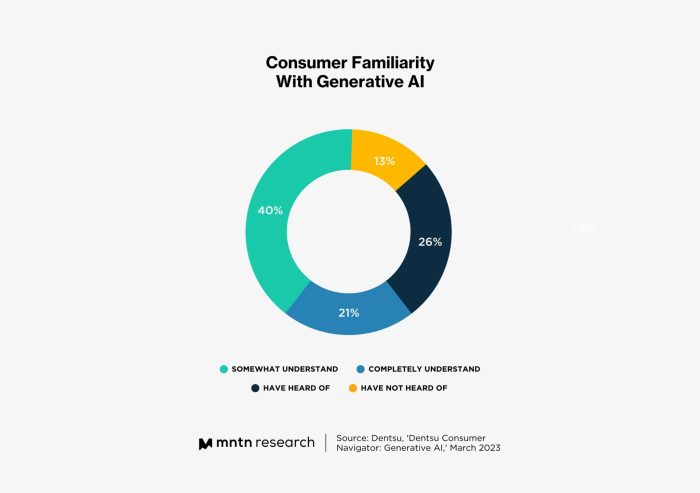
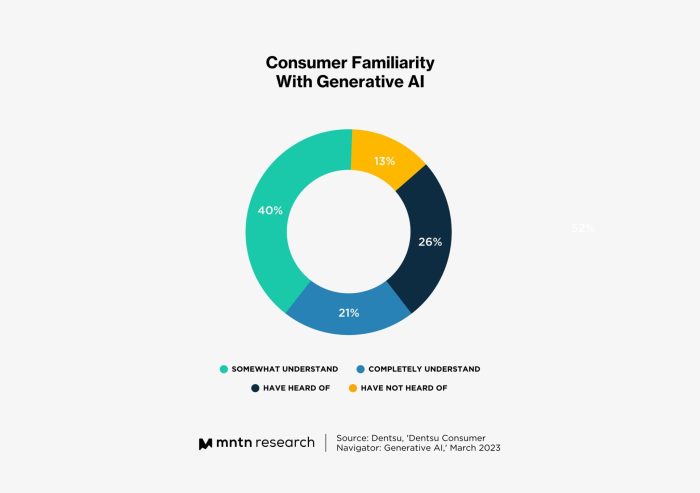
Studies reveal consumers easily detect ai generated content – Studies reveal consumers easily detect AI-generated content, highlighting a fascinating dynamic in the digital age. Consumers are surprisingly adept at identifying content crafted by artificial intelligence, showcasing a level of discernment that goes beyond simple aesthetics. This ability is influenced by a variety of factors, from the subtle stylistic choices of the AI to the context surrounding the content.
We’ll delve into the methods consumers use, the impact of content quality, and external influences on their perception.
The study explores consumer perception across different types of AI-generated content, including text, images, and videos. It examines the specific cues and indicators that signal AI authorship, providing insight into the cognitive processes involved. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for AI developers, content creators, and anyone seeking to navigate the evolving landscape of digital media.
Consumer Perception of AI-Generated Content
Consumers are increasingly exposed to AI-generated content, from articles and social media posts to images and videos. This exposure has led to a complex and evolving perception, marked by both curiosity and skepticism. Understanding this perception is crucial for developers, marketers, and consumers alike, as AI’s role in content creation continues to grow.Consumer perceptions of AI-generated content are nuanced and often depend on the specific type of content and the context in which it’s presented.
Factors like the perceived quality, the intended use, and the source of the content all play a role in how consumers react. This includes the perceived sophistication of the AI model, the perceived effort and creativity behind the content, and the user’s prior experience with AI-generated content.
Factors Influencing Detection of AI-Generated Content
Consumer ability to detect AI-generated content is influenced by various factors. The level of sophistication in the AI model, and the specific characteristics of the content itself, significantly impact the likelihood of detection. For instance, early iterations of AI-generated text often displayed tell-tale signs of unnatural phrasing and grammatical errors, making them easily identifiable. However, advancements in AI technology are making it increasingly difficult to discern AI-generated content from human-created content.
Recent studies show consumers are surprisingly good at spotting AI-generated content, which is interesting given the ongoing debate about how to best identify it. This ability to detect AI-generated content might be particularly important when considering social media platforms like Twitter and Instagram, where the lines between human-created and AI-generated content are often blurry. For example, comparing the user experience of Twitter vs Instagram Threads ( twitter vs instagram threads ) reveals that distinguishing between the two might become even more critical in the future.
This highlights how crucial it is for platforms to be transparent about AI use, ultimately benefiting the user experience. The studies’ findings reinforce the need for clear guidelines and markers to help users discern AI-generated content from human-created content.
Furthermore, the specific format of the content and the context in which it is presented also influence detection. A polished and contextually relevant AI-generated article might be less easily recognizable than an AI-generated image with obvious stylistic inconsistencies.
Potential Biases and Limitations in Consumer Assessments
Consumer assessments of AI-generated content are not always objective. Preconceived notions about AI, the source of the content, and personal biases can significantly affect perceptions. For example, if a consumer distrusts a particular website or social media platform, they might be more likely to perceive content from that source as AI-generated, even if it’s not. Likewise, a consumer’s familiarity with the specific type of AI model used can also influence their assessment.
Additionally, the presence of stylistic or factual inconsistencies does not always guarantee that the content is AI-generated, as human error and creative choices can also lead to similar outputs.
Common Characteristics of Easily Recognizable AI-Generated Content
Consumers often identify AI-generated content through certain patterns. These include repetitive phrasing, unnatural sentence structure, and inconsistencies in tone or style. The lack of nuance, a tendency towards generic or overly positive descriptions, and a superficial level of detail are also common indicators. In images, a lack of natural lighting, unusual proportions, or repetition of similar elements can suggest AI generation.
In videos, unnatural movements or awkward interactions between characters are sometimes noticed.
Comparison of AI-Generated Content Detectability
| Content Type | Factors Affecting Detectability | Common Indicators of AI Generation |
|---|---|---|
| Text | Grammatical errors, unnatural phrasing, repetitive patterns, lack of nuance, generic descriptions | Awkward sentence structures, abrupt shifts in tone, inconsistent style, excessive use of s |
| Images | Unnatural lighting, proportions, and composition, lack of realism, repeated patterns or objects, unrealistic details | Obvious inconsistencies in lighting or shading, unnatural details, repeated or cloned elements |
| Videos | Unnatural movements, awkward interactions between characters, unrealistic facial expressions, lack of emotional depth, generic or repetitive actions | Jump cuts, abrupt transitions, awkward camera angles, repetitive or robotic movements, unrealistic facial expressions |
Detection Methods and Strategies

Consumers are increasingly adept at recognizing AI-generated content, often employing a combination of subtle cues and intuitive judgments. This growing awareness highlights the evolving relationship between humans and artificial intelligence, particularly in the realm of creative expression and information dissemination. Understanding the methods consumers use to identify AI-generated content is crucial for both creators and AI developers. This knowledge allows for more transparent and ethical practices surrounding AI-generated output.Consumers employ a variety of methods to discern AI-generated content, ranging from conscious analysis of stylistic elements to unconscious recognition of patterns.
This multifaceted approach reflects the complex interplay between conscious and subconscious cognitive processes in content evaluation. These methods are further influenced by individual experiences, prior knowledge, and the specific type of content being assessed.
Cognitive Processes in Detection
Consumers often engage in a combination of analytical and intuitive processes when evaluating content. Analysis involves scrutinizing the content for inconsistencies, unnatural phrasing, and stylistic deviations from typical human expression. Intuition plays a significant role in recognizing the “feel” of a text or image, drawing upon prior experiences with similar content produced by humans. The interplay of these cognitive processes results in a nuanced and often subconscious evaluation of authenticity.
Specific Cues and Indicators
Consumers frequently rely on specific cues to identify AI-generated content. These cues can be related to inconsistencies in writing style, such as unnatural sentence structures, awkward phrasing, or a lack of emotional depth. Image generation often reveals imperfections in the image’s composition, texture, or details. Inconsistencies in the logic or coherence of the information presented can also serve as a significant indicator.
Detection Methods by Content Type
| Content Type | Detection Methods |
|---|---|
| Text | Inconsistencies in writing style, unnatural sentence structures, lack of emotional depth, repetitive phrasing, or unusual vocabulary choice. |
| Images | Imperfections in composition, texture, or details, unnatural lighting or perspective, lack of natural transitions between objects, or inconsistent object proportions. |
| Audio | Monotonous or robotic tone, lack of natural inflection, or unnatural pacing in speech. |
| Videos | Awkward movements or unnatural expressions, inconsistencies in background or object movements, and noticeable repetition in action sequences. |
Demographic Variations in Effectiveness
The effectiveness of detection methods varies across different demographics. Younger generations, particularly those who have grown up with AI-generated content, often demonstrate a heightened awareness and ability to identify AI-generated text and images. Individuals with higher levels of education or experience in evaluating written or visual content may also exhibit better performance in recognizing AI-generated material. Furthermore, cultural background can play a role in perceptions of what constitutes “natural” content.
Impact of Content Quality and Style
The quality and style of AI-generated content play a significant role in its detectability. Consumers are becoming increasingly adept at recognizing patterns and inconsistencies in machine-generated text, making it crucial for AI content creators to understand how these factors influence the likelihood of detection. A well-crafted piece, regardless of its origin, is more likely to be perceived as authentic and convincing.Sophisticated AI models, while capable of producing remarkably human-like text, can still exhibit telltale signs of their artificial nature if the underlying content quality is poor.
The stylistic choices made by the AI, coupled with the overall quality of the writing, directly influence consumer perception.
Quality of AI-Generated Content and Detectability
The quality of AI-generated content significantly impacts its detectability. Poorly written content, marked by grammatical errors, illogical flow, and a lack of nuanced expression, is readily identifiable as AI-generated. This is because such content often reveals a lack of understanding of the subject matter and an inability to adapt language to the specific context. Conversely, well-written, high-quality AI-generated content that demonstrates a strong understanding of the topic and effectively conveys the intended message is often more difficult to detect.
Stylistic Choices and Detection Likelihood
Stylistic choices can influence the likelihood of AI detection. For instance, the use of overly formal or overly informal language can flag content as artificial. An AI struggling to maintain a consistent tone throughout a piece might be more readily detected. Likewise, the repetition of certain phrases or patterns of sentence structure, often a byproduct of limited training data, can signal to discerning readers that the content was not authored by a human.
Recent studies highlight how easily consumers spot AI-generated content, which is a major hurdle for marketers. This makes it crucial to optimize your sales funnel to effectively connect with real people and build trust, ensuring that your efforts don’t fall flat. A well-structured make sales funnel convert better is key to this; ultimately, the ability to craft authentic and engaging content is vital for any business trying to succeed in today’s increasingly discerning market.
Correlation Between AI Model Sophistication and Detection Difficulty
The sophistication of AI models correlates with the difficulty of detection. Early AI models often produced content with readily apparent flaws, making detection straightforward. More advanced models, however, are better equipped to mimic human writing styles, making detection significantly more challenging. This increasing sophistication necessitates a constant evolution in detection methods and consumer awareness.
Impact of Content Format on Detection Rates
Content format, such as formal versus informal, can affect detection rates. An AI trained on formal academic writing might struggle to produce an engaging blog post or a witty social media update. Similarly, an AI trained on informal conversational styles might not be able to adhere to the structure and tone of a legal document. This variation in format can serve as a cue for consumers to scrutinize the content’s authenticity.
Role of Context and Surrounding Information in Detection
The context and surrounding information play a crucial role in aiding consumer detection. For example, a seemingly coherent paragraph within a poorly researched article might still be identified as AI-generated due to the surrounding content. Consumers, by considering the broader context, are more likely to identify inconsistencies and detect artificiality. This is further reinforced by comparisons with other sources on the same topic, where the AI-generated content might deviate from the general consensus or demonstrate a lack of nuanced understanding.
External Factors Affecting Detection
Consumer understanding of AI-generated content isn’t solely dependent on the content itself. Various external factors play a crucial role in shaping how readily individuals identify AI-generated text or imagery. These external influences can significantly impact a consumer’s ability to discern authentic content from AI-produced output.Understanding these external factors is essential for developing effective strategies to mitigate the spread of misinformation and enhance consumer trust in the digital sphere.
Factors like prior experience, media portrayals, technological advancements, and cultural contexts all contribute to how easily consumers recognize AI-generated content.
Prior Experience with AI-Generated Content
Consumer familiarity with AI-generated content significantly impacts their ability to detect it. Individuals who have encountered and interacted with AI-generated content in the past are more likely to develop a keen eye for the telltale signs of artificial authorship. This prior exposure cultivates a heightened awareness of potential inconsistencies, stylistic quirks, and logical fallacies often associated with AI-generated output.
Repeated encounters allow for the formation of a mental catalog of characteristics that help consumers identify AI-generated content. For example, a user familiar with the repetitive language patterns of certain AI text generators will be better equipped to spot similar patterns in other generated content.
Impact of Media Portrayals of AI and its Capabilities
Media depictions of AI and its capabilities shape public perception, influencing how consumers perceive and react to AI-generated content. If media portrays AI as a sophisticated and powerful tool capable of creating near-perfect replicas of human-created content, consumers may become less vigilant in detecting AI-generated outputs. Conversely, portrayals emphasizing the limitations and potential flaws of AI tools might encourage a more critical approach to such content.
The portrayal of AI as a tool for misinformation or manipulation can lead to increased vigilance, but also can lead to the rejection of authentic content created by AI if consumers are overly wary. For instance, if a news outlet frequently features stories about AI-generated deepfakes, consumers might be more sensitive to the subtle signs of manipulated content.
Recent studies show consumers are surprisingly adept at spotting AI-generated content, which is a huge hurdle for marketers. This highlights the need for authenticity and genuine engagement, especially when trying to re-engage dead email subscribers. Strategies like re-engaging dead email subscribers require a thoughtful approach, focusing on value-added content and personalized interactions. Ultimately, the ability of consumers to easily detect AI-generated content reinforces the importance of human connection in marketing efforts.
Technological Sophistication of AI Tools
The sophistication of AI tools directly affects consumer detection abilities. As AI tools become more advanced, they generate content that is increasingly difficult to distinguish from human-created content. This progress in AI technology often outpaces consumer awareness, making it harder for individuals to identify the artificial origins of content. A simple example is the evolution of image generation tools.
Early image generators produced noticeably artificial images, while newer models can create remarkably realistic and convincing visuals. This constant evolution necessitates a constant adaptation of detection methods and strategies.
Cultural Differences in Consumer Reactions
Cultural background and societal norms significantly influence consumer reactions to AI-generated content. Cultures that place a high value on originality and human creativity may exhibit a stronger aversion to AI-generated content. Conversely, cultures with a more pragmatic approach to technology may be more accepting of AI-generated content, perhaps seeing it as a useful tool. For example, a culture that emphasizes the authenticity of written language may have a more rigorous approach to identifying AI-generated text.
Table: External Factors Affecting Detection
| External Factor | Potential Impact on Detection Rates |
|---|---|
| Prior experience with AI-generated content | Higher exposure leads to improved detection abilities |
| Media portrayals of AI | Positive portrayals may decrease vigilance; negative portrayals may increase it. |
| Technological sophistication of AI tools | Increased sophistication makes detection more challenging. |
| Cultural differences | Cultural values influence acceptance and detection of AI-generated content. |
Illustrative Examples of AI-Generated Content: Studies Reveal Consumers Easily Detect Ai Generated Content
AI-generated content is rapidly evolving, impacting various sectors. Understanding its characteristics is crucial for discerning its authenticity. This section provides concrete examples to illustrate different forms of AI-generated content, highlighting their unique features and potential stylistic cues.
AI-Generated Text Sample
AI text generators are becoming increasingly sophisticated, producing outputs that mimic human writing. A typical example might be a news article about a recent scientific discovery. The generated text would likely exhibit a coherent structure, including an introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. However, closer examination reveals potential stylistic inconsistencies. For instance, the language might sound overly formal or overly casual in places, a telltale sign of automated creation.
Repeating certain phrases or sentences is another possibility. The text might use vocabulary that feels somewhat generic or predictable.
AI-Generated Image
AI image generators create visuals that are sometimes realistic but can also exhibit a particular style. A generated image could depict a stylized portrait of a historical figure, with a distinctive artistic style and colors. The image may feature intricate details that are difficult to achieve manually, but these details may also exhibit patterns or repetitions. The facial features might be slightly exaggerated or the background may contain unrealistic textures or gradients.
Analyzing the image for consistency in style and potential technical artifacts, such as the presence of “artifacts” in the background, can help discern its origin.
AI-Generated Video, Studies reveal consumers easily detect ai generated content
AI-generated videos are emerging as a powerful tool for content creation. An example could be a short promotional video for a new product, showcasing its features in a dynamic way. The video might feature realistic but somewhat generic movements and actions. The background and visual effects may seem seamless, but there may be slight inconsistencies in the movements or animations.
The audio, though likely clear and understandable, may lack the natural nuances and variations of human speech or sound design. Analyzing the audio and visual elements in tandem for unnatural transitions, abrupt changes, or a lack of emotional range in the characters is crucial.
Identifying Stylistic Cues
Analyzing AI-generated content involves looking for patterns that distinguish it from human-created content. Common stylistic cues include repetitive phrasing, predictable vocabulary, inconsistent tone, and unusual sentence structures. The use of clichés or generic imagery is another indication. The absence of personal experiences, unique perspectives, and nuanced emotional responses is often a marker of AI-generated content.
Comparing and Contrasting with Human-Created Content
Comparing AI-generated content with human-created content helps establish a baseline for authenticity. A comparison would involve analyzing the depth of the content, the originality of ideas, and the emotional impact. Human-created content often displays unique perspectives, personal experiences, and genuine emotions. In contrast, AI-generated content may lack these elements. The writing style, visual features, and overall message of AI-generated content may appear overly generic or predictable, while human-created content often displays originality and unique expressions.
Content Analysis Framework
Analyzing consumer responses to AI-generated content requires a structured approach to understand how individuals perceive and detect such output. This framework aims to systematically evaluate consumer reactions, moving beyond simple detection to a deeper understanding of the factors influencing those judgments. It combines quantitative and qualitative data to provide a comprehensive picture of the process.A robust framework for analyzing consumer reactions to AI-generated content is crucial for understanding the nuances of human perception and the development of strategies for improving AI content generation.
By dissecting consumer responses, we can identify the specific characteristics of AI-generated content that trigger suspicion and develop targeted methods to mitigate those issues.
Consumer Behavior Categorization
Understanding consumer responses necessitates a systematic categorization of behaviors. The following table categorizes various aspects of consumer behavior in response to AI-generated content. This framework allows for a structured evaluation of the diverse reactions and provides a common language for analyzing results.
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Detection Accuracy | Measures the proportion of AI-generated content correctly identified by consumers. Higher accuracy indicates a stronger ability to distinguish between human and AI-created content. |
| Reasoning for Detection | Explores the specific cues that lead consumers to identify AI-generated content. This might include grammatical errors, stylistic inconsistencies, or perceived lack of emotional depth. |
| Content Quality Perception | Evaluates consumers’ perception of the overall quality of the AI-generated content. Factors like coherence, factual accuracy, and originality are considered. |
| Emotional Response | Examines the emotional reactions elicited by AI-generated content, such as trust, skepticism, or a sense of disengagement. |
| Contextual Impact | Investigates how the context in which AI-generated content is presented influences consumer perception. This includes the platform, the purpose of the content, and the perceived authority of the source. |
Quantitative Data Analysis Methods
Quantitative data, such as survey responses and click-through rates, provides measurable insights into consumer behavior. Statistical analysis techniques, including correlation and regression analysis, can reveal relationships between different aspects of AI-generated content and consumer reactions. For example, analyzing click-through rates on AI-generated advertisements versus human-written ones can reveal the effectiveness of the generated content.
Qualitative Data Analysis Methods
Qualitative data, such as interviews and focus groups, offers rich insights into the reasons behind consumer reactions. Thematic analysis and grounded theory methods can be employed to identify recurring patterns and themes in consumer feedback. Analyzing open-ended responses in surveys can reveal nuances and motivations that may be missed in quantitative analyses.
Reliability and Validity
Ensuring the reliability and validity of the analysis framework is paramount. The framework should be tested using multiple samples and different types of AI-generated content to verify consistent results. Inter-rater reliability should be established by having multiple researchers independently code the data to ensure consistency. Furthermore, the framework’s validity can be assessed by comparing the results to existing literature on consumer behavior and perception.
Using a validated scale to measure trust and credibility in AI-generated content is a good example of increasing validity.
Epilogue
In conclusion, the ability of consumers to detect AI-generated content is multifaceted and influenced by a complex interplay of factors. From the inherent stylistic limitations of current AI models to the context and quality of the content, consumers are proving to be remarkably astute judges. This awareness underscores the need for greater transparency and potentially, the development of more sophisticated AI tools that can better mimic human creativity.
The ongoing evolution of AI and consumer perception will undoubtedly shape the future of digital content creation and consumption.