What is GDPR and how it effects you? This guide dives deep into the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), exploring its impact on individuals and organizations. We’ll examine its history, scope, key principles, and the rights it grants to individuals, along with the obligations of companies handling personal data. From the basics to practical applications and the role of technology, we’ll cover it all.
GDPR, in essence, is a set of rules designed to protect your personal data. It gives you control over how your information is collected, used, and shared. Understanding GDPR is crucial for both individuals and businesses to navigate the complexities of data protection in the digital age. This comprehensive overview will help you understand the nuances of GDPR, from its fundamental principles to its real-world implications.
We’ll look at specific examples and scenarios to make the concepts easier to grasp.
Introduction to GDPR
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a comprehensive set of rules governing how organizations handle personal data within the European Union (EU). It’s designed to empower individuals with greater control over their personal information and to ensure that companies collect, use, and store this data responsibly. This regulation has significant implications for businesses operating in the EU or handling the data of EU citizens, irrespective of their location.GDPR aims to establish a unified standard for data protection across the EU, providing a framework for businesses to comply with and fostering trust between individuals and organizations.
It’s not just about preventing data breaches; it’s about promoting responsible data handling practices and protecting fundamental rights.
Definition of GDPR
GDPR, or the General Data Protection Regulation, is a set of EU laws designed to protect the fundamental rights and freedoms of individuals regarding the processing of personal data. It Artikels specific rules for collecting, using, storing, and transferring personal data, with the core goal of enhancing individual control over their information.
Purpose of GDPR
The core purpose of GDPR is to enhance individual rights regarding their personal data. It seeks to create a unified framework for data protection across the EU, giving individuals greater control over their personal information and empowering them to understand how organizations use their data. This framework is designed to foster trust between individuals and organizations.
Key Principles behind GDPR
GDPR is built upon several fundamental principles that guide its application. These principles ensure that personal data is processed fairly, lawfully, and transparently.
- Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency: Data processing must be lawful, fair, and transparent to the individual. This includes clear communication about how data is being used.
- Purpose limitation: Data should only be collected for specified, explicit, and legitimate purposes. Collecting data for reasons other than those originally stated is prohibited.
- Data minimization: Only the necessary data should be collected and stored. Collecting excessive data is discouraged.
- Accuracy: Data should be accurate and kept up-to-date. Individuals have the right to request corrections if their data is inaccurate.
- Storage limitation: Data should not be kept longer than necessary for the specified purposes. This prevents unnecessary data accumulation.
- Integrity and confidentiality: Data processors must ensure the security and confidentiality of personal data.
- Accountability: Organizations are accountable for complying with GDPR’s requirements. This includes maintaining records of data processing activities.
History and Evolution of GDPR
The GDPR’s history traces back to concerns about the fragmented approach to data protection across different EU countries. The need for a unified, comprehensive framework became evident, leading to the development and adoption of GDPR. The regulation’s evolution reflects a growing recognition of the importance of individual privacy in the digital age.
Comparison of GDPR with Other Data Protection Laws
The following table compares GDPR with the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) highlighting key differences.
| Feature | GDPR | CCPA | Key Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | Applies to organizations processing the personal data of EU citizens, regardless of the organization’s location | Applies to businesses that collect, sell, or share personal information of California residents | GDPR has a broader geographic reach |
| Data Subject Rights | Comprehensive set of rights, including the right to access, rectification, erasure, restriction of processing, data portability, and the right to object | Focuses on the right to know, delete, opt-out, and the right to non-discrimination | GDPR offers a wider array of rights |
| Enforcement | High fines for non-compliance | Fines for non-compliance are lower than GDPR | GDPR carries stronger enforcement mechanisms |
| Exemptions | Limited exemptions | More exemptions for certain types of businesses | GDPR offers fewer exemptions |
Scope of GDPR
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a sweeping piece of legislation that impacts how organizations handle personal data. Understanding its scope is crucial for businesses operating within the European Union (EU) and globally, as it impacts their data processing activities. This section delves into the various aspects of GDPR’s reach, from the types of organizations it affects to the types of personal data it covers.GDPR isn’t a simple set of rules; it’s a comprehensive framework designed to protect individuals’ rights regarding their personal information.
Its broad scope means organizations of varying sizes and types must adapt their data handling practices to comply.
Organizations Subject to GDPR
GDPR applies to any organization processing personal data of EU residents, regardless of their location. This encompasses a wide range of entities, from multinational corporations to small businesses.
- Companies operating within the EU, even if their headquarters are elsewhere.
- Organizations offering services or goods to EU residents.
- Organizations that monitor EU citizens’ behaviour online, regardless of location.
- Businesses that handle personal data of employees located in the EU, even if the company is not based there.
These examples highlight the broad application of GDPR, demonstrating that companies need to carefully consider their interactions with EU residents when it comes to data handling.
Geographical Scope of GDPR
GDPR’s reach extends beyond the physical borders of the EU. It applies to any organization processing personal data of EU citizens, even if the processing takes place outside the EU.
- Extra-territorial reach: GDPR’s impact transcends geographical boundaries. If a company processes data of EU citizens, it must adhere to GDPR, even if the company itself is located outside the EU.
- Example: A US-based social media company collecting data from EU users needs to comply with GDPR, even if its servers are located in the US.
This demonstrates the international implications of GDPR, requiring global businesses to understand and comply with EU data protection regulations.
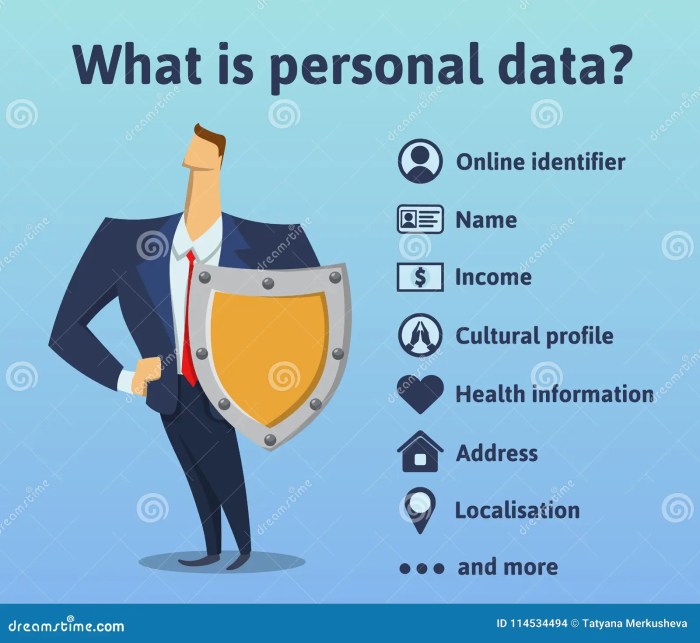
Types of Personal Data Covered by GDPR
GDPR covers a wide array of personal data, including both explicit and implicit information. It’s not limited to obvious identifiers.
- Information about individuals: This includes any information relating to an identified or identifiable natural person. This could range from name, address, and phone number to more nuanced details like browsing history, purchasing habits, and even genetic data.
- Examples of personal data: Name, address, phone number, email address, IP address, online activity, financial data, health information, and biometric data.
This broad definition underscores the expansive nature of GDPR’s coverage, encompassing a vast amount of information that organizations may handle.
Categories of Data Processors Under GDPR
Understanding the different roles and responsibilities within data processing is critical.
| Category | Description | Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Controller | The entity that determines the purposes and means of processing personal data. | Defines the purpose of data collection, sets data retention policies, and ensures compliance with GDPR principles. |
| Processor | The entity that processes personal data on behalf of the controller. | Acts under the controller’s instructions, is responsible for ensuring data security, and complies with GDPR requirements. |
This table highlights the distinct roles and responsibilities of controllers and processors, emphasizing the importance of clear lines of accountability in data processing activities.
Key Rights of Individuals under GDPR: What Is Gdpr And How It Effects You
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) grants individuals significant rights over their personal data. These rights are designed to empower individuals and ensure they have control over how their information is collected, used, and stored. Understanding these rights is crucial for both individuals and organizations handling personal data.The core principle behind these rights is to give individuals a voice and agency in the digital age.
They are not just abstract concepts; they translate into tangible actions individuals can take to protect their privacy and ensure data accuracy.
Right to Access
Individuals have the right to obtain confirmation from an organization about whether personal data concerning them is being processed and, if so, access such data. This right enables individuals to know what data is held about them, how it is used, and by whom. It promotes transparency and accountability by organizations. For example, a user might request to see the personal data held about them by a social media platform, including the types of data collected, how it’s used, and who has access to it.
Right to Rectification
Individuals can request that inaccurate personal data be corrected or completed. This right is essential for maintaining the accuracy and completeness of personal data held by organizations. Imagine a user finds an incorrect address associated with their account on an online retailer. This right allows them to request the correction, ensuring the accuracy of their data.
Right to Erasure (the Right to be Forgotten)
Individuals can request the erasure of their personal data in certain circumstances. This “right to be forgotten” allows individuals to limit the data an organization holds about them, often in situations where the data is no longer necessary for the purpose for which it was collected. A prime example would be an individual who wishes to have their old social media profile deleted after many years of inactivity.
Right to Restriction of Processing
In some cases, individuals can request that processing of their personal data be restricted. This is useful when the individual contests the accuracy of the data or the processing is unlawful. This right allows individuals to temporarily halt the processing of their data while a dispute is resolved. For instance, an individual might request the restriction of their data if they believe it is being used for marketing purposes they did not consent to.
Right to Data Portability
Individuals have the right to receive the personal data concerning them, which they have provided to an organization, in a structured, commonly used, and machine-readable format and to transmit that data to another controller without hindrance from the controller to whom the personal data was initially provided. This right promotes data portability and interoperability. This allows users to transfer their data from one service provider to another without losing access to it.
A common example is transferring data from one email provider to another.
Right to Object
Individuals have the right to object to the processing of their personal data in certain circumstances, such as direct marketing. This right empowers individuals to limit the ways in which their data is used. For instance, a user might object to receiving marketing emails from a company if they do not want to be contacted for such purposes.
Right to Complain to a Supervisory Authority
Individuals have the right to lodge a complaint with a supervisory authority if they believe their rights under the GDPR have been violated. This mechanism provides a recourse for individuals to seek redress when necessary. This is critical in holding organizations accountable and safeguarding individual rights. If an individual feels their data has been mishandled, they can complain to the appropriate supervisory authority for investigation.
Summary Table of Rights
| Right | Description | Impact on Individuals |
|---|---|---|
| Right to Access | Obtain confirmation of data processing and access to it. | Transparency and knowledge of data held about them. |
| Right to Rectification | Correct inaccurate or incomplete data. | Ensures data accuracy and completeness. |
| Right to Erasure | Request deletion of personal data. | Limits the data held about them, especially when no longer necessary. |
| Right to Restriction of Processing | Restrict processing of personal data. | Temporarily halt data processing while a dispute is resolved. |
| Right to Data Portability | Receive and transmit data in a structured format. | Facilitates data transfer between providers. |
| Right to Object | Object to certain types of processing, like direct marketing. | Limits unwanted data use and marketing contacts. |
| Right to Complain | Lodge a complaint with a supervisory authority. | Seek redress when rights are violated. |
Obligations of Controllers and Processors

The GDPR doesn’t just Artikel individual rights; it also imposes specific responsibilities on organizations handling personal data. These obligations, for both controllers and processors, are crucial for ensuring compliance and protecting individuals’ rights. Understanding these obligations is key to navigating the complexities of GDPR effectively.
Controller Obligations
Controllers are responsible for determining the purposes and means of processing personal data. This means they have a significant role in ensuring the legality and fairness of data handling. They must establish and maintain clear policies, procedures, and safeguards to protect the data.
- Data Minimization: Controllers must collect and process only the data strictly necessary for the stated purpose. Collecting excessive data can raise concerns about privacy violations. For example, if a company needs email addresses for customer service, collecting phone numbers and addresses without clear justification might be a breach of data minimization.
- Purpose Limitation: Data must be processed only for the specified, explicit, and legitimate purposes for which it was collected. A company collecting data for marketing purposes shouldn’t suddenly use it for unrelated activities like targeted advertising without explicit consent.
- Accuracy and Integrity: Controllers must ensure the data is accurate and kept up-to-date. This includes implementing mechanisms to rectify inaccuracies promptly. A company holding customer records needs procedures to correct errors in those records when they arise.
- Storage Limitation: Data should not be kept longer than necessary. Clear retention policies and deletion schedules are essential. For example, financial records may have specific legal retention requirements, but other data may be kept only for a specific period, such as marketing preferences.
- Transparency and Accountability: Controllers must be transparent about their data processing activities. This includes providing clear information to individuals about how their data is used and maintained. Websites should include clear privacy policies and data processing notices.
Processor Obligations
Data processors are organizations that process personal data on behalf of a controller. Their role is crucial, but their responsibilities are specific and defined. They are obligated to follow the controller’s instructions, but they also have their own obligations to uphold.
- Contractual Binding: A crucial aspect is the contract between the controller and processor. This contract must Artikel the obligations and responsibilities of the processor, ensuring that data protection principles are followed. This contract will specify what the processor can do with the data, and under what circumstances.
- Compliance with Instructions: Processors must adhere strictly to the instructions given by the controller. This adherence is paramount to ensure the data is processed according to the controller’s established principles. Deviation from these instructions could have serious implications.
- Implementing Appropriate Technical and Organizational Measures: Processors must put in place technical and organizational measures to protect the data from unauthorized or unlawful processing. This may include security protocols and access controls.
- Data Security: Data processors must maintain robust security measures to protect the data from breaches. Implementing multi-factor authentication and encryption protocols are crucial in data security.
Demonstrating GDPR Compliance
Demonstrating compliance is a continuous process, not a one-time event. Controllers and processors must consistently monitor and review their practices to adapt to changes in the legal landscape.
| Action | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Establish clear data policies | Detailed policies outlining data collection, use, and storage practices. |
| Implement data protection training | Educating staff about GDPR obligations and data handling procedures. |
| Maintain secure data storage | Implementing encryption, access controls, and other security measures. |
| Document data processing activities | Keeping records of data processing activities, including purposes, recipients, and retention periods. |
| Appoint a data protection officer (DPO) | If necessary, appointing a DPO to oversee data protection matters. |
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Navigating the digital world often involves handling personal data, and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets strict rules for how organizations manage this information. Failure to adhere to these rules can lead to severe consequences, impacting not only an organization’s financial standing but also its reputation and legal standing. Understanding these repercussions is crucial for any entity dealing with EU citizens’ data.
Potential Penalties for Non-Compliance
GDPR violations can trigger a wide array of penalties, ranging from substantial fines to significant reputational damage. These repercussions are designed to incentivize compliance and protect individuals’ rights.
Impact of GDPR Violations on Organizations
Non-compliance can severely disrupt an organization’s operations. A violation can lead to significant operational challenges, including investigations, legal proceedings, and even reputational damage, which can negatively impact business relationships and investor confidence. Moreover, the need for remediation efforts can be costly, consuming significant resources.
GDPR, or the General Data Protection Regulation, basically means your personal data online is protected. It’s a big deal for how websites handle your information, impacting everything from user experience to website design, like the elements of user experience website design and making sure they’re compliant. Ultimately, understanding GDPR ensures your data is safe and handled ethically.
Reputational Damage from Non-Compliance
A breach of GDPR can irrevocably damage an organization’s reputation. Negative publicity, loss of customer trust, and difficulty attracting new business are just some of the consequences. The reputational damage can be particularly severe for organizations dealing with sensitive data, like healthcare providers or financial institutions.
Financial Penalties for Non-Compliance
The financial penalties associated with GDPR non-compliance can be substantial. Fines can vary depending on the severity of the violation, the nature of the data breach, and the organization’s ability to demonstrate due diligence. In extreme cases, these penalties can cripple a company financially.
Legal Repercussions for Non-Compliance
Legal repercussions can extend beyond financial penalties. Organizations that fail to comply with GDPR may face legal action from individuals whose data has been mishandled, leading to costly lawsuits and protracted legal battles. Furthermore, regulatory bodies may impose additional sanctions or restrictions on the organization’s operations.
Table of Potential Fines and Consequences
The severity of GDPR violations directly correlates with the potential penalties. A nuanced understanding of the different levels of non-compliance is critical for organizations seeking to navigate the regulations effectively.
| Violation Severity | Potential Fines (EUR) | Other Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Minor, technical violations | Up to €10 million or 2% of global annual turnover (whichever is higher) | Corrective action, warnings, and potential audits. |
| Significant breaches, impacting a large number of individuals | Up to €20 million or 4% of global annual turnover (whichever is higher) | Public disclosure, legal proceedings, and restrictions on processing further data. |
| Willful or repeated violations, severe data breaches | Up to €40 million or 6% of global annual turnover (whichever is higher) | Significant reputational damage, criminal prosecution, and complete restrictions on data processing. |
Practical Application of GDPR
Navigating the world of data privacy can feel overwhelming, especially for small businesses. GDPR, while comprehensive, isn’t designed to cripple small enterprises. Instead, it provides a framework for handling personal data responsibly and ethically. Understanding the practical application of GDPR principles empowers businesses of all sizes to comply with the regulations and build trust with their customers.Small businesses can effectively implement GDPR by focusing on core principles of data minimization, purpose limitation, and data security.
By streamlining their data practices and adopting a proactive approach, they can ensure compliance while fostering a positive customer experience.
Applying GDPR Principles to Small Businesses
Small businesses often operate with limited resources, making a full-fledged data protection department unnecessary. A proactive approach and a commitment to data protection can be implemented through simple yet effective steps. Focusing on data minimization, purpose limitation, and data security is crucial. Data minimization means collecting only the data necessary for a specific purpose. Purpose limitation involves clearly defining why data is collected and using it only for those defined purposes.
Data security is paramount, requiring measures to prevent unauthorized access, loss, or misuse of personal data.
Practical Steps for Implementing GDPR
Implementing GDPR involves a series of practical steps that can be tailored to fit the size and scope of any business. These steps can range from simple to more complex depending on the nature of the business and the volume of data processed. A crucial aspect of GDPR compliance is to be transparent with customers about how their data is handled.
Clear communication builds trust and fosters a positive customer experience.
- Data Inventory: Create a comprehensive inventory of all personal data collected, stored, and processed. This includes identifying the types of data, sources, and recipients.
- Data Protection Policy: Develop a data protection policy that clearly Artikels data handling practices, ensuring transparency and accountability. This document serves as a guide for all employees involved in data processing.
- Data Security Measures: Implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. This may involve strong passwords, encryption, and regular security audits.
- Individual Rights: Familiarize yourself with the rights of individuals under GDPR. This includes the right to access, rectification, erasure, restriction of processing, and data portability.
Strategies for Data Protection and Privacy Management
Effective data protection and privacy management are crucial for GDPR compliance. Data breaches can have significant financial and reputational consequences, highlighting the importance of proactive measures.
GDPR, or the General Data Protection Regulation, essentially gives you more control over your personal data. Understanding how it affects you is key, especially when businesses collect and use your information. Knowing how to optimize your marketing strategies, like the 5 techniques with the greatest return on marketing investment, like these , can help you build a stronger relationship with customers while staying compliant.
Ultimately, understanding GDPR empowers you to make informed decisions about your data and how businesses use it.
- Data Minimization: Collect only the minimum necessary data for specific purposes. Avoid collecting unnecessary data points that could potentially expose individuals to risks.
- Purpose Limitation: Define clear and specific purposes for collecting and processing data. Data should not be used for purposes beyond those explicitly stated.
- Data Security: Implement robust security measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. This includes regular security assessments and updates.
- Data Breach Response Plan: Develop a plan to handle data breaches promptly and effectively. This plan should include notification procedures and steps to minimize damage.
Obtaining Consent from Individuals
Obtaining consent from individuals is a critical aspect of GDPR compliance. Consent must be freely given, specific, informed, and unambiguous. It is essential to clearly communicate the purpose of data collection and how the data will be used.
Consent must be freely given, specific, informed, and unambiguous.
- Explicit Consent: Obtain explicit consent from individuals when collecting sensitive personal data.
- Transparency: Be transparent about the purpose of data collection and how the data will be used. Provide clear and concise information to individuals.
- Data Subject Rights: Provide individuals with clear information on their rights under GDPR, including the right to withdraw consent.
- Document Consent: Document all instances of consent obtained, ensuring a clear record of the process.
Best Practices for Securing Personal Data
Securing personal data is paramount for GDPR compliance. Implementing robust security measures can help mitigate risks and prevent data breaches.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive personal data both in transit and at rest.
- Access Controls: Implement strict access controls to limit access to personal data only to authorized personnel.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Employee Training: Provide comprehensive training to employees on data protection principles and GDPR requirements.
Developing a Data Protection Policy
A well-defined data protection policy is essential for demonstrating compliance with GDPR. It acts as a guiding document for all employees involved in data processing.
- Scope of Policy: Clearly define the scope of the policy, outlining the types of data processed and the individuals affected.
- Data Processing Activities: Describe the specific data processing activities undertaken by the organization.
- Data Security Measures: Artikel the security measures in place to protect personal data.
- Individual Rights: Detail how individual rights under GDPR will be addressed.
GDPR Compliance Checklist
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Inventory Data | Identify all personal data collected, stored, and processed. |
| Develop Policy | Create a data protection policy outlining data handling practices. |
| Secure Data | Implement security measures to protect personal data. |
| Train Staff | Educate employees on GDPR principles. |
| Review Consent | Ensure consent is freely given, specific, and informed. |
| Monitor Compliance | Regularly assess compliance with GDPR. |
GDPR and Technology
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) isn’t just about policies; it’s deeply intertwined with the technological landscape of modern businesses. Understanding how technology impacts GDPR compliance is crucial for organizations to effectively manage personal data and avoid costly penalties. From cloud computing to AI, the interplay between technology and data protection is complex, requiring a proactive and nuanced approach.Technology, in its myriad forms, significantly influences how organizations collect, process, and safeguard personal data.
Embracing appropriate technologies can enhance compliance, while neglecting them can lead to severe consequences. This section delves into the specific relationship between GDPR and technology, exploring the impact of cloud computing, data analytics, data management technologies, AI, and automated systems, ultimately aiming to provide a practical guide for effective data protection.
Impact of Cloud Computing on GDPR Compliance
Cloud computing has become ubiquitous, offering scalability and cost-effectiveness. However, it introduces new complexities for GDPR compliance. Organizations must ensure that their chosen cloud providers have appropriate security measures in place and adhere to GDPR principles. Data location, access controls, and data encryption are key considerations when using cloud services. Selecting cloud providers with strong GDPR compliance certifications is essential to mitigate risk.
Role of Data Analytics in GDPR Compliance
Data analytics plays a vital role in understanding customer behavior and preferences. However, the use of analytics must be carefully managed to ensure compliance with GDPR’s principles. Data minimization, purpose limitation, and data security are paramount. Data analytics tools should be selected based on their ability to adhere to these principles and minimize the risk of data breaches.
Transparency about data usage and retention policies is critical.
Technologies for Managing and Protecting Personal Data
Effective data management and protection are critical for GDPR compliance. This encompasses data encryption, access controls, and secure storage. Implementing robust data loss prevention (DLP) solutions is essential to safeguard sensitive information. Employing a centralized data repository and establishing clear data governance policies are crucial steps in managing and protecting personal data. Furthermore, regularly auditing and updating these processes are important.
GDPR, or the General Data Protection Regulation, basically means companies have to be way more careful about how they handle your personal information. This directly impacts your data privacy, but it also has interesting implications for how marketers measure their effectiveness. For instance, a crucial part of that is understanding how to accurately track and analyze customer data while staying compliant with GDPR guidelines.
To delve deeper into measuring marketing effectiveness, check out our recap here: measuring marketing effectiveness recap. Ultimately, understanding GDPR is about ensuring your data is protected and used responsibly, which is crucial for both you and businesses operating ethically.
Impact of AI and Automation on GDPR, What is gdpr and how it effects you
Artificial intelligence (AI) and automation are transforming many business processes. Their use requires careful consideration of GDPR implications. AI systems may need to be adjusted to comply with the principles of data minimization, transparency, and accountability. Bias in algorithms and the potential for discriminatory outcomes need careful scrutiny and mitigation. AI systems should be designed with data subject rights in mind, enabling users to exercise their rights easily.
Managing Data Breaches with Technology
Data breaches are a significant risk, and organizations need proactive strategies to mitigate their impact. Employing intrusion detection systems, firewalls, and secure network configurations are critical. Implementing a robust incident response plan, including automated alerts and notification systems, is essential. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments help identify and address potential weaknesses. Furthermore, robust data backup and recovery systems are crucial.
Examples of Technologies Enhancing GDPR Compliance
Several technologies can significantly enhance GDPR compliance. These include encryption software, access control systems, and data loss prevention tools. Employing blockchain technology for data provenance and immutability can further enhance transparency and accountability. Using secure messaging platforms and other communication tools for data transfer also contributes to compliance.
Table: Technologies for GDPR Compliance
| Technology | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Data Encryption | Protects sensitive data at rest and in transit | Can be complex to implement and manage, potential performance impact |
| Access Control Systems | Limits access to sensitive data, enhances security | Requires careful configuration and regular review, potentially hinders efficiency |
| Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Tools | Identifies and prevents unauthorized data transfers | May impact user experience, potentially expensive |
| Secure Cloud Storage | Scalable storage, cost-effective, enhanced security | Reliance on third-party providers, potential security risks if not chosen carefully |
| Blockchain | Enhances data integrity, traceability, and transparency | Limited adoption, potential for technical complexity |
Data Protection Officer (DPO)
The Data Protection Officer (DPO) plays a crucial role in ensuring organizations comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). This dedicated individual acts as a point of contact and advisor for all things data protection, safeguarding the rights of individuals whose data is processed. Their expertise is invaluable in navigating the complex landscape of GDPR requirements.
DPO Requirements
A Data Protection Officer is not required for every organization. Specific criteria dictate whether an organization needs a DPO. These criteria are essential to understand the applicability of DPO requirements.
Circumstances Requiring a DPO
Organizations that handle certain types of data processing, or those meeting specific size and scope criteria, are mandated to appoint a DPO. The need for a DPO is directly tied to the volume and sensitivity of data processed.
- Public authorities, except for those whose processing activities are limited to internal administrative purposes.
- Organizations whose core activities include large-scale monitoring of individuals.
- Organizations that regularly process special categories of personal data (e.g., health information, criminal records) on a large scale.
- Organizations whose core activities involve systematic and widespread monitoring of individuals on a large scale.
- Organizations that are considered large, based on the criteria specified in the GDPR (typically based on the number of employees and data processing activities).
Responsibilities of a DPO
The responsibilities of a DPO encompass a wide range of tasks aimed at ensuring GDPR compliance. These responsibilities are multifaceted and crucial for maintaining the integrity of personal data.
- Advising the organization on GDPR compliance.
- Assisting with data protection impact assessments.
- Ensuring compliance with data protection principles.
- Monitoring data processing activities to detect potential risks.
- Responding to data subject requests.
- Assisting with the investigation of data breaches.
- Providing training to employees on data protection.
Qualifications of a DPO
A DPO’s qualifications must reflect a strong understanding of data protection principles and laws. Specialized knowledge is essential for effective DPO roles.
- A proven understanding of GDPR.
- Knowledge of data protection laws.
- Strong analytical skills.
- Ability to advise on data protection issues.
- Experience in managing data protection projects.
Process for Appointing a DPO
The process for appointing a DPO involves careful consideration of the individual’s qualifications and experience. A thorough vetting process is essential to ensure the DPO is well-suited to the organization’s needs.
- Identifying suitable candidates with appropriate experience and knowledge.
- Evaluating candidates’ qualifications and experience.
- Selecting the most qualified candidate.
- Notifying the supervisory authority of the appointment.
- Ensuring the DPO has the necessary resources and support.
DPO Responsibilities and Required Organizations
| Responsibilities | Types of Organizations |
|---|---|
| Advising on GDPR compliance | All organizations processing personal data |
| Conducting data protection impact assessments | Organizations processing personal data that may have a significant impact on individuals’ rights |
| Monitoring data processing activities | All organizations processing personal data |
| Responding to data subject requests | All organizations processing personal data |
| Investigating data breaches | All organizations processing personal data |
| Providing training to employees | All organizations processing personal data |
Closing Summary
In conclusion, understanding what is GDPR and how it affects you is vital in today’s digital landscape. By grasping the principles, rights, and obligations Artikeld in GDPR, both individuals and businesses can ensure responsible data handling and maintain trust. This guide has provided a thorough overview, enabling you to navigate the complexities of data protection and make informed decisions.





