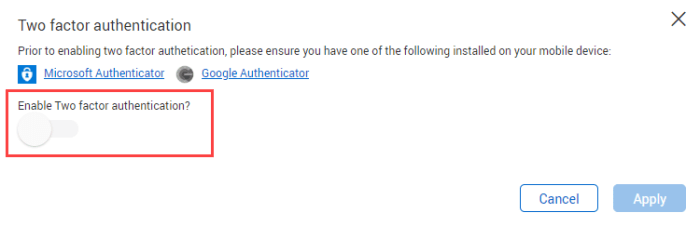
Two factor authentication setup is crucial in today’s digital landscape. It’s about adding an extra layer of security to your online accounts, making them significantly harder to breach. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the world of 2FA, explaining the concept, different methods, and practical steps for setting up 2FA across various platforms, from email to online banking.
From simple SMS codes to more sophisticated authenticator apps and hardware tokens, we’ll explore the pros and cons of each method, helping you choose the best approach for your needs. We’ll also tackle potential security risks and common setup issues, providing solutions and best practices to keep your accounts safe.
Introduction to Two-Factor Authentication Setup
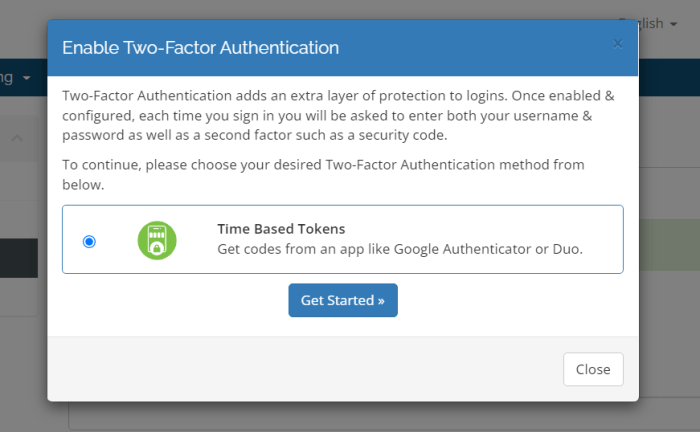
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a crucial security measure that adds an extra layer of protection to your online accounts. It significantly enhances the security of your sensitive data by requiring two forms of verification—something you know (like a password) and something you have (like a code from a phone). This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access even if a hacker manages to obtain your password.FA works by verifying your identity in two distinct ways.
This dual authentication process creates a strong barrier against unauthorized access. This robust approach is increasingly essential in today’s digital landscape, where cyber threats are constantly evolving.
Understanding Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
FA is a security system that requires two methods of authentication to verify a user’s identity. This is more secure than traditional single-factor authentication (like a password alone). The concept of 2FA has evolved over time, becoming a standard security measure for online services.
A Brief History of 2FA
Early forms of 2FA were used in the 1960s and 1970s with physical tokens. The development of more sophisticated methods and widespread adoption by major companies began in the early 2000s. The increasing prevalence of online banking and e-commerce led to a significant rise in the need for robust authentication measures, pushing the development and implementation of 2FA solutions.
Different Types of 2FA Methods
Various methods are used for 2FA, each with its own security, convenience, and cost implications. These methods range from simple SMS messages to more sophisticated hardware tokens.
Setting up two-factor authentication is crucial for online security, especially now that more businesses are offering online services. This is particularly important when considering a new digital marketplace like the one launched by Clicta Digital Agency, clicta digital agency launches new digital marketplace for affordable marketing services. With so much online activity, robust security measures are vital, and two-factor authentication remains a top priority for protecting accounts and data.
- SMS-based 2FA: This method sends a one-time code via text message to your phone. It’s relatively simple to implement, but security concerns exist due to potential vulnerabilities in SMS channels. This method can be susceptible to SIM swapping or interception, potentially exposing your account to risk.
- Authenticator App-based 2FA: This uses dedicated mobile applications (like Google Authenticator or Authy) to generate time-based one-time passwords. These apps offer higher security compared to SMS as they are less prone to interception. The apps use cryptography to ensure the security of the generated codes.
- Hardware Token-based 2FA: These physical devices generate one-time passwords that are used for authentication. They are considered the most secure 2FA method as they are generally less vulnerable to hacking attempts. They typically rely on a strong cryptographic system, ensuring a high level of security.
Benefits of Using 2FA
Implementing 2FA offers significant benefits for online security. It dramatically reduces the risk of unauthorized access to your accounts and protects sensitive information. This added layer of protection makes your accounts much harder to compromise, even if your password is leaked.
Comparison of 2FA Methods
| Method | Security | Convenience | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| SMS | Moderate; susceptible to SIM swapping and interception | High; widely available and easy to use | Low; often integrated into existing phone plans |
| Authenticator App | High; less vulnerable to interception | High; convenient and user-friendly | Low; apps are usually free |
| Hardware Token | Very High; physically secure and cryptographically robust | Moderate; requires a physical device | High; can be more expensive than other methods |
Setting up Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security to your online accounts, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access. This crucial step strengthens your digital defenses against phishing attacks and other malicious activities. It essentially requires two forms of verification – something you know (like a password) and something you have (like a code from an authenticator app).Setting up 2FA is a straightforward process, though the specific steps may vary slightly depending on the platform.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview, covering popular platforms and different authentication methods. The added security provided by 2FA is a worthwhile investment in protecting your sensitive information.
Setting up 2FA for Email Accounts
Email accounts are prime targets for malicious activity. Securing your email with 2FA is vital for preventing unauthorized access and protecting your personal information. The process usually involves navigating to your account settings and enabling the 2FA option. Instructions often vary slightly between email providers.
Setting up 2FA for Social Media Platforms
Many social media platforms now offer 2FA. Activating this feature significantly enhances your account security. The process typically involves visiting your account settings, locating the 2FA section, and choosing your preferred authentication method. This proactive measure helps mitigate the risk of your account being compromised.
Setting up 2FA for Online Banking
Online banking security is paramount. Enabling 2FA for your online banking accounts adds a robust layer of protection. The exact steps for setting up 2FA will vary between banks, but typically involve accessing your account settings, finding the 2FA option, and selecting a preferred method.
Configuring Different 2FA Methods
Several methods are available for 2FA. One common method is using a dedicated authenticator app, such as Google Authenticator or Authy. These apps generate time-based one-time passwords (TOTP). Another method is receiving codes via SMS or email.
Step-by-Step Guide for Setting up 2FA Using an Authenticator App
This guide provides a step-by-step process for configuring 2FA using an authenticator app:
- Download and install an authenticator app on your smartphone or other device.
- Navigate to the account settings page on the platform you want to secure.
- Locate the 2FA setup section.
- Select the option to enable 2FA using an authenticator app.
- Scan the QR code displayed by the platform using the authenticator app.
- Enter the verification code generated by the app.
- Confirm the setup.
Common Problems Encountered During 2FA Setup and Their Solutions
Setting up 2FA can sometimes encounter issues. Troubleshooting these problems efficiently is key to successful implementation.
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Incorrect verification code | Ensure the code is entered correctly. Verify the authenticator app is generating the code and syncing properly. Check your internet connection for stability. |
| QR code scanning failure | Ensure the QR code is visible and clear. Verify that the QR code matches the platform’s instructions. Try scanning the code again or using a different authenticator app. |
| Device compatibility issues | Ensure the authenticator app is compatible with your device. Check the app’s support page for compatibility information. |
| Problems with the platform’s website or app | Contact the platform’s support team for assistance. Provide detailed information about the problem. |
Security Considerations in 2FA Setup
Two-factor authentication (2FA) significantly enhances account security by requiring two forms of verification. However, the effectiveness of 2FA hinges on careful setup and ongoing vigilance. This section delves into the security considerations that arise during the 2FA implementation process.Proper implementation of 2FA is crucial to mitigate risks and ensure the security of your accounts. This involves understanding potential vulnerabilities, selecting robust methods, and diligently safeguarding your 2FA secrets.
Potential Security Risks Associated with 2FA Setup
Implementing 2FA adds an extra layer of security, but it’s crucial to understand the potential risks associated with its setup. Compromised authenticator apps or weak passwords for the 2FA setup process can leave accounts vulnerable. Phishing attempts targeting 2FA codes or credentials for access to the authenticator app or hardware token are also significant risks. The lack of awareness or appropriate training on how to secure the 2FA method can expose accounts to potential threats.
Setting up two-factor authentication (2FA) is crucial for bolstering security. It’s a simple process that adds an extra layer of protection, but choosing the right digital adoption platform can be tricky. For example, if you’re trying to figure out which platform is better for onboarding new users, a good place to start your research is by checking out this comparison of Pendo and Apty, pendo vs apty which digital adoption platform reigns.
Ultimately, a robust 2FA setup is essential for safeguarding your accounts against unauthorized access.
Choosing a Secure 2FA Method
Selecting a secure 2FA method is paramount. Consider factors like the security of the service provider, the reliability of the method, and its compatibility with your devices. Hardware tokens offer a high level of security, relying on physical devices to generate codes. Authenticator apps, though convenient, can be vulnerable to malware if not managed properly. SMS-based 2FA, while readily available, is less secure due to vulnerabilities in SMS channels.
The choice of method should align with the risk tolerance and security requirements for your accounts.
Importance of Keeping 2FA Secrets Secure
Your 2FA secrets, such as codes generated by authenticator apps or hardware tokens, are vital to maintaining account security. Never share these codes with anyone. Protecting your authenticator app or hardware token is essential as well. Do not disclose the codes or any sensitive information that could compromise your 2FA secrets. Strong passwords for access to your accounts and applications are essential to further protect these secrets.
Protecting Your Authenticator App or Hardware Token
Protecting your authenticator app or hardware token is critical. Regularly update your authenticator app to patch security vulnerabilities. Install robust security software on your devices to prevent malware infections. Avoid using public Wi-Fi networks when accessing your authenticator app. Keep your hardware token in a secure location.
This approach ensures that your 2FA secrets remain confidential.
Best Practices for Securing Accounts Using 2FA
Following best practices for securing your accounts using 2FA significantly enhances security.
- Use strong, unique passwords for all accounts.
- Enable multi-factor authentication wherever possible.
- Keep your software and operating systems updated.
- Be wary of suspicious emails or messages requesting your 2FA codes.
- Regularly review your account activity for any unauthorized access.
- Implement a strong password manager to manage and generate complex passwords.
- Use a separate device for accessing your authenticator app or hardware token.
These practices can help you minimize vulnerabilities and protect your accounts effectively.
Different 2FA Methods
Two-factor authentication (2FA) significantly enhances security by requiring two independent verification steps. This multifaceted approach adds an extra layer of protection, making it harder for unauthorized individuals to access accounts even if they obtain a password. Understanding the various 2FA methods available is crucial for choosing the best option for your needs and maintaining a robust security posture.Different methods offer varying levels of security and usability.
Choosing the right method depends on individual preferences and the specific security requirements of the platform being protected. Factors such as convenience, technical capabilities, and potential vulnerabilities need careful consideration when selecting a 2FA solution.
Comparison of 2FA Methods
Different 2FA methods vary significantly in terms of security and usability. A comprehensive evaluation considers factors like ease of implementation, cost, and the inherent risks involved.
- SMS-based 2FA: This method utilizes text messages to send a one-time code to a registered mobile phone. It’s widely accessible, but security concerns arise from potential SIM swapping attacks. The code is delivered in a short time, but it relies on the availability of a mobile device and a functional network connection. Vulnerabilities include SIM swapping, where an attacker gains access to a victim’s SIM card, potentially intercepting the verification code.
Securing your online accounts is crucial, and two-factor authentication setup is a great first step. To streamline your booking process, consider creating a booking form in WordPress; this will significantly reduce manual tasks and increase your efficiency. A great resource for learning how to create a booking form in WordPress is available here: how to create a booking form in wordpress.
Once you’ve got that sorted, you’ll find that the two-factor authentication setup is even more important to protect your newly automated booking system.
- Authenticator App-based 2FA: Dedicated apps like Google Authenticator generate time-based, one-time codes. These apps are more secure than SMS-based methods as they eliminate the risk of SIM swapping. The apps operate independently, typically using a strong cryptographic algorithm. These codes are refreshed at regular intervals, ensuring a constant stream of unique codes. The app also typically has an offline backup, which can be helpful if the device is lost or damaged.
- Hardware Token-based 2FA: Physical devices, often resembling small USB drives, generate one-time codes. These are generally considered the most secure method due to their physical separation from the network. They are less susceptible to phishing attacks, although they require a physical device that needs to be stored securely. Hardware tokens offer robust security by physically generating the code, making it difficult for attackers to intercept or manipulate the verification process.
- Email-based 2FA: This approach sends a one-time code to a registered email address. It’s a convenient method for those who frequently access their email, but it is less secure than authenticator apps or hardware tokens. The vulnerability lies in potential email compromises or phishing attempts. A malicious actor could intercept the email and gain access to the verification code.
Importance of Regular Review
Regularly reviewing your 2FA settings is essential for maintaining a strong security posture. Security threats evolve constantly, and the vulnerabilities associated with a particular method might change. Regularly updating your settings and reviewing the procedures in place helps to address any potential weaknesses.
- Staying Updated: Technology is constantly evolving. Regularly updating your 2FA settings, or changing the settings for a particular platform, can enhance security and address any new vulnerabilities.
- Security Practices: Keeping abreast of security updates and practices is vital. This includes staying informed about potential threats and adjusting your approach to ensure your security measures are up-to-date.
Role of Strong Passwords
Strong passwords are crucial in conjunction with 2FA. Even with 2FA enabled, a weak password can be exploited by attackers who might already have access to your account.
Strong passwords are essential in conjunction with 2FA.
Hardware Token Flowchart
The following flowchart illustrates the steps involved in using a hardware token for 2FA:[Diagram: A simple flowchart showing the steps:
- User initiates login attempt.
- System requests 2FA code.
- User inserts hardware token.
- Token generates one-time code.
- User enters code into the system.
- System verifies code.
- User is granted access if code is valid; otherwise, access is denied.]
Mobile Device Setup for 2FA
Mobile devices have become the primary method for receiving 2FA codes. Their ubiquity and constant connectivity make them a convenient choice for verifying user identities. However, the reliance on mobile devices also introduces specific security concerns that need careful consideration. This section details how to secure your mobile device for 2FA, including the security measures offered by mobile operating systems.Mobile devices are frequently used for 2FA due to their widespread availability and ease of access.
Users often receive time-based codes, push notifications, or one-time passwords (OTPs) via applications or text messages on their mobile devices. This convenience, however, necessitates a robust security posture to protect against unauthorized access.
Common 2FA Methods Using Mobile Devices
Various methods leverage mobile devices for 2FA. These include authenticator apps like Google Authenticator and Authy, which generate time-based codes. SMS messages delivering OTPs are also common, although they are less secure than authenticator apps. Push notifications, sent directly to the device, provide a more secure method compared to SMS, reducing the reliance on network vulnerabilities.
Security Implications of Mobile Device Use for 2FA
Using mobile devices for 2FA introduces several security vulnerabilities. A compromised device can grant unauthorized access to sensitive accounts. Malware infections, lost or stolen devices, and social engineering attacks can all jeopardize the security of 2FA. It’s crucial to understand these risks and implement appropriate security measures.
Securing Your Mobile Device for 2FA
Protecting your mobile device is critical for safeguarding your 2FA setup. Regularly updating your operating system and applications is essential. Enable strong passwords, and consider using biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, for enhanced security.
Security Features Provided by Mobile Operating Systems
Mobile operating systems like iOS and Android offer built-in security features to enhance 2FA protection. These include the ability to lock the device with passwords or biometrics. Features like device encryption, app permissions, and two-step verification further strengthen security. Furthermore, operating systems often include robust security features to detect and prevent malicious software.
Checklist for Securing Your Mobile Device and 2FA Applications
Implementing these security measures will significantly enhance the protection of your 2FA setup. The checklist below Artikels steps for securing your mobile device and applications used for 2FA.
- Regularly Update Operating System and Applications: Keeping software updated ensures you have the latest security patches to address vulnerabilities.
- Enable Strong Passwords: Choose complex passwords that are difficult to guess. Use a password manager for secure storage.
- Use Biometric Authentication: Employ fingerprint or facial recognition for added security when possible.
- Enable Two-Step Verification: Enable two-step verification for your device and all associated accounts.
- Secure Your Network Connection: Use a secure Wi-Fi network whenever possible and avoid public Wi-Fi for sensitive activities.
- Install and Maintain Antivirus/Anti-malware Software: Regularly scan your device for malware and viruses to protect against unauthorized access.
- Regularly Review App Permissions: Carefully review permissions granted to applications to ensure they are necessary and not excessive.
- Enable Device Encryption: Encrypt your device to protect data in case of loss or theft.
- Monitor Device Activity: Regularly check for suspicious activity on your device and accounts.
- Avoid Phishing Attempts: Be cautious of unsolicited emails or messages asking for personal information.
- Secure Your Wi-Fi Connection: Ensure your Wi-Fi network is protected with a strong password.
- Backup Your Data Regularly: Create backups of your device data to recover information in case of device loss or damage.
Troubleshooting 2FA Setup Issues: Two Factor Authentication Setup
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a crucial security measure, but sometimes setting it up can be challenging. This section will detail common problems encountered during 2FA setup and provide step-by-step solutions, real-world examples, and support contact information. Understanding these issues will help you navigate potential roadblocks and ensure your accounts are protected.
Common 2FA Setup Issues
Setting up 2FA often presents hurdles, such as incorrect account credentials, incompatibility between applications or devices, and issues with authenticator apps. Common challenges span across the various 2FA methods and the user’s technical proficiency. Identifying these issues is the first step to resolving them effectively.
- Incorrect Account Credentials: Users may enter incorrect login credentials during the 2FA setup process, leading to authentication failures. This is often due to typos, incorrect capitalization, or a forgotten password.
- Incompatibility Issues: Some applications or devices may not be compatible with specific 2FA methods. This is particularly true for older systems or software versions.
- Authenticator App Problems: Users may encounter problems with their authenticator apps, such as network issues, incorrect configuration, or app malfunctions.
- Device Issues: Mobile device problems, such as low battery, outdated operating system, or network connectivity problems, can hinder 2FA setup.
- Third-Party Software Conflicts: Antivirus software or other third-party security applications might interfere with 2FA processes.
Resolving 2FA Setup Issues
Addressing 2FA issues requires careful analysis and methodical steps. This section details how to diagnose and fix common problems.
- Incorrect Account Credentials: Verify credentials by checking for typos and ensuring the correct capitalization. If the problem persists, reset the password using the platform’s password recovery methods. Always use strong, unique passwords for added security.
- Incompatibility Issues: Ensure that the application and device are compatible with the chosen 2FA method. If compatibility is an issue, consider switching to a different 2FA method or contacting the platform’s support for alternative solutions.
- Authenticator App Problems: Check the authenticator app’s connection status and ensure that the app is correctly configured. Restart the authenticator app or download a new one. If the issue persists, contact the authenticator app provider for technical assistance.
- Device Issues: Ensure the device has sufficient battery power. Restart the device and ensure network connectivity. If the problem persists, update the operating system to the latest version for compatibility.
- Third-Party Software Conflicts: Temporarily disable third-party security software to see if it’s causing the problem. If disabling it resolves the issue, update or configure the software to avoid conflicts with 2FA.
Real-World Examples and Resolutions, Two factor authentication setup
A user experienced issues setting up 2FA for their banking app due to an outdated authenticator app. The solution involved updating the app to the latest version, which resolved the incompatibility.Another example involved a user whose antivirus software blocked the 2FA authentication process. Temporarily disabling the antivirus software resolved the issue, and the user then configured the software to allow the specific 2FA app.
Contacting Support for Assistance
If you’ve exhausted troubleshooting options, contacting support is crucial. Review the platform’s support documentation for specific contact details, such as phone numbers, email addresses, or online chat options. Describe the problem clearly and concisely, providing details about the steps you’ve already taken.
FAQ
- Q: Why is my 2FA setup failing?
- A: This could be due to incorrect credentials, incompatibility issues, or problems with the authenticator app or device. Verify your input, ensure compatibility, and troubleshoot your authenticator app or device.
- Q: How do I reset my 2FA if I’ve lost access to my authenticator app?
- A: Contact the platform’s support to initiate the recovery process. They will provide steps based on the specific platform and security protocols.
Advanced 2FA Concepts
Two-factor authentication (2FA) has evolved beyond basic SMS codes and app-based verification. Advanced implementations leverage multiple factors, biometrics, and intricate security protocols, significantly enhancing security postures. This section delves into these more complex approaches, outlining their strengths and limitations, and showcasing real-world applications.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication goes beyond the two factors of traditional 2FA. It requires the user to provide authentication through multiple independent channels, adding another layer of security. For instance, a user might be required to enter a code from a dedicated authentication app, followed by a fingerprint scan. This approach significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, as a single compromised factor is insufficient to gain access.
Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication leverages unique physical characteristics for identification, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or voice patterns. These methods provide a strong layer of security as they are inherently tied to the individual. Fingerprint scanners are commonly used in mobile devices and enterprise environments, while facial recognition is becoming more prevalent for access control. The accuracy and reliability of biometric systems are constantly improving, making them a powerful tool for enhanced security.
Levels of Security in Different 2FA Methods
Different 2FA methods offer varying levels of security. SMS-based codes, while widely adopted, are susceptible to interception and SIM swapping attacks. App-based codes, generated by dedicated authentication apps, are generally more secure, mitigating the risks of interception. Biometric methods, utilizing unique physical characteristics, offer the highest level of inherent security, as compromising the biometric data of an individual is extremely difficult.
Examples of 2FA Implementation in Various Industries
FA is critical across many industries. Financial institutions extensively use 2FA to protect customer accounts from unauthorized access. Healthcare providers utilize it to safeguard patient data, adhering to stringent regulations. Government agencies employ 2FA to secure sensitive information and maintain national security. E-commerce platforms use 2FA to protect customer payment information and prevent fraudulent transactions.
These examples demonstrate the broad applicability of 2FA across different sectors.
Future Trends in 2FA Technology
Future 2FA trends focus on enhancing convenience and security. The increasing prevalence of hardware security tokens and the integration of 2FA with emerging technologies like blockchain are promising developments. Furthermore, the rise of privacy-preserving technologies like federated learning will likely play a crucial role in developing more secure and user-friendly 2FA methods. The integration of 2FA with AI and machine learning could allow for more adaptive and dynamic authentication processes, potentially detecting anomalies and preventing unauthorized access more effectively.
Security Best Practices for Enterprise-Level 2FA Implementations
Implementing 2FA at an enterprise level requires careful planning and execution. Regular security audits and penetration testing should be conducted to identify vulnerabilities in the system. Employee training is crucial to ensure users understand the importance of secure practices. A multi-layered approach to 2FA, combining different methods, provides a more robust security posture. Furthermore, the security of the underlying infrastructure supporting the 2FA system must be prioritized.
Concluding Remarks
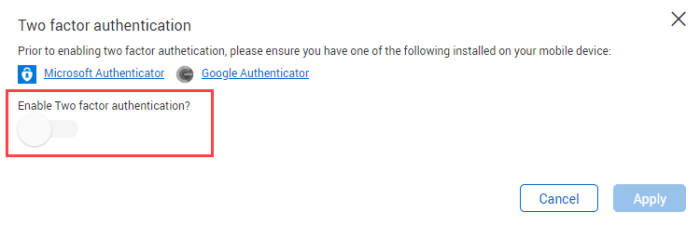
In conclusion, setting up two factor authentication setup is an essential step towards securing your digital life. By understanding the various methods, potential risks, and troubleshooting steps, you can significantly enhance the security of your online accounts. Remember, a strong first line of defense is always the best approach in the digital age. Take control of your security and empower yourself with the knowledge to protect your sensitive data.