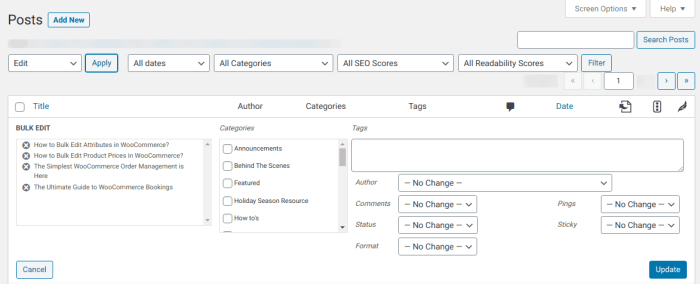
The differences between posts and pages in WordPress are crucial for website structure and . Understanding these distinctions allows you to organize your site effectively, guiding users through your content and optimizing it for search engines. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the nuances of posts and pages, examining their intended use, organization, functionality, and considerations.
WordPress posts are typically used for blog-style content, articles, and news updates. They often appear in chronological order and are excellent for showcasing dynamic content. Pages, on the other hand, are static, providing crucial information like “About Us,” “Contact,” or product descriptions. This clarity in purpose is key to a well-structured website.
Defining Posts and Pages
WordPress posts and pages are fundamental building blocks for any website. Understanding their distinctions is crucial for effectively structuring content and managing your site’s information architecture. Posts are typically used for time-sensitive, frequently updated content, while pages are designed for static, informational elements. This difference dictates their use and presentation on your website.Understanding the nuances between posts and pages allows you to organize your content strategically, maximizing user experience and search engine optimization.
This distinction ensures that your website is not only visually appealing but also functional and well-structured.
Defining WordPress Posts, The differences between posts and pages in wordpress
WordPress posts are dynamic, time-stamped entries. They are intended for frequently updated content, such as blog articles, news items, or reviews. Posts are inherently tied to a publication date and are often organized chronologically. Their dynamic nature allows for ongoing updates and interactions, such as comments and sharing. This is ideal for content that needs to be regularly refreshed, like news articles or personal musings.
Defining WordPress Pages
WordPress pages are static, informational elements designed for permanent content. They provide information about your site, such as an “About Us” page, a “Contact Us” page, or a “Services” page. Pages are not typically updated with the same frequency as posts, and they often serve as the foundation for navigating your site. This is essential for conveying permanent information about your site.
Fundamental Differences
The core difference lies in their intended purpose. Posts are for dynamic, time-sensitive content that can be updated frequently. Pages are for static, informational content that remains consistent over time. This difference impacts the way they are displayed and managed within the WordPress platform. This also influences how users interact with the content.
Typical Use Cases
Posts are excellent for:
- Blog articles
- News updates
- Product reviews
- Daily musings or reflections
Pages are ideal for:
- About Us page
- Contact information
- Services or products descriptions
- Terms and conditions
- Sitemap
The choice between a post or a page depends heavily on the nature of the content and its expected lifespan.
Comparison Table
| Characteristic | Post | Page |
|---|---|---|
| Use | Dynamic, time-sensitive content (e.g., blog posts, news articles) | Static, informational content (e.g., “About Us,” “Contact Us”) |
| Visibility | Often displayed in reverse chronological order, with recent posts appearing first. | Typically accessed directly through navigation menus or links. |
| Structure | Can incorporate various formatting elements like headings, images, and videos. | Generally focuses on clear, concise information. |
The table highlights the key distinctions between posts and pages, providing a clear comparison of their attributes. This aids in understanding their individual roles in website structure.
Functionality and Features
Posts and pages, while both vital components of a WordPress website, serve distinct purposes and offer different functionalities. Understanding these differences is crucial for effectively structuring your website’s content and maximizing its potential. Knowing which content type to use for specific information is essential for a well-organized and user-friendly experience.WordPress’s flexible system allows for tailoring content based on its purpose, whether it’s for showcasing static information or dynamic, frequently updated material.
Posts and pages are managed differently, impacting how they appear on the site and how they are updated. This section will delve into the key features that differentiate posts from pages.
Post-Specific Features
Posts are designed for dynamic, time-sensitive content like blog articles, news updates, or any material needing frequent revisions. They are intrinsically linked to the concept of a blog. Crucially, posts are typically organized chronologically, allowing for easy tracking of updates and recent content.
Page-Specific Features
Pages, in contrast, are ideal for static information that doesn’t require constant updating. Think about “About Us,” “Contact,” or “Services” pages. Pages are less focused on a chronological order and are better for presenting information that is more permanent in nature.
WordPress Admin Panel Management
The WordPress admin panel offers distinct interfaces for managing posts and pages. Posts are usually managed through a list view that displays the title, date, and author. This list format facilitates efficient management of multiple posts. Pages are typically organized in a hierarchical structure, allowing for easy navigation and organization.
Content Types
Posts and pages can accommodate various content types. Posts excel at blog-style articles, news pieces, and discussions. Pages can effectively host more complex layouts, including tables, galleries, and embedded media, often used for static information and complex content.
Display on the Website
Posts, often arranged chronologically, appear in a designated area on a website, often used for a blog feed or news section. Pages, being static, are typically accessed through a menu or navigation bar. Their location on the site is more predictable and consistent.
Creating Posts and Pages with Attributes
Creating a post involves filling out fields like title, content, categories, and tags. Creating a page is similar but allows for more customization regarding page templates and layout. For example, a page might incorporate a specific layout or have a different template compared to a blog post. These templates allow the presentation of information in a manner tailored to its purpose.
Visibility Control
WordPress allows controlling the visibility of both posts and pages. You can choose to make them public, visible only to specific users, or even hide them entirely. This flexibility enables you to manage the flow of information on your website.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Post | Page |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Dynamic, time-sensitive content | Static, unchanging information |
| Organization | Chronological | Hierarchical |
| Management | List view in admin panel | Hierarchical structure in admin panel |
| Content Types | Blog posts, news updates | About Us, Contact, Services |
| Display | Usually in a blog feed | Typically accessed via menu |
| Visibility | Can be public, private, or password protected | Can be public, private, or password protected |
Considerations
Optimizing your WordPress site for search engines is crucial for attracting organic traffic. Understanding the nuances of how posts and pages are treated by search engines allows you to strategically improve your site’s visibility and rankings. This section dives into best practices for both post and page types, helping you tailor your content for optimal search engine indexing and user experience.Search engines crawl and index both posts and pages, but their intended purposes often influence how these elements are treated.
Posts, typically used for time-sensitive or frequently updated content, are often seen as more dynamic. Pages, on the other hand, are usually for static or more enduring information, treated as more stable. This understanding is key to effective strategy.
Ever wondered about the difference between posts and pages in WordPress? Posts are great for dynamic content like blog articles, while pages are usually for static content like “About Us” or “Contact.” Knowing this structure is crucial, especially when you’re optimizing your website for search engines. For example, recent changes in AdWords, like the introduction of new promotion extensions, custom intent audiences, and ad variations testing, adwords introduces new promotion extensions custom intent audiences ad variations testing , highlight the importance of a well-organized site.
This is all interconnected with the fundamental structure of WordPress; understanding posts and pages is key to building a website that’s both engaging and search-engine friendly.
Post Differences
Posts, due to their dynamic nature, are frequently updated and usually cover a wide range of topics. This inherent variability can make them ideal for attracting visitors interested in trending or timely subjects. For example, a blog post on a recent technological advancement will likely attract readers seeking current information.
Page Differences
Pages are typically used to showcase more permanent information like “About Us,” “Contact Us,” or “Services.” This static nature allows search engines to better understand the page’s purpose and content. For instance, a “Services” page with details on different product offerings should be clearly indexed and understood as a source of information.
Structure Impact on
Well-structured content is key to successful . Posts and pages should use headings (H1-H6) to organize content logically. Use subheadings to break up large blocks of text, improving readability and helping search engines understand the hierarchy of information. This approach also improves the user experience. Use descriptive, -rich titles and meta descriptions for both posts and pages to entice clicks from search engine results pages.
Search Engine Indexing Differences
Search engines index posts and pages differently, primarily based on their intended use. Posts are often treated as newer, more frequently updated content, indexed and ranked accordingly. Pages, with their static nature, tend to be indexed as reliable and comprehensive resources. Search engines look at the overall structure, including s, headings, and content quality.
Optimization Best Practices
Optimizing posts and pages for search engines requires a multifaceted approach. Using relevant s naturally within the content is vital. Avoid stuffing; instead, focus on providing valuable and comprehensive information. Optimize images with alt text, which helps search engines understand the image content. Ensure your site is mobile-friendly and loads quickly.
Use internal and external linking strategies to improve navigation and demonstrate authority. The use of schema markup can provide additional context to search engines, which can positively influence rankings.
Understanding the difference between posts and pages in WordPress is key for effective content organization. Posts are dynamic, perfect for articles and blog entries, while pages are static, ideal for “about us” or “contact” information. Knowing this, you can craft a content strategy that resonates with your audience and enhances your online presence. This directly relates to how to use content marketing to improve your online reputation how to use content marketing to improve your online reputation.
Ultimately, choosing the right format for your content helps you build a strong online identity and connect with potential customers.
Site Navigation and User Experience
Organizing posts and pages logically improves site navigation and user experience. A clear site structure with well-defined categories and tags for posts enhances user exploration and encourages them to spend more time on your site. Using a logical hierarchical structure for pages, such as organizing “About Us” pages under a main navigation section, improves site usability.
Best Practices Table
| Feature | Post | Page |
|---|---|---|
| Content Type | Dynamic, frequently updated | Static, less frequently updated |
| Structure | Use clear headings and subheadings, cater to current trends | Use headings, organize logically for enduring information |
| s | Focus on relevant s, avoid stuffing | Use s naturally, describe the page’s content |
| Indexing | Indexed as dynamic content | Indexed as comprehensive resources |
| Optimization | Optimize for current search trends, focus on timeliness | Optimize for consistent, in-depth information |
| Navigation | Categorize and tag posts for better site exploration | Organize pages logically to improve site usability |
User Experience (UX) and Navigation
Posts and pages are the fundamental building blocks of a WordPress website, directly impacting the user experience. Effective navigation between them is crucial for guiding visitors smoothly through the site’s content and achieving their goals. A well-structured site design, employing posts and pages strategically, can significantly enhance user engagement and satisfaction. Understanding how these elements contribute to the overall user experience is essential for creating a successful online presence.Clear navigation is paramount for a positive user experience.
Users should intuitively understand how to access different sections of the site, whether it’s exploring blog posts or accessing crucial information on a dedicated page. The website’s architecture, defined by the placement of posts and pages, directly influences user engagement and satisfaction. Poor navigation can lead to frustration and abandonment, while a well-organized structure encourages exploration and deeper engagement.
Contribution to User Experience
Posts, typically used for blog articles, news updates, or short-form content, are excellent for showcasing dynamic information. They help keep the website fresh and encourage readers to return. Pages, designed for static information like “About Us,” “Contact,” or “Services,” provide a structured way to access essential details. The combination of these two content types provides a balanced and comprehensive user experience, catering to different information needs.
Importance of Clear Navigation
Navigational elements, such as menus, breadcrumbs, and internal links, play a critical role in guiding users. Well-placed links facilitate seamless transitions between posts and pages, allowing users to explore related content without difficulty. A clear navigation system helps users quickly locate the information they need, boosting user satisfaction and engagement. Poor navigation, on the other hand, can lead to a frustrating user experience and lost opportunities.
Ever wrestled with WordPress posts versus pages? Understanding the difference is key, just like knowing how to track your marketing success is crucial. For example, if you’re looking at how to measure your marketing agency’s (MA) success, you’ll need to determine which content best serves that purpose. Think of posts as a blog’s dynamic content, perfect for quick updates, while pages are static, like landing pages.
Knowing this helps you decide what content type to use for specific goals, much like how how to measure MA success will depend on the metrics you’re tracking. Ultimately, understanding these differences allows you to build a more effective and targeted WordPress site.
Placement and User Engagement
The placement of posts and pages directly influences user engagement. Strategic placement of key pages, such as “About Us” or “Contact,” in prominent areas of the website ensures that crucial information is easily accessible. Posts can be grouped into categories or tags, allowing users to easily explore related topics. For instance, organizing blog posts by category makes it easier for users to find articles relevant to their interests.
Guiding Users Through the Website
Strategic use of posts and pages can effectively guide users through the website. For example, a “Getting Started” page with links to related posts can provide a step-by-step process for new users. Internal links between posts and pages help users discover related content and deepen their engagement with the website. This strategic linking creates a user journey that’s not only informative but also enjoyable.
User Flows on a Website
A well-designed website provides a clear path for users to accomplish their goals. This is illustrated by user flows.
| User Flow | Posts | Pages | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| New User Exploring | Blog posts showcasing recent articles | “About Us” page for site introduction | New visitors will explore the blog, learn about the site’s purpose and values from the “About Us” page. |
| Existing User Seeking Specific Information | Posts relevant to the search term | Dedicated page with details on the search term | Returning users can find specific information through relevant posts or pages with detailed explanations. |
| User Looking for a Service | Posts showcasing the process of the service | Page with detailed service information and pricing | Users looking for a service can find information about the process and details on a dedicated page. |
Practical Examples
Understanding the nuances of posts and pages in WordPress isn’t just about theory; it’s about practical application. Knowing when to use a post versus a page is crucial for a website’s structure and functionality. This section will delve into real-world examples, demonstrating how posts and pages work together to create a robust and user-friendly online experience.Effective website design hinges on a thoughtful division of content into posts and pages.
The distinction isn’t always obvious, but understanding the purpose of each allows for optimal user experience and search engine optimization ().
Real-World Example of a Website Utilizing Posts Effectively
A popular technology blog, like “TechCrunch,” heavily relies on posts. Each new piece of news, analysis, or review is published as a post. This allows for a dynamic, frequently updated feed of information. The chronological order of posts facilitates easy navigation through recent developments and trends. Readers can easily find the latest news on specific topics by scanning the blog’s homepage, which often features a selection of recent posts.
This structure is perfect for keeping the audience informed and engaged in current happenings.
Real-World Example of a Website Utilizing Pages Effectively
A corporate website for a software company, like “Salesforce,” often uses pages to present static information. Sections like “About Us,” “Our Team,” “Products,” and “Pricing” are typically pages. This structure allows for detailed explanations of the company, its offerings, and services. These pages provide important background information and remain consistent, allowing users to find specific information easily.
The “About Us” page, for example, will typically not change as often as a news post.
How the Use of Posts and Pages is Specific to a Particular Website
The choice between using a post or a page depends heavily on the nature of the content and the website’s overall goal. A blog will naturally lean toward using posts, whereas a company website will frequently utilize pages for presenting company information. The structure of a news site, for example, will need to feature numerous, frequently updated posts, whereas a portfolio website might use pages to showcase individual projects or clients.
Demonstrating How to Use Posts to Create a Blog
To create a blog, a WordPress user should create a series of posts. These posts can be about anything, from personal experiences to technical guides. A blog about gardening might feature posts on various plants, while a travel blog could document recent trips. The key is consistency; regular posting keeps readers engaged. Posts can be organized by categories or tags to facilitate easy navigation within the blog.
Demonstrating How to Use Pages to Create Important Website Information Sections
Pages are ideal for static information, such as “Contact Us,” “Terms and Conditions,” and “Privacy Policy.” These are crucial for providing essential information to users and ensuring legal compliance. A “Services” page, for instance, can clearly Artikel the offerings of a company, providing potential customers with comprehensive information. These pages do not need frequent updates.
Table Illustrating a Website Using Both Posts and Pages in Different Sections
| Section | Content Type | Example Content |
|---|---|---|
| Homepage | Posts | Recent blog posts, featured articles, or news items. |
| About Us | Page | Detailed history, mission, and team information. |
| Services | Page | Descriptions of services offered, pricing, and client testimonials. |
| Blog | Posts | Articles on industry topics, tips, or company news. |
| Contact | Page | Contact form, address, phone number, and email address. |
Epilogue: The Differences Between Posts And Pages In WordPress
In conclusion, understanding the differences between WordPress posts and pages is vital for creating a user-friendly and search-engine-optimized website. By strategically using posts for dynamic content and pages for static information, you can enhance user experience and improve your site’s visibility. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the key distinctions, enabling you to make informed decisions about content organization and structure.