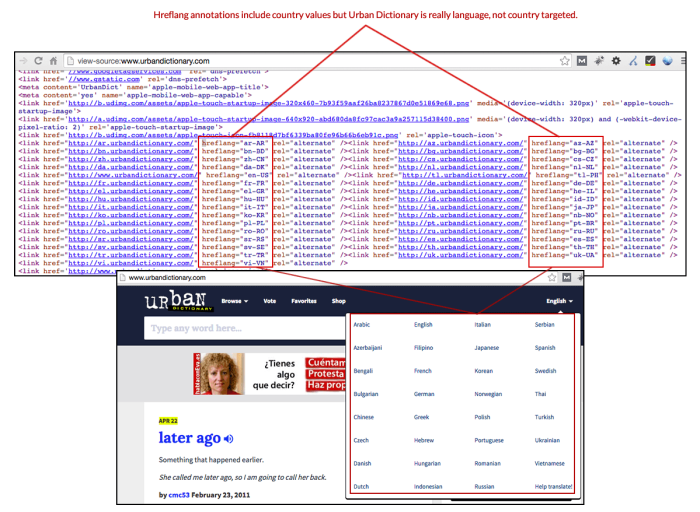
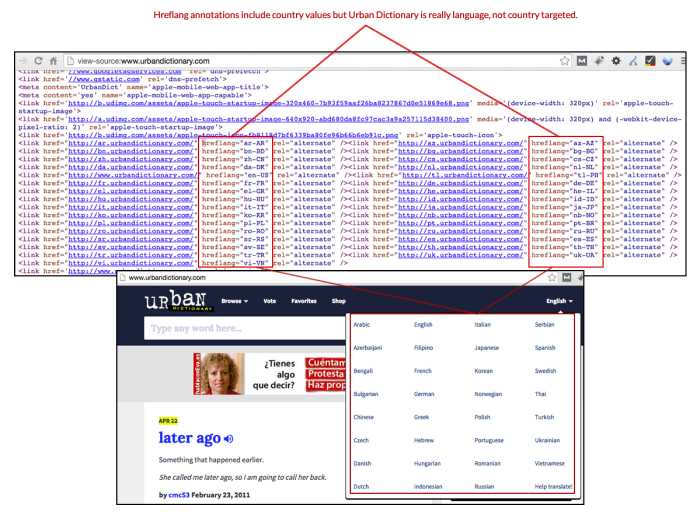
The most common hreflang mistakes infographic dives deep into the often-overlooked but crucial aspect of international . Understanding these pitfalls is essential for websites aiming to reach global audiences and rank well in search results. This guide will cover everything from fundamental hreflang concepts to advanced strategies, including the common mistakes you should avoid.
This infographic breaks down the top errors in hreflang implementation, highlighting the technical, content-related, and geographic targeting issues that can negatively impact your website’s visibility and user experience. Learn to identify and fix these errors, ensuring a seamless multilingual experience for your international visitors.
Introduction to Hreflang
Hreflang tags are crucial for international , guiding search engines to the correct localized version of your website for users in different countries or regions. They essentially tell search engines which page corresponds to a particular language or geographic location. This helps avoid issues like duplicate content penalties and ensures users see the most relevant content. Proper implementation is key for a positive user experience and improved search rankings.Hreflang tags work by providing instructions to search engines.
These instructions specify which URLs are suitable for users in different countries or regions. By implementing hreflang correctly, you can ensure that search engines understand the relationship between your website’s different language or country-specific versions. This leads to improved visibility and better rankings for targeted audiences.
Fundamental Concepts of Hreflang Implementation
Hreflang tags are implemented using HTML attributes within the
section of your website’s HTML. They establish relationships between different versions of your website for different countries or regions. This allows search engines to deliver the appropriate version of your content to users based on their location and preferred language.Importance for Search Engines and Users
Accurate hreflang implementation is vital for search engines to understand your website’s international presence. It assists in avoiding duplicate content issues, improving user experience, and ensuring search results are relevant to the user’s location. For example, if a user in Spain searches for a product, the correct Spanish version of your product page should be displayed.
Hreflang Tag Structure
The following table Artikels the basic structure of an hreflang tag, including attributes and values.
| Attribute | Value | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
href |
URL of the linked page | The URL of the page intended for a specific country or region. | https://www.example.com/es/products |
rel |
alternate |
Specifies that the linked page is an alternative version of the current page. | alternate |
hreflang |
Language or region code (e.g., es, es-ES, fr, en-US) |
Identifies the language or region the linked page is optimized for. | es |
Common Hreflang Mistakes
Hreflang tags are crucial for international , ensuring search engines understand which version of your website a user should see based on their location. However, implementing them correctly is a challenge, and even small errors can significantly impact your website’s visibility. This section dives into the most prevalent hreflang implementation mistakes and their consequences.Hreflang tags are a complex part of , and making a single mistake can lead to reduced traffic and search engine rankings.
These mistakes often stem from a misunderstanding of the nuances of hreflang implementation, the different types of hreflang tags and their use cases, and the importance of proper testing and validation. Understanding the common errors can help you avoid these pitfalls and optimize your international strategy.
Top 5 Hreflang Implementation Errors
Common mistakes in hreflang implementation can have a significant impact on a website’s visibility. Misconfigured tags can lead to confusion for search engines, resulting in incorrect indexing and delivery of content to users. This section highlights five of the most frequent errors.
- Incorrect Target URLs: Using incorrect or incomplete target URLs in hreflang tags is a major error. This can result from mistyping URLs, failing to include necessary parameters like language codes, or missing the correct path structure. This problem often arises when hreflang tags are not carefully validated against the actual website structure.
- Missing or Incomplete Language Codes: Failing to include the required language codes (e.g., ‘en-US’, ‘fr-CA’) or using incorrect codes is another common mistake. Search engines need explicit language codes to accurately understand the language of a specific page. The lack of proper language codes often results in search engines misinterpreting the intended language and potentially delivering the wrong content to users.
This can also cause issues with crawling and indexing.
- Inconsistent Tag Usage: Inconsistent use of hreflang tags across different pages on a site is another frequent error. For instance, not applying tags to all relevant pages or including conflicting tags can lead to a confusing signal to search engines. Search engines may struggle to determine which page to prioritize for specific regions, resulting in unpredictable indexing and ranking.
- Incorrect or Missing Canonical Tags: Mixing up canonical tags with hreflang tags or neglecting to use canonical tags altogether can lead to problems. Canonical tags help specify the preferred version of a page for search engines, while hreflang tags direct users based on their location. This mistake causes conflicts, especially when handling variations like product pages with different attributes for different markets.
Failure to properly set canonical tags can confuse search engines and impact ranking.
- Ignoring Subdomains and Variations: Not considering subdomains (e.g., www.example.com vs. example.com) or other variations (e.g., mobile vs. desktop versions) in hreflang tags can lead to significant issues. This is particularly crucial for sites with different subdomains or mobile-specific pages. Ignoring these variations can cause search engines to incorrectly interpret the target pages, potentially leading to decreased visibility and traffic.
Impact on Website Traffic and Rankings
The impact of these mistakes can vary, but they can lead to a decline in organic search traffic and lower search engine rankings. Search engines might struggle to understand the relationship between different versions of a website, leading to incorrect indexing and ultimately affecting user experience. This can result in lower click-through rates and a drop in overall traffic from search engines.
Comparison of Correct and Incorrect Hreflang Implementations
| Aspect | Incorrect Implementation | Correct Implementation | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target URLs | Incorrect or incomplete URLs, missing language parameters. | Precise and complete URLs with relevant language codes. | Using correct URLs ensures search engines can identify the appropriate localized page. |
| Language Codes | Missing or incorrect language codes (e.g., ‘en’, ‘es’). | Properly defined language codes (e.g., ‘en-US’, ‘es-ES’). | Correct language codes are essential for accurate interpretation by search engines. |
| Canonical Tags | Mixing or missing canonical tags. | Proper use of canonical tags with consistent relationship to hreflang tags. | Canonical tags and hreflang tags work together to specify the preferred version of a page. |
| Subdomains/Variations | Ignoring variations like subdomains or mobile versions. | Including variations like subdomains and mobile versions in hreflang tags. | All variations should be explicitly covered to avoid confusion. |
Technical Issues and Errors
Hreflang implementation isn’t just about correctly specifying languages; technical accuracy is crucial for search engine crawlers to understand and properly interpret your internationalization strategy. Errors in syntax, missing elements, or incorrect language codes can lead to significant problems in reaching your target audience. This section delves into common technical problems and how to effectively troubleshoot them.Incorrect hreflang implementation can lead to issues like search engine confusion, rendering your internationalized pages inaccessible to target audiences, and negatively impacting organic search rankings.
That infographic on the most common hreflang mistakes is super helpful, but you also need to nail your home page headline to get the most out of your international SEO. A strong headline, like the ones discussed in the ultimate home page headline guide, can significantly boost your site’s visibility in different regions. Ultimately, a well-crafted home page headline will complement a correct hreflang implementation and make sure your website is reaching the right audience.
Understanding these technical pitfalls is vital for optimizing your hreflang strategy and ensuring a seamless user experience.
Common Syntax Errors
Many hreflang errors stem from simple but critical mistakes in the markup. These range from incorrect tag structures to missing attributes, which can make the tags ineffective or even harmful. Understanding the correct syntax is fundamental for avoiding such errors.
- Incorrect Syntax: Using the wrong HTML structure or misplacing attributes within the tags can render the hreflang directives useless. For example, including the language code as part of the URL instead of as an attribute within the link is incorrect. The correct structure should include the `rel=”alternate”` attribute and the `hreflang` attribute inside the ` ` tag.
- Missing Tags: Entirely missing the ` ` tags with the `rel=”alternate”` and `hreflang` attributes is a critical oversight. This completely prevents the search engines from recognizing the internationalized content.
- Mismatched Language Codes: Using incorrect or non-standard language codes is another common error. Employing codes not in the ISO 639-1 standard can lead to interpretation issues. Using a language code like “en-us” instead of “en” for English can lead to errors.
Examples of Broken Hreflang Tags
Consider these examples of incomplete or incorrect hreflang tags and their consequences:
- Incorrect Language Code: ` `. The hreflang attribute is set to “fr-fr”, but the URL points to a Canadian French page. This mismatches the code and the content, leading to indexing issues.
- Missing Hreflang Attribute: ` `. The tag is present, but the `hreflang` attribute is missing. This prevents the search engine from understanding the relationship between the pages.
- Incorrect Structure: ` `. The `rel` attribute is incorrectly used in the anchor tag, not the link tag. This makes the tag invisible to the search engines.
Troubleshooting Technical Problems
Effective troubleshooting involves identifying the root cause of the error. Start by carefully examining the HTML code for the problematic pages. Use browser developer tools to inspect the `
` section and check for correct syntax, missing tags, and the correct use of language codes.Table of Hreflang Tag Syntax Errors and Solutions
| Error Type | Example | Explanation | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incorrect Language Code | `` | Using a non-standard language code | Use standard ISO 639-1 language code (`en`) |
| Missing Hreflang Attribute | `` | The hreflang attribute is missing | Add the `hreflang` attribute, e.g., `` |
| Incorrect Tag Structure | `` | Using the anchor tag instead of the link tag | Use the `` tag, e.g., `` |
| Incorrect URL | `` | The URL does not match the language code | Ensure the URL corresponds to the correct language and region. |
Content-Related Mistakes
Incorrect hreflang implementation often stems from mismatches between the content being targeted and the language or region specified in the tags. This can lead to a frustrating user experience for international visitors, and negatively impact search engine visibility.
Understanding these content-related pitfalls is crucial for successful multilingual .Content targeting and hreflang implementation should be meticulously aligned to ensure the correct content is served to the right audience. Failing to do so can lead to significant losses in organic traffic and conversions. Inaccurate content matching often results in a confused search engine and a poor user experience, which can significantly harm your site’s reputation.
Content Mismatches
Inaccurate hreflang tags can arise when the content language doesn’t match the specified language in the tag. For instance, if a Spanish-language page is linked to a tag indicating English content, search engines might incorrectly index it, potentially leading to the wrong content being displayed to users in the target region. This issue is exacerbated if the actual content on the page doesn’t match the language implied by the hreflang tag.
Language Setting Discrepancies
Another common pitfall is when the language setting on a page doesn’t align with the hreflang tag. This can occur if the page is set to display in one language, but the hreflang tag points to a different language. Search engines may struggle to understand the true content language, and this can affect search ranking and user experience.
Impact on Visibility and User Experience
These mistakes can significantly impact content visibility. Search engines may struggle to understand the true language and context of the content, leading to lower rankings in search results for the intended region. Consequently, users searching in a specific language may be served irrelevant or inaccurate content, diminishing the overall user experience. This could cause users to abandon the site, impacting conversion rates and overall site performance.
Correct Content Localization Strategies
Implementing correct hreflang implementation requires a meticulous approach to localization. Matching the content language with the targeted language in the hreflang tag is paramount. This includes not only the language but also the correct cultural nuances and regional variations. Here’s a table illustrating this concept:
| Content Language | Targeted Region/Language (hreflang) | Content Targeting Strategy | hreflang Implementation Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| English (US) | English (UK) | Ensure the content is relevant to UK English usage and conventions. Adapt any phrasing, idioms, or cultural references accordingly. | |
| French | Canadian French | Adapt content to Canadian French conventions. This may include specific vocabulary, grammar, or cultural references. | |
| Spanish | Mexican Spanish | Ensure the content aligns with Mexican Spanish, including regional vocabulary and cultural references. | |
| German | Austrian German | Tailor content to Austrian German conventions. Consider any subtle differences in vocabulary, grammar, or cultural references. |
Geographic Targeting and Hreflang
Effective website localization requires understanding and implementing hreflang tags correctly. This crucial aspect of helps search engines identify the correct language and regional version of your content for users in different parts of the world. This process improves user experience and search engine rankings, as users are presented with the most relevant content, driving traffic and conversions.Hreflang tags act as a roadmap for search engines, guiding them to the most appropriate version of your content for a specific user based on their location and language preferences.
Proper implementation ensures your content is seen by the right audience, enhancing both user satisfaction and performance.
Country Codes and Language Codes
Using the correct country and language codes is fundamental to accurate hreflang targeting. These codes are standardized identifiers that specify the language and region your content is optimized for. This precision is crucial for effective targeting. Misuse of codes can lead to search engines incorrectly displaying content to users, impacting both user experience and results.
Proper Hreflang Implementation Examples
Several factors influence the implementation of hreflang tags. For example, if your website is available in English for the US and the UK, you’d need distinct hreflang tags for each. Here’s how it might be structured:
- For the English version of your website targeted at users in the US, the hreflang tag would include the country code for the United States (us) and the language code for English (en).
- For the English version of your website targeted at users in the UK, the hreflang tag would include the country code for the United Kingdom (gb) and the language code for English (en).
Examples of Correct Hreflang Implementation
The following table demonstrates the correct use of hreflang tags for targeting specific regions based on their language and country codes. Each row represents a different country and language combination, demonstrating the precision required in hreflang implementation.
| Canonical URL | Country Code | Language Code | Hreflang URL |
|---|---|---|---|
| https://www.example.com/en | us | en | |
| https://www.example.com/fr | fr | fr | |
| https://www.example.com/es | es | es | |
| https://www.example.com/de | de | de |
Tools and Resources for Hreflang

Optimizing your hreflang implementation is crucial for international success. The right tools can identify and address issues early, saving you time and effort. Effective monitoring ensures that your hreflang tags are functioning as intended, maintaining a consistent user experience across different regions.Comprehensive hreflang analysis tools provide valuable insights into your site’s international presence.
These tools empower you to troubleshoot issues and ensure your site’s global visibility is maximized.
Hreflang Analysis Tools
Various tools are available to analyze and optimize your hreflang implementation. These tools range from free, basic options to more comprehensive paid services, each offering different levels of functionality. Selecting the right tool depends on your specific needs and budget.
- Google Search Console: A free and widely used tool by Google, Search Console provides crucial insights into your site’s performance, including hreflang issues. It allows you to submit sitemaps and identify crawl errors. Search Console’s reports can highlight potential problems in your hreflang markup, enabling you to address these issues proactively. By using the Search Console, you can monitor crawl errors and submit your sitemap, helping to optimize your hreflang implementation and improve your site’s global visibility.
- Semrush: This paid tool provides in-depth hreflang analysis, going beyond basic checks. Semrush examines your site’s hreflang structure, identifying potential issues and offering recommendations for improvement. It allows you to examine your site’s crawl performance and identify issues in your site’s structure, aiding you in identifying areas where hreflang implementation can be improved. Semrush is a powerful tool for detailed hreflang analysis.
- Ahrefs: Similar to Semrush, Ahrefs is a comprehensive tool that offers hreflang analysis capabilities. Ahrefs can help identify issues like missing tags or incorrect attribute values. It also helps with comprehensive site audits, identifying potential technical problems, including hreflang issues.
- Moz: Moz offers hreflang analysis as part of its broader suite. It provides reports and recommendations for improving your hreflang implementation. It helps with comprehensive site audits, including hreflang analysis, providing recommendations for optimization. The reports provide insights into your site’s hreflang implementation and suggest improvements.
- Screaming Frog: This tool is invaluable for technical audits, including hreflang analysis. It crawls your site to identify and pinpoint potential hreflang implementation problems, such as incorrect tags or missing attributes. It’s excellent for checking the structure of your sitemap, ensuring that the structure matches your hreflang configuration. Screaming Frog’s crawling capabilities are especially useful for identifying structural issues that might hinder hreflang effectiveness.
Using Tools to Monitor Hreflang Effectiveness
Regular monitoring is crucial for maintaining the effectiveness of your hreflang tags. Tools provide data on how users are accessing your site from different regions, indicating whether your hreflang strategy is successful. Monitoring tools show which URLs are being served to users in different countries, helping you identify any discrepancies or problems in your hreflang implementation.
- Analyze regional traffic patterns: Tracking traffic sources by region helps determine if users are directed to the appropriate language and country versions of your site. Tools like Google Analytics can be used to analyze where your users are coming from, helping you to determine whether your hreflang implementation is effective.
- Review click-through rates (CTR): Analyze CTRs for different language and regional versions of your content to identify issues. High CTRs on the correct language versions indicate a successful hreflang strategy. Tools allow you to compare the performance of different versions, identifying problems in your hreflang configuration.
- Track crawl errors: Monitor crawl errors reported by tools like Google Search Console to identify potential issues in your hreflang implementation. Identifying crawl errors in your hreflang implementation allows you to fix any problems in your site’s structure.
Example: Using Google Search Console for Hreflang Analysis, The most common hreflang mistakes infographic
Google Search Console provides a comprehensive overview of your site’s hreflang implementation. It allows you to submit your sitemap, ensuring Google understands your international targeting strategy. By submitting a sitemap, you are providing Google with a structured understanding of your website’s international structure, which can help in avoiding potential crawl errors.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Hreflang Errors | This section displays any detected issues with your hreflang tags, including missing or incorrectly formatted tags. |
| Sitemap Submission | This feature allows you to submit a sitemap containing your hreflang markup to Google. This ensures Google understands the relationship between your different language and regional versions. |
| Crawl Errors | This section shows any errors Google encountered while crawling your site, including errors related to hreflang tags. These errors can point to problems in your implementation. |
| Indexed URLs | This shows which URLs Google has indexed, and whether the indexed URLs are the correct language and country versions. This helps you understand if Google is serving the right content to the correct users. |
Practical Examples of Hreflang Implementation
Hreflang tags are crucial for search engines to understand the language and regional variations of your website’s content. Proper implementation ensures that users in different regions see the correct version of your site, improving user experience and search engine rankings. A well-structured hreflang strategy is key to global expansion and maximizing your website’s potential.Effective hreflang implementation involves careful consideration of your website’s structure, content, and target audience.
This section will demonstrate how to correctly implement hreflang tags for various scenarios, from simple multilingual sites to complex product-based e-commerce platforms. By understanding the nuances of different implementations, you can ensure your site is accessible and understood by global audiences.
Multilingual Website Implementation Strategy
A multilingual website often has separate pages for different languages. A strategic approach involves mapping these language versions to their corresponding target audiences. This necessitates creating hreflang tags that direct search engines to the correct language version for each user’s location. The strategy is fundamental to and user experience.
Hreflang Tags for Multiple Language Versions
To set up hreflang tags for a website with multiple language versions, you must identify the different language codes (e.g., `en`, `fr`, `es`). For each language version of a page, create a corresponding ` ` tag within the `
` section of the HTML document. This tag points to the appropriate language-specific page. This meticulous approach ensures that search engines understand the relationship between different language versions.For example, if you have an English page at `https://www.example.com/en/products`, and a French page at `https://www.example.com/fr/products`, you would use the following tags:“`html“`within the `` section of the English page, and“`html“`within the French page.Hreflang Tags for Product Pages with Different Translations
Product pages, especially in e-commerce, demand careful hreflang implementation. Each translated product page needs a corresponding hreflang tag pointing to the correct original product page. This ensures that users searching for a specific product in a particular language are directed to the translated version. The specific hreflang tags should be placed in the corresponding translated pages.Consider a product page for a “Laptop” in English (`https://www.example.com/en/products/laptop`) and its French translation (`https://www.example.com/fr/products/laptop`).
The English page would include a hreflang tag linking to the French page, and vice versa.
That infographic on the most common hreflang mistakes is a great starting point, but for truly comprehensive international SEO, understanding how to implement custom events in Google Analytics 4, like custom events Google Analytics 4 , is crucial. This helps you track user behavior across different languages and regions, which ultimately improves your hreflang strategy. Ultimately, getting hreflang right is about more than just targeting the right pages; it’s about understanding user engagement across the board.
Comprehensive Table of Hreflang Implementation Strategies
This table illustrates different website scenarios and their corresponding hreflang implementation strategies.
| Website Scenario | Language Version | Product Version | Hreflang Implementation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multilingual blog | English, Spanish | N/A | Include hreflang tags for each language version of blog posts, pointing to the correct language version. |
| E-commerce store | English, French, German | Laptop, Smartphone | Create hreflang tags for each translated product page, pointing to the corresponding original product page. Include hreflang tags for each language version of the homepage and category pages. |
| International website | English, Chinese, Japanese | N/A | Implement hreflang tags for each language version of all pages, ensuring all pages are linked to the correct language version. |
| Website with regional variations | English (US), English (UK) | N/A | Include hreflang tags to differentiate between regional variations of the same language version, pointing to the appropriate regional version. |
Advanced Hreflang Strategies: The Most Common Hreflang Mistakes Infographic
Hreflang implementation is crucial for international , but truly mastering it involves understanding and implementing advanced strategies, particularly for dynamic content and complex websites. These techniques are vital for ensuring accurate targeting and avoiding crawl issues that can negatively impact search rankings. This section will cover handling dynamic content, specific use cases, optimizing for complex structures, and providing best practices for various scenarios.Implementing advanced hreflang strategies is about going beyond basic configurations and proactively addressing the unique needs of your website.
This involves understanding how to adapt hreflang tags to changing content, account for the specific requirements of e-commerce platforms, and handle multilingual structures with varying degrees of complexity. Careful planning and implementation are key to maximizing the impact of hreflang on international visibility.
Ever tripped up on hreflang tags? The infographic on common mistakes is a great starting point, but mastering international SEO is a multifaceted process. If you’re looking to optimize your Instagram presence, a deep dive into the intricacies of Instagram Stories might be the next logical step in your international strategy, like in marketers guide to instagram stories.
Understanding the nuances of different audiences and their preferred platforms is crucial. Ultimately, getting hreflang right is still paramount for a solid international strategy.
Handling Dynamic Content
Dynamic content, such as product pages with varying attributes or user-generated content, requires careful consideration within hreflang implementation. Simply applying a fixed set of hreflang tags to all possible URLs is insufficient. Instead, the tags must dynamically adjust to reflect the variations in the content. This often necessitates server-side implementation of hreflang, allowing the server to determine the appropriate language and region for each URL.
Examples for Specific Use Cases (E-commerce)
E-commerce sites often have a large number of product pages, each with its own variations in language and region. For example, a product listing for a “Red T-Shirt” in English might have variations in French, Spanish, and German. The hreflang tags must precisely target the correct language and region for each product variation, including size, color, and other attributes.
This can be achieved through server-side tagging that utilizes parameters in the URLs. This ensures that search engines understand the specific product variant and its associated language and region.
Optimizing for Complex Multilingual Structures
Websites with complex multilingual structures, including multiple languages and regions, demand a comprehensive hreflang strategy. This includes accurately mapping each language and region to the corresponding URLs. A detailed understanding of the site’s multilingual architecture is essential for effectively implementing hreflang. This might involve using a structured approach to URL mapping and ensuring that the correct language and region are associated with each URL.
For example, if a website has a blog section in multiple languages, the hreflang tags must correctly target the appropriate language version for each blog post.
Best Practices for Different Scenarios
| Scenario | Dynamic Content | Complex Sites | E-commerce Stores |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dynamic Content | Utilize server-side generation of hreflang tags, incorporating parameters from URLs to target specific variations. Implement logic to determine appropriate language and region based on content attributes. | Map URLs meticulously to ensure accuracy in language and region targeting. Create a detailed taxonomy of URLs and associated language/region information. | Use parameters in URLs for product variations, ensuring hreflang tags accurately target each variation in the correct language and region. |
| Complex Sites | Ensure that server-side logic correctly determines the appropriate language and region based on user location and content attributes. | Implement a structured approach to URL mapping, creating a clear hierarchy for multilingual content. | Employ detailed URL mapping for each product variant and corresponding language/region. |
| E-commerce Stores | Use URL parameters for product variations to tailor hreflang tags. | Employ structured URL patterns to accurately represent multilingual content, enhancing understanding by search engines. | Utilize a robust system for handling product variations across multiple languages and regions, allowing for the accurate targeting of each product. |
Illustrative Infographic Elements
This section details the visual components crucial for a compelling infographic on common hreflang mistakes. A well-designed infographic will not only inform but also engage the reader, making complex information easily digestible. The visual representation of each mistake is vital for clarity and impact.The infographic should adopt a clean, modern design aesthetic, avoiding clutter and maintaining a clear hierarchy of information.
The color palette should be chosen to enhance readability and reinforce the key concepts. Consistent use of icons and shapes will improve the visual coherence of the infographic. Each section will be clearly labeled with concise titles to guide the reader through the information.
Infographic Structure
The infographic will be structured as a series of interconnected panels, each dedicated to a specific category of hreflang mistakes. This structure will facilitate easy navigation and comprehension. A central panel will introduce the concept of hreflang and its importance. Surrounding panels will delve into the different types of errors.
Visual Representation of Mistakes
Each mistake will be represented visually using a combination of icons, shapes, and colors. For example, incorrect language targeting will be depicted using a map with incorrect markers in red. A missing hreflang tag will be shown as a broken link icon with a red Artikel.
Color Palette
A calming color palette will be used to maintain visual appeal and clarity. A primary color, such as a deep teal, will be used for the main headings and background of each panel. Secondary colors, such as light blue and lavender, will be used to highlight key points and call attention to specific elements. Red will be used for highlighting errors or warnings.
Shapes and Icons
Consistent use of shapes and icons will reinforce the visual identity of the infographic. A rounded rectangle can represent the correct implementation of hreflang, while a jagged rectangle will highlight an error. Icons will be used to represent actions, like a download icon for downloadable resources. A globe icon will visually link to the concept of geographic targeting.
Example: Missing hreflang Tag
- A red, broken link icon will be prominently featured, signifying the missing tag.
- A jagged rectangle will visually represent the incomplete hreflang implementation.
- A brief explanation beneath the visual will explain the consequences of the missing tag (e.g., “Search engines may not understand the language targeting”).
Example: Incorrect Language Targeting
- A world map with a few specific country flags in red will be used to represent the incorrect targeting.
- A tooltip will explain why the targeting is incorrect and the potential impact on search visibility.
- A visual comparison will be included next to a correctly targeted example to highlight the difference.
Example: Incorrect Attribute Values
- A table will be used to clearly illustrate the correct and incorrect attribute values, using a light blue color for correct examples and red for incorrect ones.
- A tooltip will highlight the correct syntax and provide a clear explanation of why the incorrect value is problematic.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the most common hreflang mistakes infographic provides a comprehensive overview of potential pitfalls and offers actionable solutions. By understanding these common errors, you can refine your hreflang implementation and achieve optimal results in international . Remember to meticulously check your setup, and consult the resources and tools provided to ensure accurate targeting and maximum reach.