Why do emails get delivered to gmail s promotions tab – Why do emails get delivered to Gmail’s Promotions tab? This deep dive explores the intricate mechanisms behind email categorization, from sender reputation to user preferences, shedding light on the factors influencing where your emails land in Gmail.
Gmail’s sophisticated filtering system uses a multifaceted approach to sort incoming emails. Understanding this system is key to ensuring your emails reach the inbox, rather than the Promotions tab. Factors like sender reputation, email content, and user interaction history all play a crucial role.
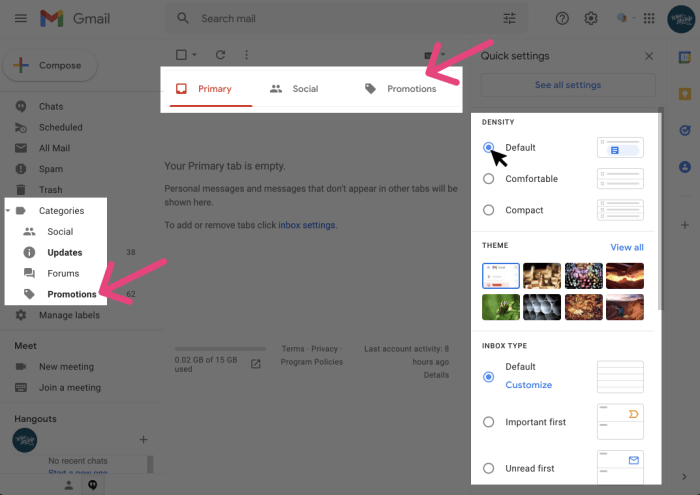
Email Filtering Mechanisms

Gmail’s sophisticated filtering system meticulously sorts incoming emails, ensuring a well-organized inbox. This system is crucial for managing the deluge of messages and preventing important emails from getting lost in a sea of less critical ones. It’s a complex process that leverages various techniques to categorize emails based on various factors.Gmail’s filtering system is a multi-faceted approach, employing several criteria to determine where an email should be placed.
This approach prioritizes user experience and minimizes the burden of managing an overwhelming inbox.
Gmail’s Filtering Criteria
Gmail uses a combination of factors to categorize incoming emails. Sender reputation plays a significant role, as emails from known spammers or unreliable sources are automatically flagged. Content analysis is also employed, identifying suspicious words or phrases commonly associated with spam. Header information, such as the “From” address and subject line, also influences the sorting process.
Ever wondered why some emails end up in Gmail’s Promotions tab? It often boils down to factors like sender reputation and email list hygiene. However, Google’s constant tweaking of algorithms and testing, like with google tools testing measurement data , plays a significant role. These ongoing tests, often unseen by users, shape how emails are categorized.
Ultimately, understanding how Google’s tools analyze email delivery data is key to improving email deliverability.
Email Categorization Methods
Emails are flagged for placement in specific folders based on various criteria. For instance, emails from known senders or those with specific s in the subject line are often moved to designated folders. The sender’s reputation, as assessed by Gmail’s spam filtering system, plays a critical role. Emails from senders with a low reputation score are more likely to be placed in the Promotions tab.
Determining Promotions Tab Placement
Gmail’s algorithm determines if an email should be placed in the Promotions tab through a complex evaluation process. This process involves assessing the sender’s reputation, analyzing the email content for promotional elements, and considering the user’s past interactions with similar emails. If an email is deemed promotional in nature, based on these factors, it is directed to the Promotions tab.
This system strives to separate promotional emails from other communications, keeping the primary inbox focused on essential messages.
Email Placement in Gmail Folders
This table illustrates the typical placement of different email types in Gmail’s inbox folders. Note that these are general guidelines, and individual user preferences or settings may influence the placement.
| Email Type | Typical Placement |
|---|---|
| Transactional emails (e.g., order confirmations, shipping updates) | Primary inbox |
| Promotional emails (e.g., marketing campaigns, newsletters) | Promotions tab |
| Spam emails | Spam folder |
| Social media notifications | Social tab (if enabled) or Primary inbox |
| Important emails (marked as important by the user) | Primary inbox |
| Emails from trusted senders | Primary inbox |
Sender Reputation and Email Deliverability: Why Do Emails Get Delivered To Gmail S Promotions Tab
Your email’s journey to a recipient’s inbox isn’t just about the content; it’s also heavily influenced by your sender reputation. A strong reputation ensures your emails are treated with respect by mail servers, increasing the chance of reaching the inbox instead of the spam or promotions folder. Conversely, a damaged reputation can lead to your emails being automatically filtered into unwanted categories, significantly reducing their impact.
This section dives into the critical role sender reputation plays in email deliverability and how it affects the likelihood of your messages ending up in the Promotions tab.Sender reputation is a metric that email providers, like Gmail, use to assess the trustworthiness and reliability of an email sender. It’s essentially a score reflecting the sender’s history of sending emails.
A high sender reputation means your emails are more likely to be delivered directly to the inbox, while a low reputation leads to increased filtering and a higher chance of ending up in the Promotions tab.
Factors Influencing Sender Reputation
Sender reputation is built over time based on various factors. Consistent delivery of relevant, valuable content to a healthy, engaged subscriber list is crucial. Spam complaints, bounce rates, and the quality of the email list are key indicators that affect your reputation.
Ever wondered why some emails land in Gmail’s Promotions tab instead of your inbox? It often boils down to sender practices. One crucial factor is whether the sender’s email server is using secure connections. For example, if the server hasn’t implemented the redirect HTTP to HTTPS protocol, it can trigger Gmail’s spam filters. This is a key way to improve deliverability, which is why a seamless transition from HTTP to HTTPS is vital for your email campaigns to reach the intended inbox.
So, while there are other reasons, a secure connection is definitely a factor to consider when dealing with email deliverability.
Common Practices Damaging Sender Reputation
A sender’s reputation can be severely impacted by several common practices. These practices often result in email filtering, leading to reduced deliverability and a higher likelihood of your emails being categorized as promotions.
- Sending to invalid or unsubscribed email addresses.
- Using deceptive or misleading subject lines and sender names.
- Sending bulk emails without proper consent from recipients.
- Sending emails with excessive or irrelevant content.
- Using a compromised or shared IP address.
These actions can lead to higher bounce rates and increased spam complaints, ultimately impacting your sender score and leading to emails being filtered into the Promotions tab.
Examples of Sender Behaviors Triggering Gmail’s Filters
Several sender behaviors can trigger Gmail’s filters, causing emails to be categorized as promotions.
- Sending emails to unsubscribed addresses: A high rate of emails sent to unsubscribed recipients directly signals to the email service provider that the sender is not respecting recipient preferences, significantly lowering sender reputation. This is a strong indicator of a disregard for user privacy and consent.
- Using misleading subject lines: Subject lines that are misleading or irrelevant to the content of the email raise suspicion. This behavior is often indicative of an attempt to trick or deceive the recipient.
- High bounce rates: A high percentage of emails that fail to deliver to valid addresses can significantly damage a sender’s reputation. This indicates a problem with the email list or the sending process.
- High spam complaints: Numerous complaints from recipients marking your emails as spam signals a significant issue with the content or the sender’s behavior.
These examples highlight how specific sender behaviors can trigger Gmail’s filters, leading to the unwanted placement of emails in the Promotions tab.
Factors Influencing Email Deliverability and Its Relation to the Promotions Tab
Several factors directly impact email deliverability, influencing whether an email ends up in the inbox or the Promotions tab.
- Sender reputation: A strong sender reputation increases the likelihood of emails reaching the inbox. Conversely, a poor reputation can lead to emails being filtered.
- Email list quality: An accurate and engaged email list contributes significantly to deliverability. A list with a high percentage of invalid or inactive addresses negatively impacts reputation.
- Email content and design: The content of the email and its design should be relevant to the recipient. Spammy content or misleading subject lines can cause filtering.
- Sending frequency: Sending emails too frequently can be perceived as spam and trigger filters. A balanced and appropriate sending schedule is crucial.
These factors are interconnected and influence the overall deliverability of your emails, affecting whether they reach the inbox or are routed to the Promotions tab.
Email Content and Subject Lines
Email delivery to Gmail’s inbox, rather than the Promotions tab, hinges significantly on the content and subject line. While sender reputation and filtering mechanisms play crucial roles, the actual message itself dictates its final destination. This section dives into the specific elements of email content that influence Gmail’s categorization process.Email content and subject lines act as the first line of defense against being categorized as promotional.
Gmail’s algorithms assess various factors, including the content’s tone, the language used, and the overall purpose of the email. A poorly crafted email, regardless of sender reputation, often ends up in the Promotions tab.
Email Content Characteristics Affecting Categorization
The content of an email directly influences Gmail’s categorization. The algorithm analyzes the presence of promotional elements, marketing language, and excessive commercialization. Emails focused solely on promoting products or services are more likely to be relegated to the Promotions tab.
- Promotional language and offers: The use of terms like “limited-time offer,” “special discount,” “exclusive access,” and phrases emphasizing urgency are strong indicators that an email might be categorized as promotional. Examples include discount codes, flash sales, and new product announcements.
- Excessive commercialization: Emails with an overwhelming focus on selling products, featuring multiple product advertisements, or heavy use of sales jargon frequently trigger the Promotions tab. Consider emails with multiple call-to-actions or a relentless push to buy.
- Irrelevant content: If the email’s content doesn’t align with the recipient’s prior interactions or interests, it might be considered irrelevant and relegated to the Promotions tab. This is especially true for emails that seem unsolicited or unrelated to previous communication.
Subject Line Influence on Placement
The subject line acts as a crucial first impression. It directly impacts how Gmail classifies the email. A well-crafted subject line can entice the recipient to open the email and ensure its placement in the inbox, while a poorly crafted one can lead to the Promotions tab.
- Clear and concise subject lines: Subject lines that clearly communicate the email’s purpose and are concise often result in inbox placement. An example would be “Meeting Schedule Confirmation” instead of “Important Information Regarding Our Upcoming Meeting.” The former is direct and avoids unnecessary words.
- Relevance to previous communication: Subject lines that directly relate to previous conversations or interactions with the recipient increase the likelihood of inbox placement. For instance, if a user has previously engaged in discussions about a specific product, a subject line referencing that product will likely be placed in the inbox.
- Clickbait subject lines: Subject lines that employ clickbait tactics, often using sensational or misleading language, frequently land in the Promotions tab. Examples include subject lines that use provocative questions or imply a hidden benefit without clearly stating the email’s purpose.
Types of Emails Often Routed to the Promotions Tab
Certain types of emails are more prone to being routed to the Promotions tab. This is due to their inherent promotional nature and the specific content characteristics discussed previously.
- Promotional offers: Emails that advertise sales, discounts, or new products fall squarely into the promotional category. They are frequently placed in the Promotions tab, even if the recipient has expressed interest in similar products.
- Marketing campaigns: Emails that form part of a larger marketing campaign often use promotional language and may include various offers, all of which can trigger the Promotions tab.
- Newsletter sign-ups: Emails designed to encourage sign-ups for newsletters or mailing lists are often classified as promotional, especially if the recipient hasn’t explicitly opted in.
User Preferences and Historical Data
Gmail’s sophisticated email filtering system goes beyond just sender reputation and content analysis. A crucial component is the meticulous tracking of user preferences and historical data. This allows Gmail to refine its categorization process over time, learning from individual user behavior. This personalized approach ensures that important emails don’t get lost in a sea of promotions, while less relevant ones are appropriately placed.User interactions with emails, especially those marked as spam or not spam, play a significant role in shaping future email placement.
Gmail’s algorithms analyze this feedback, building a profile of each user’s email preferences. This data-driven approach adapts to individual needs and helps maintain a user’s inbox organization.
User Preference Impact on Email Delivery
User preferences significantly impact email delivery. Gmail analyzes various user actions, including how often a user opens emails from a specific sender, how long they spend reading the email content, and whether they take action on the email. These actions provide invaluable insights into user engagement and help predict the value of an email. A user consistently opening and interacting with emails from a certain sender signals Gmail to prioritize those emails in the inbox, while infrequent interaction suggests a lower priority.
Gmail’s Use of Historical Data for Email Placement
Gmail leverages historical data to predict the type of email. For example, if a user frequently marks emails from a particular retailer as not spam, Gmail learns to categorize similar emails from that retailer as “not spam” in the future. This anticipatory placement helps ensure that emails from trusted sources aren’t inadvertently placed in the promotions tab. Conversely, if a user consistently marks emails from a specific sender as spam, Gmail will be more inclined to place future emails from that sender in the promotions tab, or even directly in the spam folder.
Role of User Feedback in Email Categorization
User feedback is a critical element in shaping future email categorization. Marking emails as spam or not spam is a direct signal to Gmail’s algorithms. Each action, whether marking an email as spam or not spam, contributes to the overall profile of the user’s email preferences. This continuous feedback loop allows Gmail to adapt its filtering mechanisms to the user’s specific needs, minimizing the likelihood of important emails being miscategorized.
Examples of User Actions Affecting Future Filtering
Numerous user actions influence future email filtering. For instance, if a user frequently clicks on links in emails from a specific news source, Gmail will likely prioritize future emails from that source in the inbox. Similarly, if a user consistently deletes emails from a specific sender, Gmail will likely place future emails from that sender in the promotions tab or spam folder.
Conversely, if a user regularly archives emails from a specific sender, Gmail may classify those emails as important, leading to their placement in the primary inbox.
How Gmail’s Algorithms Use Historical Data to Predict Email Types
Gmail’s algorithms employ historical data to predict email types. By analyzing patterns in user interactions with emails from various senders, Gmail can predict the likelihood of an email being important, promotional, or spam. This predictive capability is crucial in maintaining a user’s inbox organization and ensuring important emails are delivered to the primary inbox, while less relevant emails are appropriately placed in other tabs.
For example, if a user frequently opens and interacts with emails from a bank, Gmail can predict that future emails from that bank are likely to be important and place them accordingly.
Spam Filters and Email Marketing
Email marketing, a cornerstone of modern business communication, often faces a hurdle: the dreaded Promotions tab in Gmail inboxes. Understanding how spam filters work and how your email marketing practices might trigger them is crucial for maintaining deliverability and maximizing campaign effectiveness. This section delves into the specifics of Gmail’s spam filters, common pitfalls in email marketing, and strategies to ensure your messages reach the intended recipients.Gmail employs a sophisticated array of spam filters to sift through the deluge of emails, striving to deliver valuable messages while quarantining potentially harmful ones.
These filters utilize a multifaceted approach, incorporating various techniques to identify and categorize messages.
Gmail’s Spam Filtering Mechanisms
Gmail employs a combination of techniques to identify and classify emails as spam or legitimate. These mechanisms work in tandem to create a robust filter system. Sophisticated algorithms analyze various factors, including sender reputation, email content, and user engagement patterns.
Email Marketing Practices That Trigger Spam Filters
Certain email marketing practices can inadvertently trigger Gmail’s spam filters, leading to emails being relegated to the Promotions tab. These practices often stem from a lack of understanding or compliance with best practices.
Ever wondered why some emails end up in Gmail’s promotions tab? It’s often a combination of factors, like sender reputation and email list hygiene. Recently, our AI domain migrated to a more secure platform, ai domain migrated to a more secure platform , which may have impacted how some emails are categorized. This change might also affect email deliverability, potentially pushing emails into the promotions tab.
It’s a complex web of factors, but hopefully, this helps clarify some of the mystery behind those promotions tab mishaps!
- Excessive Use of Spam Triggering Words and Phrases: The use of overly promotional language, urgent calls to action, or excessive use of exclamation points can trigger spam filters. Words or phrases associated with scams or unsolicited advertisements often result in emails being flagged.
- Poorly Constructed Subject Lines: Subject lines that are misleading, overly generic, or contain spam-triggering s significantly impact deliverability. Avoid subject lines that are clickbait or contain aggressive sales tactics.
- High Volume and Frequency of Emails: Bombarding recipients with emails too frequently or sending emails at an unsustainable rate can result in your emails being perceived as spam. Consistency is key but not at the expense of overwhelming subscribers.
- Lack of Sender Authentication: Using email addresses without proper sender authentication can cause Gmail to flag your emails as suspicious. Proper authentication methods such as SPF, DKIM, and DMARC enhance sender reputation and help maintain deliverability.
- Low Open and Click-Through Rates: If recipients consistently do not open or interact with your emails, it signals a lack of engagement, potentially triggering Gmail to classify your emails as spam.
Common Email Marketing Practices that Negatively Impact Deliverability
Beyond spam triggers, certain email marketing practices directly impede deliverability. These practices are detrimental to campaign success and require careful consideration.
- Buying Email Lists: Using purchased email lists can significantly harm your sender reputation. These lists often contain inactive or invalid email addresses, leading to high bounce rates and poor deliverability.
- Poor List Management Practices: Failing to segment your email lists or manage unsubscribes can negatively impact your sender reputation. Removing inactive or unengaged subscribers is vital for maintaining a healthy list.
- Sending Emails to Unsolicited Recipients: Sending emails to individuals who have not opted in or consented to receive them can result in your emails being flagged as spam.
Email Marketing Strategies and their Impact on Email Placement
This table illustrates how different email marketing strategies can impact the placement of your emails in the Gmail Promotions tab.
| Email Marketing Strategy | Impact on Email Placement |
|---|---|
| High-volume, low-quality email campaigns | High likelihood of placement in Promotions tab |
| Targeted, personalized email campaigns | Increased likelihood of reaching the primary inbox |
| Spammy subject lines and content | High likelihood of placement in Promotions tab |
| Compliant and authentic sender authentication | Increased likelihood of reaching the primary inbox |
Techniques to Improve Email Deliverability
Various techniques can improve your email deliverability and prevent your emails from ending up in the Promotions tab. These are critical to achieving optimal results.
- Implement Sender Authentication (SPF, DKIM, DMARC): These authentication protocols help verify the legitimacy of your emails, improving deliverability.
- Segment Your Email Lists: Segmenting your lists allows you to send targeted and personalized messages, improving open and click-through rates.
- Monitor Email Deliverability Metrics: Regularly monitoring metrics like open rates, click-through rates, and bounce rates provides insights into campaign performance and allows for adjustments.
- Maintain a Healthy Email List: Regularly remove inactive or unengaged subscribers to maintain a healthy list.
- Focus on Engaging Content: Delivering high-quality content that resonates with your subscribers is crucial for building trust and maintaining deliverability.
Technical Aspects of Email Delivery
The digital mail stream, though seemingly simple, is a complex network of interconnected systems. Understanding the technical aspects of email delivery is crucial for marketers and senders alike. A deep dive into the process reveals the intricacies behind email routing, header information, and the factors influencing whether an email reaches the inbox or the dreaded Promotions tab.The journey of an email from sender to recipient involves a series of steps, each with its own technical considerations.
From the initial creation and validation of the message to the final delivery and confirmation, many technical processes work behind the scenes. Email headers, often overlooked, are crucial in this process.
Email Headers and Categorization
Email headers contain metadata about the email, including the sender’s information, the recipient’s address, the date and time of transmission, and crucial routing information. These headers are critical for email servers to understand the email’s origin, destination, and other relevant details. Specifically, the “Received” headers, along with the “From,” “To,” and “Subject” fields, are vital components of this metadata.
Email filtering systems use this data to understand the email’s origin and potential for spam.
Email Routing and Delivery Mechanisms
Email routing is a complex process involving multiple mail servers and protocols. Emails traverse a network of servers, each relaying the message closer to its final destination. The path an email takes is determined by several factors, including the sender’s and recipient’s email server configurations, domain names, and the chosen delivery mechanisms. The process typically follows these stages:
- Initial Transmission: The sending server initiates the transmission using protocols like SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol).
- Relaying: Intermediate mail servers (relays) accept and forward the email, often following specific rules and guidelines.
- Destination Server: The recipient’s email server receives the email and processes it for delivery.
- Delivery Confirmation: The recipient’s server often sends a confirmation back to the sender.
Technical Issues Causing Miscategorization, Why do emails get delivered to gmail s promotions tab
Several technical glitches can lead to emails being misclassified, potentially landing in the Promotions tab. These problems often stem from inconsistencies in email headers or server configuration issues.
- Incorrect Sender Reputation: If a sender’s domain or IP address has a poor reputation due to previous spam or abuse issues, the email might be automatically flagged as spam, even if the content is legitimate.
- Header Inconsistency: Inaccurate or missing headers, like the “DKIM” (DomainKeys Identified Mail) signature, can cause email servers to view the email as suspicious and therefore deliver it to the Promotions tab.
- High Volume or Unexpected Traffic: A sudden surge in emails from a specific sender can cause email servers to trigger filters to prevent overloading, even if the emails are legitimate.
- Technical Issues on the Recipient’s End: The recipient’s email client or server might have configuration issues that cause emails from a particular sender to be redirected to the Promotions tab.
Relationship Between Email Headers and Promotions Tab
The Promotions tab often filters emails based on a combination of sender reputation, email content analysis, and email headers. A high volume of “Received” headers from different mail servers might trigger a spam filter. A sender with a poor reputation might see a high percentage of emails being delivered to the Promotions tab, regardless of the email’s content. A missing or invalid DKIM signature is a strong indicator of a potentially malicious or unwanted email.
If an email server receives an email that doesn’t have a valid DKIM signature, it is highly likely to be misclassified. Emails from unknown senders or senders with a history of spam often land in the Promotions tab.
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, Gmail’s Promotions tab isn’t a random dumping ground for unwanted emails. It’s a result of complex algorithms analyzing sender reputation, email content, and user interaction history. By understanding these factors, you can optimize your email marketing campaigns and ensure your messages reach the intended recipients. Careful consideration of these elements is essential for successful email delivery and avoiding the Promotions tab.