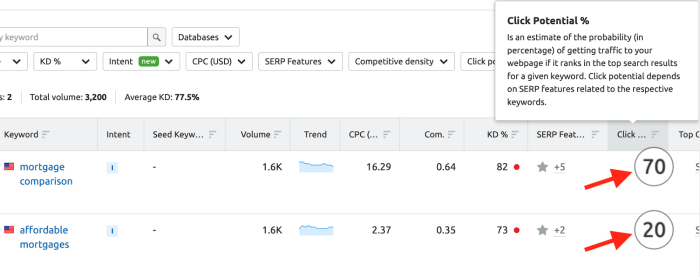
Understanding serp how it works and its features – Understanding SERP, how it works and its features, is crucial for anyone looking to succeed in the digital landscape. SERPs (Search Engine Result Pages) are the gateways to information, and understanding their intricacies allows you to better navigate and optimize your online presence. This deep dive explores the mechanics behind search engine results, from the fundamental components to the advanced features, helping you unlock the secrets to higher rankings and better visibility.
This exploration will cover everything from the basic structure of a SERP to the complex algorithms that dictate its content. We’ll dissect the different types of search results, examining their characteristics and how search engines determine the appropriate result type for each query. Furthermore, we’ll analyze the impact of user behavior on SERP rankings, and delve into the ever-evolving nature of SERPs, and the optimization strategies for different search result types.
Introduction to Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs)
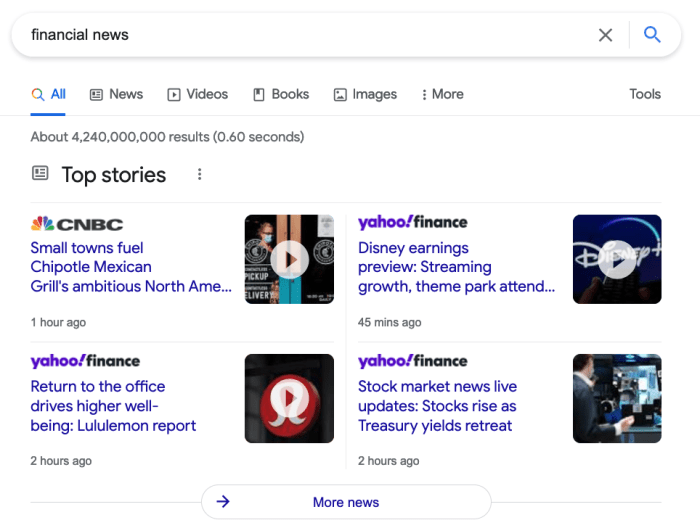
Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs) are the curated lists of web pages that search engines display in response to a user’s search query. They are the gateway to the vast expanse of information available online, presenting results in an organized and easily digestible format. Understanding how SERPs work is crucial for anyone who wants to effectively utilize search engines or optimize their website’s visibility.
Components of a SERP
SERPs are more than just a list of links; they are dynamic displays designed to provide comprehensive and relevant information to the user. They typically incorporate various elements that aim to cater to different user needs and search intent. Understanding these components is key to comprehending the overall functionality of search engines.
| Component Name | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Organic Results | These are the unpaid, naturally-ranked listings that appear on the SERP. They are determined by search engine algorithms based on factors such as relevance, authority, and quality. | Provide unbiased, trustworthy results based on search engine algorithms. These are often the most valuable results for users seeking in-depth information. |
| Paid Ads | These are advertisements that appear prominently on the SERP, often marked with a “Sponsored” or similar label. Businesses pay search engines to have their ads displayed. | Provide a way for businesses to promote their products or services to users actively searching for related terms. They are often positioned at the top or side of the SERP. |
| Featured Snippets | These are concise answers or summaries displayed directly on the SERP, often in a dedicated box. They are intended to quickly address common user questions. | Provide immediate answers to common user queries, directly on the SERP, without needing to click through to a web page. |
| Knowledge Panels | These are boxes that display structured information about a specific topic or entity. They may include images, summaries, and related links. | Offer a quick overview of information related to a specific topic or entity, often sourced from reputable knowledge bases and databases. |
| Image Results | These are image results displayed for visual searches, typically organized in a grid format. | Cater to visual search queries, offering images related to the search terms. |
| Local Pack/Map Results | These results show local businesses, often including reviews, addresses, and directions, specifically targeted for location-based searches. | Provide local business information to users searching for services in a specific area. |
Ranking of Search Results
Search engines employ complex algorithms to rank results. The purpose is to present the most relevant and useful information to the user. The precise algorithms are proprietary and constantly evolving, but some key factors that influence ranking include:
- Relevance: The degree to which a webpage’s content aligns with the user’s search query.
- Authority: The trustworthiness and credibility of a website, often determined by factors like the age and reputation of the site.
- Quality: The overall value and usefulness of the content on a webpage. This includes factors like clarity, accuracy, and depth of information.
- User Engagement: Metrics such as click-through rate (CTR) and time spent on a page can indicate the user’s interest and satisfaction with a result.
- Technical Factors: Website performance, mobile-friendliness, and security measures are also considered.
Understanding Ranking Factors: Understanding Serp How It Works And Its Features
Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs) are dynamic displays of web results tailored to a user’s query. Understanding the factors that influence a website’s position on these pages is crucial for any online business. Ranking factors aren’t static; Google constantly refines its algorithms to provide users with the most relevant and helpful information. This necessitates ongoing adaptation and optimization.The key to achieving high rankings involves a multifaceted approach encompassing content quality, technical , and user experience.
Effective strategies consider these interconnected elements to improve a website’s visibility and ultimately, its success.
Content Quality and Relevance
Content quality and relevance are paramount in determining a website’s SERP ranking. Google prioritizes websites that provide valuable, informative, and engaging content directly addressing user search intent. This means focusing on creating high-quality, original content, free from plagiarism.
Technical Elements
Technical elements play a significant role in website visibility. These elements impact how search engine crawlers interact with a website, affecting its ranking. Factors like site speed, mobile-friendliness, and crawlability are essential for a positive user experience and search engine ranking. Slow loading times and non-responsive designs negatively impact user experience and search engine rankings.
User Experience (UX)
User experience is another critical ranking factor. Google aims to provide users with the best possible experience. This means focusing on aspects like site navigation, readability, and overall ease of use. A well-designed website with intuitive navigation, clear calls to action, and concise, readable content enhances user experience, which positively impacts SERP rankings.
Comparison of Ranking Factors
Ranking factors often interact and influence each other. For instance, high-quality content typically leads to better user experience. Technical elements ensure search engines can effectively crawl and index the site, facilitating the visibility of valuable content. This interconnectedness underscores the importance of a holistic approach.
Ranking Factor Categories and Descriptions
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Content | Content quality, relevance to search queries, originality, and optimization directly influence rankings. |
| Technical | Site speed, mobile-friendliness, crawlability, and site architecture affect how search engines access and interpret website content. |
| User Experience (UX) | Website navigation, readability, ease of use, and time on site contribute to user satisfaction, influencing search engine rankings. |
| Backlinks | The quality and quantity of backlinks from reputable websites are strong indicators of website authority and credibility. |
| Page Structure | Well-structured pages with clear headings, subheadings, and internal linking improve user experience and site navigation, contributing to better search engine rankings. |
Types of Search Results
Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs) are dynamic displays of information tailored to user queries. Beyond just web pages, SERPs present a diverse array of content formats, each designed to satisfy specific information needs. Understanding these different result types is crucial for effectively navigating and interpreting the search results landscape.The presentation of various result types, like images, videos, and news, isn’t arbitrary.
Search engines employ sophisticated algorithms to determine the most pertinent and valuable content for a given query. This involves analyzing the content’s relevance, authority, and user engagement metrics, amongst other factors. This ensures that users find the most helpful and appropriate information for their needs.
Different Result Types
Search engines display a wide range of results beyond simple web pages. These diverse formats cater to different user needs and search intents. Understanding these formats allows for a more effective use of search engines and a deeper comprehension of the SERP ecosystem.
Understanding how Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs) work and their features is crucial for anyone trying to optimize their online presence. With a surge in online activity, the increasing popularity of search engines like DuckDuckGo, which recently hit a significant milestone of 30 million daily searches, duckduckgo hits milestone 30m daily searches , highlights the importance of optimizing for search engines.
This emphasizes the need to continuously refine our understanding of how SERPs function and the elements that influence search rankings.
- Web Pages: The foundational element of SERPs. These are typically HTML documents containing text, images, and other multimedia elements. Search engines rank web pages based on their relevance to the query, as well as factors like authority, site structure, and user engagement.
- Images: Visual results often include image thumbnails and can be retrieved from various sources, including websites, blogs, and social media platforms. Search engines use algorithms to determine image relevance based on s within the image file and surrounding content, as well as user interaction data.
- Videos: Video results allow users to watch relevant videos directly within the SERP. These results often come from platforms like YouTube and Vimeo. Search engines analyze video titles, descriptions, and content to determine relevance to the query, and factors such as view count and user engagement.
- News Results: Recent news articles and reports are presented in a dedicated section. Search engines typically prioritize news sources with high credibility and up-to-date content. These results are usually displayed with publication date and source information.
- Shopping Results: For product-related queries, search engines display listings from online retailers. These results include product images, pricing, and retailer information. Search engines utilize product data feeds and pricing data to present the most relevant and up-to-date shopping results.
Determining Result Type
Search engines employ complex algorithms to determine the optimal result type for a given search query. This involves a multifaceted evaluation process that considers various factors.
- User Intent: The search query itself often provides clues about the user’s intent. For example, a query like “best Italian restaurants near me” suggests a need for local recommendations, likely leading to a local business listing result or a map.
- Content Type: The nature of the information sought influences the result type. If the user searches for a specific video tutorial, the search engine is more likely to prioritize video results.
- Relevance and Authority: The search engine analyzes the relevance of content to the query and the authority of the source. For instance, a query about a scientific topic might yield results from reputable academic journals.
- Data Availability: The availability of relevant data influences the result type. If a product is available for purchase online, the search engine is likely to display shopping results.
Result Type Characteristics
The table below summarizes the key characteristics of different result types.
| Result Type | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Web Pages | HTML documents containing text, images, and other multimedia elements. Ranked based on relevance, authority, and user engagement. |
| Images | Visual results; thumbnails retrieved from various sources. Relevance determined by s, image content, and user interaction. |
| Videos | Video results; allow users to watch directly on the SERP. Relevance determined by title, description, content, and user engagement. |
| News | Recent news articles and reports. Prioritizes credible sources and up-to-date content. |
| Shopping | Product listings from online retailers. Includes product images, pricing, and retailer information. Utilizes product data and pricing data. |
Features of Modern SERPs
Modern search engine result pages (SERPs) are far more sophisticated than their predecessors. They go beyond simply displaying a list of links; they actively aim to provide the most relevant and comprehensive answers directly on the page. This dynamic evolution is driven by the need to cater to user intent and offer a seamless, informative experience. Users no longer just want links; they want concise answers, summaries, and relevant information, often without having to click through multiple pages.This sophisticated approach has resulted in a rich tapestry of features beyond the traditional organic search results.
These features include visually appealing and highly functional components like featured snippets, knowledge panels, and People Also Ask (PAA) boxes. Understanding these elements is crucial for anyone seeking to optimize their online presence and effectively utilize the search engine ecosystem.
Featured Snippets
Featured snippets are concise answers to common search queries that appear at the top of the SERP, often above the organic results. They’re typically formatted as a paragraph, a numbered list, or a bulleted list.Example: A search for “how to bake a cake” might display a featured snippet with step-by-step instructions and a list of ingredients.
Knowledge Panels
Knowledge panels provide comprehensive summaries of well-known entities, such as people, places, or organizations. These boxes appear on the right-hand side of the SERP, often including images, biographical information, and relevant links.Example: A search for “Bill Gates” might yield a knowledge panel with a picture of him, details about his career, and a link to his official website.
People Also Ask (PAA) Boxes
People Also Ask boxes are a series of related questions and answers, often appearing below the main results. These questions are commonly asked by users related to the original search query. They help to explore related topics and offer a more comprehensive understanding of the subject.Example: A search for “best running shoes for beginners” might elicit a PAA box with questions such as “what are the key features to look for?”, “what is the best budget option?”, or “what is the most comfortable shoe?”
Understanding how search engine results pages (SERP) work and their features is crucial for online visibility. Recent news about Meta Institutes’ hiring freeze, budget cuts, and corporate restructuring, as detailed in this article meta institutes hiring freeze budget cuts corporate restructuring , might impact their SEO strategies, affecting how they appear in SERPs. This highlights the interconnectedness of business decisions and online presence, further emphasizing the importance of mastering SERP dynamics for any company.
Related Searches
Related searches are a list of queries that are closely related to the original search term. They help users expand their search or explore alternative perspectives on the topic.Example: A search for “best Italian restaurants in New York City” might generate a list of related searches like “Italian restaurants near Times Square” or “Italian restaurants with outdoor seating”.
Table Comparing SERP Features
| Feature | Structure | Purpose | Typical Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Featured Snippets | Concise answer (paragraph, list) | Provide quick answers directly on the SERP | Top of SERP, often above organic results |
| Knowledge Panels | Summary of entity (images, info, links) | Offer comprehensive information on well-known entities | Right-hand side of SERP |
| People Also Ask (PAA) | Related questions and answers | Explore related topics and provide more comprehensive information | Below main results |
| Related Searches | List of related queries | Expand search or explore alternative perspectives | Below main results or at the bottom of the SERP |
How Search Engines Process User Queries
Search engines are sophisticated information retrieval systems that constantly evolve to meet the ever-changing needs of users. Understanding how these systems process queries is crucial for optimizing content for search visibility. This process involves several intricate steps, from interpreting user intent to returning relevant results.Search engines don’t simply display web pages in a random order; instead, they employ sophisticated algorithms and complex procedures to provide users with the most relevant and useful information.
These algorithms are constantly refined to improve accuracy and efficiency, ensuring a seamless user experience.
Query Understanding and Interpretation, Understanding serp how it works and its features
Search engines analyze user queries to determine the user’s true intent. This process involves recognizing s, understanding context, and identifying nuances in language. The goal is to go beyond simply matching s and grasp the underlying meaning of the query. For instance, a query like “best Italian restaurants near me” implies a desire for recommendations and location-based results, not just a list of all websites mentioning Italian restaurants.
Matching Queries to Relevant Results
The next crucial step is to match the user’s query to relevant web pages. This involves retrieving web pages from the search engine’s index, a massive database of web content. Search engines employ sophisticated algorithms to evaluate the relevance of each page based on various factors. This is not a simple match but a comprehensive evaluation of content, authority, and user experience signals.
For example, a search for “how to bake a cake” will return pages with clear, step-by-step instructions, rather than pages just mentioning the word “cake.”
Indexing and Storing Web Pages
Search engines continuously crawl the web to discover and collect new and updated web pages. This process, known as web crawling, involves following links from one page to another to discover new content. The collected content is processed and stored in a vast index. This index is not a simple copy of the web page; it’s a structured representation of the page’s content, including s, metadata, and other relevant information.
Knowing how search engine results pages (SERPs) work and their features is crucial for any online strategy. Understanding the factors that influence ranking, from keyword optimization to site speed, directly impacts visibility. This directly connects to identifying your ideal clients, or buyer personas, for professional services marketing – a key aspect of successful online presence. For example, learning how to effectively target your audience requires an understanding of their needs and motivations, which is covered in more detail in this insightful article on how to identify buyer personas for professional services marketing and why.
Ultimately, understanding SERPs helps you refine your marketing approach, leading to better results in the long run.
Search engines use sophisticated algorithms to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the indexed data.
Query Processing Flow Chart
+-----------------+
| User Enters Query|
+-----------------+
|
V
+-----------------+
| Query Analysis |
+-----------------+
|
V
+-----------------+
| Extraction|
+-----------------+
|
V
+-----------------+
| Intent Detection |
+-----------------+
|
V
+-----------------+
| Index Retrieval |
+-----------------+
|
V
+-----------------+
| Ranking & Sorting|
+-----------------+
|
V
+-----------------+
| Results Displayed|
+-----------------+
Impact of User Behavior on SERPs
Search engines are not simply passive information retrievers; they are dynamic systems that adapt and evolve based on user behavior.
Understanding how users interact with search results is crucial for comprehending how search engine result pages (SERPs) are shaped. This dynamic interplay between user behavior and search engine algorithms directly impacts the visibility and ranking of websites.
User engagement metrics, such as click-through rates (CTR) and dwell time, are critical indicators of how relevant and useful search results are perceived by users. Search engines analyze these signals to refine their algorithms, leading to more accurate and user-centric search results. This constant feedback loop is essential for maintaining a healthy and effective search experience.
Click-Through Rate (CTR) and Ranking
Click-through rate (CTR) measures the percentage of users who click on a particular search result. A high CTR indicates that the result is highly relevant and appealing to users. Search engines interpret high CTRs as a strong signal of a relevant and helpful result, which, in turn, boosts the ranking of that result in subsequent searches. Conversely, low CTRs can signal a lack of relevance or engagement, potentially leading to lower rankings.
This dynamic feedback loop allows search engines to continuously refine their results to better meet user needs. For example, a search result for “best Italian restaurants” with a high CTR for a particular restaurant indicates to the search engine that users find that restaurant relevant to the query.
Dwell Time and Ranking
Dwell time is the amount of time a user spends on a webpage after clicking on a search result. Longer dwell times suggest that the user found the content valuable and relevant. A search engine interprets longer dwell times as a positive signal, indicating that the result provided a satisfying user experience. Conversely, short dwell times might signal that the content was not as helpful as expected.
This is a critical metric for search engines as it helps identify pages that provide high-quality content aligned with user intent. For example, a user spending an extended period on a blog post about “how to cook pasta” suggests that the content is informative and engaging.
How Search Engines Learn from User Interactions
Search engines employ sophisticated machine learning algorithms to analyze user interactions. These algorithms identify patterns and trends in user behavior, which are then used to update and refine the search algorithm. The algorithms learn from the aggregate behavior of a vast number of users across numerous searches, creating a powerful feedback loop that dynamically adapts to evolving user preferences and search trends.
For instance, if a particular query consistently results in users clicking on specific types of websites, the search engine will learn to prioritize those types of websites for future searches related to that query.
The Search Engine’s Learning Process
Search engines utilize a combination of techniques to learn from user interactions. One key component is analyzing user clicks, which provides immediate feedback on the relevance of a particular result. Another vital technique is analyzing dwell time, which reflects the overall user experience. Furthermore, search engines track how users interact with different search features, such as filters, related searches, and knowledge panels.
All of these factors contribute to a comprehensive understanding of user needs and preferences. The learning process is iterative, constantly adjusting the algorithm based on the feedback received.
Impact of Different User Actions on Rankings
| User Action | Impact on Ranking | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| High Click-Through Rate (CTR) | Increased Ranking | Indicates high relevance and user engagement. |
| Long Dwell Time | Increased Ranking | Suggests valuable and engaging content. |
| Low Click-Through Rate (CTR) | Decreased Ranking | Indicates low relevance or engagement. |
| Short Dwell Time | Decreased Ranking | Suggests content is not meeting user needs. |
| High Bounce Rate | Decreased Ranking | Indicates a lack of user engagement on the page. |
The Dynamic Nature of SERPs
Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs) are not static; they are constantly evolving. This dynamism is a direct response to user behavior changes, technological advancements, and, most importantly, the relentless pursuit of better search engine results by search engines themselves. Search engines strive to deliver the most relevant and helpful information to users, and the SERP is the visible manifestation of that effort.
This constant adaptation ensures that search results remain useful and stay aligned with the ever-changing landscape of the internet.
Search engines are constantly refining their algorithms to better understand user intent and provide more precise results. These algorithm updates, often subtle yet significant, impact the placement of websites in the search results. Factors such as the quality of content, the user experience of the website, and the relevance of s all play a role in determining a website’s ranking.
Algorithm Updates and Their Impact
Search engine algorithms are not static; they are constantly updated to improve the relevance and quality of search results. These updates can lead to significant changes in SERP rankings, sometimes resulting in substantial shifts in visibility for websites.
Factors Contributing to SERP Changes
Numerous factors influence the evolution of SERPs. User behavior is a critical component; search queries are becoming more sophisticated, reflecting a greater need for specific and nuanced information. Content quality and relevance are also pivotal; search engines favor sites with high-quality, authoritative content directly addressing user needs. Technical aspects of websites, such as site speed and mobile-friendliness, also impact rankings, as search engines prioritize a seamless user experience.
The prevalence of specific search features, such as featured snippets and knowledge panels, can further alter the SERP landscape.
Examples of Recent SERP Updates
Several recent SERP updates have noticeably altered the search landscape. For example, Google’s updates related to mobile-first indexing have significantly impacted the ranking of websites that aren’t optimized for mobile devices. Another notable update focused on improving the understanding of user intent, leading to more relevant search results for complex queries. These changes are often subtle but impactful, requiring website owners to adapt their strategies to maintain optimal visibility.
Timeline of Key SERP Algorithm Updates
| Date | Algorithm Update | Key Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 2022 | Helpful Content Update | Improved understanding of user intent, promoting content that is genuinely helpful. |
| 2021 | Core Web Vitals Update | Prioritized websites with fast loading times and a seamless user experience. |
| 2020 | BERT Update | Improved the ability of search engines to understand complex and nuanced search queries. |
| 2019 | Mobile-First Indexing | Prioritized websites that are optimized for mobile devices. |
Optimizing for Different Search Result Types
Crafting content that resonates with search engines and users requires understanding how different SERP features function. Optimizing for various result types, such as featured snippets and knowledge panels, is crucial for maximizing visibility and attracting relevant traffic. This approach allows your content to capture a wider audience and position your brand as a trustworthy source of information.
Strategies for Featured Snippets
Featured snippets are coveted real estate on the SERP, often appearing at the top of the page and highlighting concise answers to user queries. To optimize for these, focus on providing direct, concise answers within your content. Use clear headings, bullet points, and short paragraphs to break down complex information. Ensure your content accurately and completely addresses the query posed by the user.
The ideal structure for a featured snippet often includes a question-and-answer format, a numbered list, or a step-by-step procedure.
Strategies for Knowledge Panels
Knowledge panels display structured information about entities, such as people, organizations, or products. To improve your chances of appearing in a knowledge panel, ensure your online presence is consistent and accurate across various platforms. Claim and update your business profile on Google My Business, and maintain accurate and consistent information on your website and social media. High-quality backlinks from reputable websites can also contribute to your knowledge panel inclusion.
Strategies for Other SERP Features
Beyond featured snippets and knowledge panels, other SERP features like image packs, local packs, and video results each demand tailored optimization strategies. Image results are influenced by image alt text and file names, while local packs prioritize local citations and consistent business information. Video results require high-quality video content with relevant s in the title and description.
Crafting Content for Specific Search Intent
Search intent varies depending on the query. Informational queries seek knowledge, while navigational queries seek a specific website. Transactional queries aim to complete a purchase. Understanding the search intent behind a query is paramount for creating content that aligns with the user’s needs. For example, a query like “best running shoes for marathon” likely has a transactional intent, while “how to train for a marathon” has an informational intent.
Your content strategy should mirror the user’s intent.
Optimization Strategies for Different SERP Features
| SERP Feature | Optimization Strategy |
|---|---|
| Featured Snippets | Provide concise, direct answers to common questions. Use clear headings, bullet points, and short paragraphs. |
| Knowledge Panels | Ensure consistent and accurate information across all online platforms. Claim and update your business profile on Google My Business. |
| Image Packs | Use descriptive alt text and file names for images. |
| Local Packs | Optimize local citations and maintain consistent business information across various platforms. |
| Video Results | Create high-quality video content with relevant s in the title and description. |
Summary
In conclusion, understanding SERP is not just about knowing what’s displayed; it’s about grasping the intricate dance between search engines, website owners, and users. By mastering the components, ranking factors, and ever-changing nature of SERPs, you can effectively optimize your content and gain a significant competitive advantage. This knowledge empowers you to understand and shape the online experience, ultimately leading to better visibility and improved search performance.