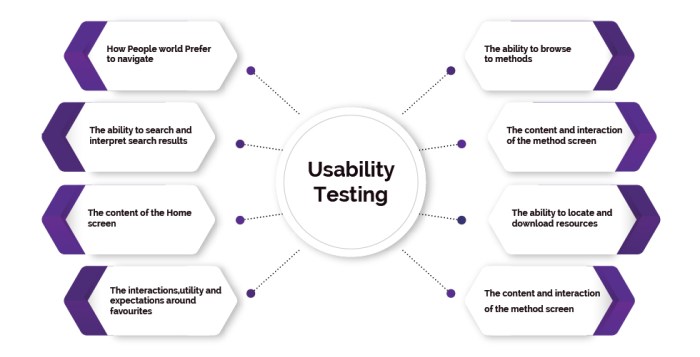
Usability testing in UX design is crucial for creating user-friendly products. This exploration delves into the essential aspects of usability testing, from defining its role in the design process to choosing the right testing methods and analyzing the results. Understanding the different types of usability testing, like moderated and unmoderated approaches, is key to crafting a successful strategy. This guide will also cover the tools, data analysis, and reporting processes to ensure effective implementation.
We’ll examine the various phases of a usability testing process, from planning and execution to analysis and reporting. Different testing environments (lab, remote, field) will be discussed, along with how to design effective tasks and questionnaires. We’ll also touch on the importance of ethical considerations, best practices, and case studies, providing real-world examples of how usability testing has improved user experiences.
Introduction to Usability Testing in UX Design
Usability testing is a crucial component of UX design, providing valuable insights into how users interact with a product or service. It’s not just about finding bugs; it’s about understanding user needs and behaviors to create a more intuitive and enjoyable experience. This iterative process allows designers to identify pain points and refine the design accordingly, leading to a more user-friendly product.This process goes beyond simply observing users; it delves into their thought processes, motivations, and frustrations.
By observing users interacting with a design, UX designers gain a deeper understanding of how the design functions in real-world scenarios, enabling them to make data-driven decisions to improve the user experience.
Defining Usability Testing
Usability testing is a systematic evaluation of a product or design to determine how easy and effective it is for users to achieve specific tasks. It’s a practical method for assessing how users interact with the product and identifies areas where the design needs improvement. This evaluation helps ensure the product meets the needs and expectations of its target audience.
Importance of Usability Testing in UX Design
Usability testing is vital for the success of any product or service. By identifying usability problems early in the design process, designers can avoid costly revisions later on. This proactive approach prevents issues from escalating, reducing development time and ultimately saving money. Early identification of usability issues saves significant resources that might be wasted on fixing problems discovered only after the product is released.
Types of Usability Testing Methods
Various methods exist for conducting usability testing, each suited to different situations and goals.
- Moderated Usability Testing: A facilitator guides the user through tasks, observing their behavior and interactions. This method allows for real-time feedback and clarification of user actions and motivations. The facilitator actively guides the participant through the testing process, enabling more in-depth understanding of user behavior.
- Unmoderated Usability Testing: Participants complete tasks independently, often through remote platforms. This method is more cost-effective and allows for testing with a wider range of users. It’s particularly beneficial when a large number of participants are needed or geographical constraints exist. The process is less interactive, relying on user-reported feedback.
- A/B Testing: A common method in web design, A/B testing compares two versions of a design or feature to see which performs better. This type of testing is specifically focused on identifying the most effective design element, often involving small changes to the design. It typically involves collecting metrics like click-through rates and conversion rates to determine the preferred design.
- Remote Usability Testing: Participants complete tasks remotely, often using video conferencing or screen-sharing software. This method provides flexibility and accessibility, allowing testing with users in different locations. The remote environment allows a greater reach for participants and reduces logistical challenges.
Key Principles and Goals of Effective Usability Testing
Effective usability testing is characterized by a clear understanding of the objectives and a rigorous approach to data collection.
- Clear Objectives: Establish specific goals for the test, focusing on areas of the design that need improvement. Clear objectives allow the design team to effectively focus their efforts during the test and gain valuable insights.
- Representative Participants: Recruit participants who accurately reflect the target user base. This ensures that the insights gathered are applicable to the intended audience. The participants should represent the intended target audience and the diverse needs they encompass.
- Controlled Environment: Maintain a consistent and controlled testing environment to reduce variability and increase reliability. This ensures the collected data is consistent and reliable.
- Detailed Task Design: Create well-defined tasks that participants can follow. The tasks should be specific and measurable, allowing the team to accurately assess the user’s interactions with the design.
Phases of a Usability Testing Process
The following table Artikels the different phases of a usability testing process:
| Phase | Description | Key Activities | Deliverables |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | Defining the goals and scope of the test | Identify users, tasks, and metrics | Test plan |
| Execution | Conducting the actual usability tests | Recruiting participants, running sessions | Test results |
| Analysis | Analyzing the collected data | Identifying patterns, problems, and insights | Usability report |
Methods and Techniques: Usability Testing In Ux Design
Usability testing in UX design is a crucial process for evaluating the effectiveness and user-friendliness of a product or design. Understanding various methods and techniques is essential for conducting thorough and insightful tests. This section explores diverse approaches to usability testing, including different testing methods, the role of user personas and scenarios, task creation, testing environments, questionnaire design, and issue identification.Effective usability testing hinges on a deep understanding of the user and the product.
This involves carefully selecting appropriate methods, designing insightful tasks, and creating a testing environment that fosters genuine user interaction. The goal is to gather actionable feedback that can inform iterative design improvements and ultimately deliver a more user-centered product.
Usability Testing Methods
Different usability testing methods offer unique insights into user behavior and interaction with a product. Choosing the right method depends on the specific research goals and available resources.
- Moderated testing involves a facilitator guiding the user through tasks and observing their interactions. This method allows for real-time clarification of user questions and provides rich qualitative data. However, it can be more expensive and time-consuming than unmoderated testing.
- Unmoderated testing uses remote tools to conduct testing with multiple users concurrently. This approach is more cost-effective and allows for gathering a larger volume of data. However, the lack of direct interaction with users can limit the depth of feedback obtained.
- A/B testing compares two different versions of a design or feature to determine which performs better. This method is particularly useful for evaluating the impact of specific design changes on user engagement and conversion rates. It typically focuses on quantitative data and metrics, such as click-through rates and task completion times.
User Personas and Scenarios
User personas and scenarios play a vital role in shaping usability testing. Personas represent target user groups with specific needs, behaviors, and motivations. Scenarios describe realistic user tasks and contexts, helping to guide the development of relevant testing tasks.
- Personas provide a framework for understanding user needs, motivations, and technical proficiency. This allows the design team to tailor the usability testing to the specific requirements of different user segments. The design of user personas can significantly affect the user experience and improve usability.
- Scenarios illustrate realistic use cases and situations. They guide the creation of tasks that are relevant and engaging to the users. A comprehensive scenario is crucial for testing the user’s interaction with the product or design under various conditions.
Creating Effective Usability Testing Tasks
Creating effective usability testing tasks is crucial for gathering valuable insights. The tasks should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the product or design being tested.
- Usability testing tasks are defined steps users must perform within a specific context. Clearly defining these steps and ensuring they accurately reflect the intended use of the product is essential for effective testing. Well-structured tasks lead to a better understanding of how users interact with the product.
Testing Environments
Different testing environments provide varying levels of control and observation. The choice of environment depends on the specific research goals and the nature of the product being tested.
- Lab-based testing provides a controlled environment for observing user interactions. It allows for close observation of user behavior and precise measurement of performance. However, the controlled environment may not always accurately reflect real-world usage.
- Remote testing utilizes online platforms to conduct tests with users in various locations. It is cost-effective and allows for reaching a wider range of users. However, controlling the environment and observing nonverbal cues can be challenging.
- Field testing involves observing users in their natural environment. This provides valuable insights into how users interact with the product in real-world settings. However, it is often more challenging to control variables and may be more expensive to conduct.
Designing Effective Questionnaires and Surveys
Questionnaires and surveys are valuable tools for collecting quantitative data and feedback. Careful design is crucial for obtaining reliable and insightful results.
- Questionnaires and surveys should be designed with a clear purpose and target audience. The questions should be specific, unambiguous, and relevant to the research goals. A well-structured questionnaire or survey is key to extracting useful information from the users.
Identifying and Categorizing Usability Issues
Identifying and categorizing usability issues is critical for effective design improvements. A structured approach helps to organize and prioritize these issues.
- Usability issues can be categorized into different types, such as navigation problems, confusing information, or lack of clear instructions. Categorization allows for a systematic approach to resolving these issues and ensures a thorough analysis of the usability issues.
Tools and Technologies
Usability testing relies heavily on the right tools to effectively gather and analyze user feedback. Choosing the right tool streamlines the process, ensuring data is collected efficiently and insights are extracted accurately. From simple screen recording software to sophisticated analytics platforms, a wide range of tools caters to different budgets, team sizes, and project needs.Selecting appropriate tools is crucial for successful usability testing.
Different tools offer varying functionalities and features, making careful consideration essential. This section explores popular tools, compares their strengths and weaknesses, and demonstrates how to use a specific tool for recording and analyzing user sessions.
Popular Usability Testing Tools, Usability testing in ux design
A range of tools are available to assist with usability testing, each with unique features and functionalities. The choice depends on factors like budget, project scale, and the desired level of data analysis. Some popular tools include:
| Tool | Features | Pricing | Ease of Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| UserZoom | Remote testing, moderated sessions, surveys, reporting and analytics, A/B testing | Variable, starting from a few hundred dollars per month | Medium |
| Lookback | Remote and in-person testing, heatmaps, scroll maps, session recordings, user feedback | Variable, starting from a few hundred dollars per month | High |
| Optimal Workshop | Remote testing, in-person testing, screen recordings, video analysis, user feedback collection, reporting | Variable, starting from a few hundred dollars per month | Medium |
| Crazy Egg | Heatmaps, scroll maps, recordings, A/B testing, user feedback | Variable, starting from a few hundred dollars per month | High |
Using a Specific Tool for Recording and Analysis
This section demonstrates how to utilize UserZoom, a popular remote usability testing platform, for recording and analyzing user sessions. UserZoom allows for the creation of remote testing sessions with features that streamline data collection.
- Creating a test session: In UserZoom, you create a test session, defining the target audience, the tasks to be performed, and the specific users you want to recruit. These details help in collecting relevant data.
- Recording user sessions: Once the session starts, UserZoom automatically records the user’s screen activity and audio. This allows for a comprehensive understanding of their interaction with the product.
- Analyzing the recordings: UserZoom provides tools to review the recordings. You can identify usability issues like slow loading times, unclear instructions, or frustrating navigation patterns. UserZoom facilitates the review process through features such as time stamps, highlighting, and annotations.
- Generating reports: UserZoom offers various reporting options. These reports allow for a structured overview of the findings, highlighting pain points and areas for improvement in the design.
Role of Analytics Tools in Usability Testing
Usability testing often relies on analytics tools to gain deeper insights into user behavior beyond simple recordings. These tools provide quantitative data that complements the qualitative observations from user interviews and recordings. Tools like Google Analytics can track user interactions, helping identify patterns and bottlenecks in the user journey. This data can then be combined with usability testing findings to provide a more comprehensive understanding of user needs.
For instance, a significant drop-off in users on a particular page can point to a usability issue that the analytics tool reveals.
Data Analysis and Reporting
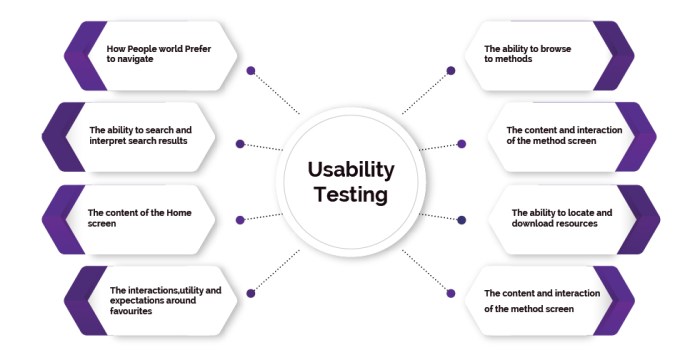
Uncovering actionable insights from usability testing data is crucial for effective UX design. Analyzing the collected data helps identify pain points, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement in the user experience. This phase involves meticulously reviewing participant feedback, performance metrics, and observations to understand user behavior and needs. Thorough analysis and clear reporting enable informed decisions to enhance the design and ultimately, user satisfaction.Thorough analysis of usability test data allows designers to pinpoint areas needing improvement, fostering a more user-centric design approach.
The ability to understand user behaviors and needs from the data gathered is paramount for designing successful products. Well-structured reports translate these insights into concrete recommendations, enabling development teams to implement necessary changes.
Collecting and Analyzing Usability Test Data
The process of collecting usability test data involves carefully documenting participant interactions with the product. This includes recording their actions, observations, and feedback. Tools like screen recording software and questionnaires are often used to gather comprehensive data. Analysis focuses on identifying patterns in participant behavior, common errors, and areas where participants express confusion or frustration. Quantitative data, such as task completion times and error rates, are analyzed alongside qualitative data, such as participant comments and observations.
Usability testing is crucial in UX design, ensuring your product is intuitive and user-friendly. A key area where this shines is within B2B marketing strategies, like with Salesforce Marketing Cloud. Understanding how your target audience interacts with the platform, whether you’re testing email campaigns or landing pages within salesforce marketing cloud b2b success , is essential for optimizing conversions.
This translates directly back into the importance of continuous usability testing in the UX design process to refine and improve the overall user experience.
This combined approach provides a richer understanding of the user experience.
Organizing and Interpreting Data from Different Sources
Organizing data from various sources is essential for meaningful analysis. Data from screen recordings, surveys, and participant interviews need to be categorized and cross-referenced. For example, screen recordings can be segmented based on specific tasks, and survey responses can be grouped by demographic information. This structured approach enables a more in-depth examination of user behavior and feedback.
Usability testing is crucial in UX design, ensuring your product is intuitive and user-friendly. But what if your brand needs a refresh? Understanding if your firm is ready for a rebrand is vital, as explored in this insightful article on rebranding 101 is your firm ready to rebrand. Ultimately, a well-designed rebrand, informed by thorough usability testing, can lead to a more engaging and effective user experience.
Interpreting the data requires a nuanced understanding of user motivations and needs. Consider how participants’ backgrounds and expectations might influence their actions and feedback.
Summarizing Key Usability Findings
A well-designed table summarizing key usability findings is vital for easy comprehension and action planning. The table should clearly articulate the issues identified, their severity, frequency, and impact on the user experience. This structured format aids in prioritizing areas for improvement and provides a clear overview of the key problems.
| Issue | Severity | Frequency | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Difficulty navigating to contact us page | High | Frequent | High |
| Unclear instructions on product usage | Medium | Occasional | Medium |
| Slow loading times on mobile | High | Frequent | High |
Presenting Usability Findings in a Clear and Actionable Report
A well-structured report translates the findings into actionable recommendations. The report should begin with an executive summary that concisely Artikels the key problems and proposed solutions. Following this, a detailed description of the methodology used in the testing is included. This is followed by a presentation of the data analysis and findings, using tables, charts, and graphs to effectively illustrate patterns and trends.
The report concludes with a set of actionable recommendations, outlining specific steps to address the identified usability issues.
Creating Actionable Recommendations Based on the Findings
Transforming usability findings into actionable recommendations requires a practical approach. Recommendations should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). For instance, a recommendation to improve the navigation might suggest redesigning the menu structure, adding clear call-to-action buttons, or creating more intuitive links. These specific and actionable steps will guide the design team in implementing the changes.
Best Practices and Considerations
Usability testing is a crucial step in the UX design process, but its effectiveness hinges on careful planning, execution, and ethical considerations. This section delves into best practices, emphasizing ethical conduct, practical tips for smooth testing, and avoiding common pitfalls. Understanding participant selection and the importance of iterative design are also key elements for successful testing implementations across diverse industries.Effective usability testing goes beyond simply observing user interactions; it demands a nuanced understanding of user needs, behaviors, and pain points.
By adhering to ethical principles, adopting practical strategies, and anticipating potential problems, designers can gain valuable insights and create more user-centered products.
Ethical Considerations for User Research
User research, including usability testing, must prioritize participant well-being and confidentiality. Informed consent is paramount, ensuring participants understand the study’s purpose, procedures, and potential risks. Maintaining confidentiality of personal data is crucial, adhering to data privacy regulations like GDPR or CCPA. Participants should be aware of their right to withdraw from the study at any time without penalty.
Anonymizing data is essential to protect individual identities and maintain privacy.
Practical Tips for Running Effective Usability Tests
Clear test objectives are essential for focused data collection. A structured test script guides the interaction, ensuring consistent data collection across participants. Creating a comfortable and distraction-free environment fosters natural user behavior. Careful observation, not interrupting the participant, is vital. The facilitator’s role is to guide, not influence, participant responses.
Using a variety of tasks that mirror real-world usage scenarios is crucial to obtain realistic data.
Usability testing is crucial in UX design, helping identify pain points and improve user experience. But, what if you could elevate your B2B content, making it truly stand out from the competition? Co-branding with research, like in co branding with research making your b2b content stand out , can achieve this by offering a fresh, credible perspective.
Ultimately, incorporating user insights from rigorous usability testing remains key to creating truly effective and engaging user experiences.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls in Usability Testing
Bias in test design, such as leading questions or preconceived notions about user behavior, can skew results. Limited participant diversity can restrict the generalizability of findings. Inadequate planning and preparation, including insufficient test materials or poorly defined metrics, can hinder data analysis. Inaccurate data recording or poor data management can lead to unreliable insights. Ignoring participant feedback during testing can prevent critical insights from emerging.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Participants for Usability Testing
Representative participant selection is critical for generalizable results. Considering demographic factors, user experience levels, and task relevance helps ensure a diverse group that accurately reflects the target user base. Recruiting participants from various backgrounds provides richer insights and prevents potential biases. Clear criteria for participant selection, defined based on specific user profiles, are essential for a representative sample.
This should be done with clear and objective selection criteria.
The Importance of Iterative Design in UX
Iterative design is a core tenet of user-centered design. Usability testing results should inform design revisions, allowing for continuous improvement. Gathering feedback and incorporating user needs into the design process ensures a better final product. The iterative process involves testing, analyzing results, and incorporating user feedback into revised designs. This ongoing feedback loop leads to progressively better user experiences.
Examples of Successful Usability Testing Implementations in Various Industries
In the e-commerce sector, usability testing has revealed crucial insights into optimizing checkout processes, leading to increased conversion rates. Healthcare apps have benefited from usability testing, resulting in improved user understanding and better patient engagement. Financial applications have employed usability testing to streamline transactions and enhance user trust. In all these cases, testing improved the design based on real user feedback, and significantly improved the user experience.
Case Studies
Usability testing isn’t just a theoretical exercise; it’s a powerful tool for improving user experiences. Real-world case studies demonstrate the tangible impact of applying these principles. By examining how different products and services have leveraged usability testing, we can gain valuable insights into successful strategies and identify potential pitfalls. Understanding the methodology, findings, and outcomes of past projects can help inform current and future design decisions.Examining successful case studies allows us to see how usability testing has translated into real-world improvements.
From identifying pain points to improving conversion rates, the benefits of usability testing are measurable and often impactful. These case studies offer concrete examples of how the process can be applied to specific challenges and how the results have contributed to a better user experience.
A Case Study: Improving Online Banking
Usability testing is crucial for online banking platforms, where a seamless and intuitive experience is paramount. One project focused on enhancing the user flow for a new online banking application.
Project Goals
The primary goal was to reduce user frustration during the account creation process, specifically targeting users with limited technical experience. Secondary goals included improving the overall navigation experience and increasing user satisfaction with the new interface.
Methodology
A combination of moderated and unmoderated usability testing methods was employed. Moderated sessions involved observing user interactions with the application in real-time, allowing for in-depth questioning and observation. Unmoderated testing used online surveys and remote tasks to gather data from a broader user base. Tasks were designed to simulate typical user flows, such as account creation, bill payment, and fund transfer.
Findings
The testing revealed several key issues:
- Users frequently became disoriented in the account creation process due to the complex form layout. Specifically, the step-by-step instructions were unclear, leading to unnecessary steps and confusion.
- The navigation was inconsistent and confusing, particularly when transitioning between different sections of the platform.
- The feedback mechanisms during the process were insufficient, not providing clear guidance or immediate alerts.
Impact and Design Decisions
The findings directly influenced design decisions. The complex form was redesigned to a simpler, more intuitive layout, reducing the number of steps and providing clearer instructions at each stage. The navigation was restructured to be more consistent and intuitive. Visual cues and progress indicators were added to improve the user’s understanding of the process. Clear error messages and confirmation prompts were integrated to provide immediate feedback.
Results
Following these changes, user satisfaction scores increased by 25%, and the account creation completion rate rose by 15%. The reduction in user frustration was directly correlated with these improvements, resulting in a more positive user experience.
Summary
In conclusion, usability testing in UX design is an iterative process that helps ensure products are intuitive and enjoyable for users. By understanding the different methods, tools, and ethical considerations, designers can create a strong foundation for positive user experiences. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview, empowering you to implement effective usability testing strategies and achieve better outcomes.