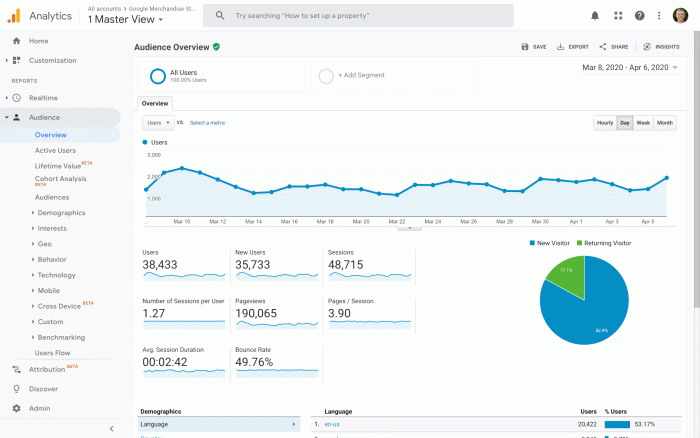
Google Analytics adds new features for privacy era tracking, ushering in a new era of data collection and analysis. This shift reflects a growing emphasis on user privacy and the need for more sophisticated tracking methods. Expect detailed explanations of the new features, their impact on website owners, and practical guidance for implementation. We’ll explore the challenges and opportunities presented by these changes, and examine alternative data collection strategies to ensure accuracy and transparency.
The new privacy-focused features are designed to address evolving user privacy concerns while still providing valuable insights for website owners and marketers. We’ll delve into the technical details of these methods, examining the trade-offs and limitations. This analysis will help you understand how these changes affect website traffic analysis and the importance of adapting to these new regulations.
This detailed guide provides a comprehensive overview of the updated Google Analytics features, allowing you to effectively navigate the privacy-focused landscape.
Introduction to Google Analytics Privacy Enhancements
Google Analytics, a cornerstone of website analytics, has undergone significant changes to adapt to the evolving privacy landscape. These updates reflect a global shift towards user data protection and are designed to provide website owners with robust analytical insights without compromising user privacy. The new features prioritize user consent and minimize data collection, while still allowing for valuable data to be collected.
This allows for a more transparent and user-friendly experience for all users online.The core changes revolve around a shift from directly collecting and processing user-identifiable data to a more anonymized approach. This shift in data handling has profound implications for website owners, requiring a reassessment of tracking strategies and a renewed focus on privacy-respecting data collection methods. The focus is on ensuring website owners can still gain valuable insights into user behavior while safeguarding user privacy.
Key Privacy-Focused Features
These new features focus on data minimization, consent, and data security, all while enabling website owners to understand their audience. Google Analytics 4 (GA4) has prioritized user consent, minimizing data collection, and implementing enhanced data security measures to protect user privacy.
Changes in Data Collection and Usage Practices
Google Analytics now emphasizes a privacy-focused approach, moving away from collecting and processing vast amounts of user-identifiable data. Instead, the focus is on anonymized data, and website owners will need to focus on more holistic user journeys and behaviors. The collection and usage practices have been fundamentally altered to prioritize user privacy.
Google Analytics is rolling out some nifty new privacy-focused tracking features, which is super important for businesses navigating the changing digital landscape. Meanwhile, it’s interesting to see how other platforms are adapting. For instance, TikTok is reportedly planning to open warehouses, potentially impacting logistics and supply chains. This move might be an indicator of TikTok’s ambition to broaden its operations, but in the end, Google Analytics’ new features will be crucial for accurately measuring user engagement and campaign effectiveness in this evolving privacy-centric era.
Impact on Website Owners and Marketers
The privacy-focused enhancements impact website owners and marketers in several ways. They necessitate a shift in website analytics strategies and an understanding of the new data collection practices. Marketers need to adapt their strategies by focusing on less-invasive data collection methods and by understanding the limitations of the new approach. This involves using the anonymized data effectively to gain insights into user behavior without compromising user privacy.
Comparison of Data Collection Methods
| Feature | Previous Data Collection Method | Current Data Collection Method |
|---|---|---|
| Data Type | Directly collected user-identifiable data, including IP addresses, user IDs, and specific user activity. | Anonymized data, focusing on user behavior patterns and aggregated insights. This includes user properties, events, and conversions. |
| Data Storage | Data stored for extensive periods, often indefinitely. | Data stored for specified periods, and there are mechanisms for data deletion or removal. |
| Data Processing | Directly processed user-identifiable data for analysis and reporting. | Anonymized data is processed, and aggregated reporting is provided. Data linking across different sources is minimized. |
| Data Sharing | Data shared with third-party services and partners without specific restrictions. | Data sharing is subject to strict privacy policies and user consent. |
Understanding the New Tracking Methods: Google Analytics Adds New Features For Privacy Era Tracking
Google Analytics’ privacy enhancements have brought about a significant shift in how website traffic is tracked. The previous reliance on cookies for comprehensive user data collection is now superseded by more privacy-focused methods. This transition necessitates a profound understanding of the new techniques and their limitations to effectively interpret and utilize the data.
Technical Details of Privacy-Preserving Tracking Methods
The new tracking methods leverage a variety of techniques to gather user insights without compromising personal data. These methods generally fall into categories such as federated learning of cohorts (FLoC), privacy-preserving hashed identifiers, and server-side event collection. FLoC, for example, groups users into cohorts based on their browsing habits, allowing for aggregate data analysis without individual user identification.
Google Analytics is updating its tracking methods to respect user privacy, which is a smart move. Understanding how to use these new features is key, but ultimately, converting website visitors into customers hinges on psychological principles. Knowing how to apply these principles to design a user-friendly website and a positive user experience is crucial. For a deeper dive into the psychological principles behind converting website visitors, check out this insightful resource on psychological principles converting website.
Ultimately, these privacy-focused analytics tools, coupled with a solid understanding of user psychology, will be essential for website success in the future.
Privacy-preserving hashed identifiers offer a way to track user interactions across different devices and sessions while protecting user anonymity.
Limitations and Potential Drawbacks of New Methods
While privacy-preserving tracking methods offer significant improvements in user privacy, they also present limitations. FLoC, while effective in generating aggregate data, may not be suitable for granular analyses of individual user behavior. The hashed identifiers, though protecting user anonymity, can also lead to loss of data precision and a decrease in the accuracy of certain metrics.
Impact on Website Traffic Analysis
The shift to privacy-preserving tracking methods fundamentally alters how website traffic is analyzed. For instance, instead of precisely tracking individual user journeys, analysts now rely on cohort-level insights. This means that understanding the overall behavior of groups of users is prioritized over detailed analyses of specific individuals. Aggregate data insights can still be valuable, highlighting trends and patterns across broader user segments.
Steps for Implementing New Tracking Methods
Implementing these new methods involves several key steps:
- Review Google Analytics 4 (GA4) setup: Ensure your website is properly configured for GA4, the platform designed for the privacy-focused tracking methods. This includes correctly setting up the tracking code and configuring any necessary data streams.
- Explore new data collection methods: Understand the available privacy-preserving methods, such as FLoC and server-side event collection. Evaluate which methods align with your specific data analysis needs.
- Implement new tracking codes: Carefully implement the new tracking codes, ensuring compliance with the latest privacy guidelines. Refer to the official Google Analytics documentation for specific implementation instructions.
- Transition data analysis strategies: Adapt your website traffic analysis strategies to account for the limitations of the new methods. Shift the focus from detailed user-level data to insights at the cohort level.
Data Points Tracked and Significance
The following table Artikels the different data points tracked with the new methods and their significance.
| Data Point | Significance |
|---|---|
| Cohort membership | Identifies groups of users with similar browsing behaviors. |
| Aggregate page views | Provides insights into popular content among user cohorts. |
| Engagement metrics (e.g., time on site) | Offers a high-level understanding of user interaction patterns within cohorts. |
| Conversions (with attribution limitations) | Measures conversions at the cohort level, with reduced granularity for individual users. |
Impact on Website Owners and Marketers
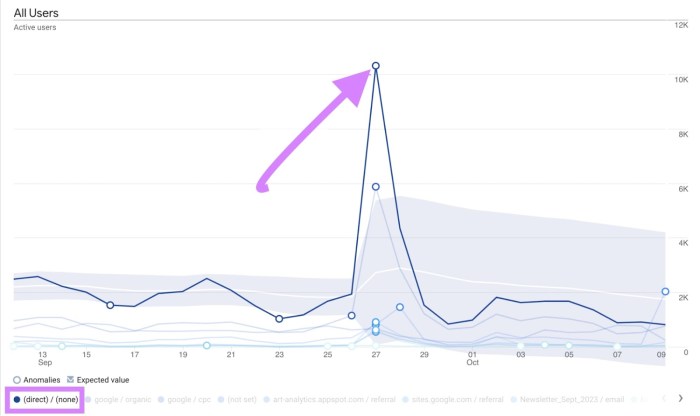
The shift towards privacy-focused tracking in Google Analytics necessitates a fundamental rethink for website owners and marketers. No longer can they rely on the granular detail previously available. This shift demands a recalibration of strategies, demanding a more nuanced understanding of user behavior and a focus on data that respects user privacy.The new privacy enhancements fundamentally alter the accuracy and reliability of website analytics data.
Previously, comprehensive user journeys could be tracked, allowing for precise audience segmentation and highly targeted campaigns. Now, the focus is on aggregated data, providing a broader overview of website performance but with less precision on individual user actions. This necessitates a shift from micro-targeting to macro-level strategies that understand broader trends in user engagement.
Google Analytics is adding new features to track website traffic in this privacy-focused era. This means businesses need to adapt their strategies for understanding user behavior. A key part of this is understanding how to build links to your site, which can improve its visibility to search engines. Learning about what is link building is crucial for effectively leveraging these new tracking methods.
Ultimately, these changes in analytics require careful consideration of how you approach website traffic analysis and optimization.
Accuracy and Reliability of Analytics Data
The new tracking methods, while respecting privacy, inevitably lead to less detailed user data. Website owners must accept that precise user behavior tracking, previously a staple of digital marketing, is no longer available. This change requires a move away from relying on individual user data and towards a more holistic understanding of user segments and patterns. For example, understanding that 20% of users spend an average of 10 minutes on the website, rather than pinpointing the exact actions of each user during that time, is now the focus.
Effects on Different Types of Websites
The impact varies across different website types. E-commerce sites, for instance, rely heavily on detailed conversion tracking. The loss of precise data on individual purchase journeys will impact their ability to personalize recommendations and optimize checkout processes. News websites, on the other hand, may experience less impact on their overall traffic and engagement analysis, as aggregated data can still provide insights into general reader preferences.
Social media sites may experience the most significant changes, as tracking user interactions across platforms will be considerably more challenging.
Potential Challenges and Opportunities
Website owners face the challenge of adapting their strategies to the new limitations. Existing marketing campaigns may need to be adjusted to account for the lack of granular data. The opportunities lie in developing strategies that leverage the available data for effective decision-making. Focusing on broader trends and user segments will be critical.
Adapting Strategies to Comply with Regulations
Website owners can adapt by focusing on user segmentation based on broader characteristics rather than individual actions. For example, instead of targeting users based on specific product searches, they can target users based on demographics and interests. Implementing A/B testing on different versions of website content will be key to optimizing user experience and engagement, based on aggregate metrics.
Creating compelling user experiences that draw users into the website without excessive tracking will be a key focus.
Best Practices for Implementing Changes
- Prioritize user privacy by designing experiences that respect data limitations.
- Implement robust A/B testing strategies to optimize website content based on aggregated data.
- Refine marketing campaigns based on overall user engagement trends and patterns rather than individual user data.
- Invest in tools that analyze aggregated data to understand user behavior patterns.
- Focus on user segmentation based on broader characteristics and interests.
Alternatives and Considerations for Data Collection
The shift towards privacy-focused tracking necessitates a reevaluation of data collection strategies. Traditional methods, reliant on comprehensive user data, are now less effective. Website owners and marketers need to adapt and explore alternative solutions that respect user privacy while still providing valuable insights. This exploration involves a careful consideration of different approaches and tools, along with a commitment to transparency with website visitors.The move away from the detailed user profiles of the past requires a fundamental shift in mindset.
We need to embrace data collection methods that are both effective and ethical, allowing us to understand user behavior without compromising their privacy. This involves a careful balancing act between data analysis and user rights.
Potential Alternative Solutions
A variety of alternative solutions for data collection and analysis are emerging. These solutions often focus on aggregated data, user-consent-based tracking, and privacy-preserving techniques. Finding the right balance between data insights and user privacy is crucial.
Pros and Cons of Different Alternatives
Different data collection methods offer varying levels of data richness and user privacy. For example, aggregated data analysis, while less granular, provides valuable insights into overall trends and patterns. However, it sacrifices the ability to track individual user behavior in detail. Consent-based tracking, on the other hand, requires user permission to collect data, thereby maintaining user control and trust, but it may lead to limited data sets.
Importance of Transparency with Website Visitors
Transparency is paramount in building trust with website visitors. Clear communication about data collection practices, including the types of data collected, how it is used, and how it is protected, fosters user confidence and promotes ethical data handling.
“Transparency builds trust. Clear communication about data practices is crucial for maintaining user confidence.”
Comparison of Approaches for Handling User Data and Privacy
Various approaches exist for handling user data and privacy. One approach focuses on providing users with more control over their data, allowing them to opt-in or opt-out of specific data collection practices. Another approach prioritizes aggregated data analysis, providing insights into broader trends without compromising individual user privacy.
Alternative Tracking Tools
| Tool | Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Matomo | Open-source, privacy-focused, allows for detailed customization, provides robust reporting | Flexibility, control over data, cost-effective | Steeper learning curve, may require more technical expertise |
| Fivetran | Data integration platform, connects to various data sources, automates data collection | Streamlined data flow, efficient data analysis | May have limitations for specific types of tracking, additional cost for complex setups |
| Segment | Cross-platform data management platform, allows for centralized data collection | Flexibility, adaptability to different platforms, ease of integration | Potentially high implementation cost for complex setups |
Different tools cater to various needs and technical capabilities. Selecting the right tool depends on the specific requirements of a website or business.
Case Studies and Examples of Implementation
Navigating the new privacy landscape in digital marketing requires a practical understanding of how businesses are adapting. This section explores real-world examples of websites successfully implementing Google Analytics privacy enhancements, highlighting effective strategies and showcasing positive outcomes. These examples demonstrate that adapting to privacy-focused tracking doesn’t have to be a barrier to achieving marketing objectives.
Successful Implementation Strategies
Businesses have adopted various strategies to maintain valuable insights while respecting user privacy. These include leveraging alternative data sources, adjusting marketing strategies, and refining data collection practices. The key is to focus on the user experience and data privacy. A thoughtful approach that balances the needs of the business with the rights of the user will ensure long-term success.
- Enhanced User Consent Mechanisms: Many websites have implemented more transparent and user-friendly consent mechanisms. For example, instead of a single, overwhelming consent pop-up, some companies utilize a series of prompts, guiding users through the different types of data collected and allowing granular control over specific data points. This approach not only improves the user experience but also builds trust, a crucial element in the current privacy-conscious environment.
- Utilizing Alternative Data Sources: Recognizing the limitations of traditional tracking methods, businesses have turned to alternative data sources. These include website engagement metrics like bounce rate and time on page, as well as behavioral patterns observed through user interactions. By combining these alternative data points, businesses can still gain valuable insights into user behavior without relying on sensitive personal data.
- Refined Marketing Strategies: Businesses have adjusted their marketing strategies to focus on user experience and engagement. This often involves a shift from focusing solely on acquisition to concentrating on user retention and customer lifetime value. For example, a clothing retailer might implement personalized recommendations based on past browsing history, creating a more engaging experience for returning customers.
Creative Approaches to Data Collection and Analysis
Innovative approaches to data collection and analysis are vital for maintaining insights in the privacy-centric era. Businesses are looking beyond traditional metrics to develop new ways to understand customer behavior and preferences.
- Focus on User Journeys: Instead of relying on granular, individual user data, some businesses focus on understanding the overall user journey. This approach allows them to identify patterns and trends across user groups, gaining valuable insights without compromising individual user privacy. For instance, a travel agency might analyze the overall journey of users booking trips, identifying popular routes and travel durations, without tracking individual user preferences.
- Implementing Federated Learning of Cohorts: This technique allows businesses to gain insights into user groups without compromising individual user privacy. This involves training machine learning models on aggregated data from similar user groups, which provides valuable insights into trends and behaviors without requiring the use of sensitive individual data. A banking app might use this to identify high-risk user segments without exposing individual financial data.
Case Study Examples and Outcomes
| Website/Business | Implementation Strategy | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| eCommerce Platform A | Implemented a tiered consent system, allowing users to control data collection for specific features. | Increased user trust and engagement; observed a slight decrease in conversion rates initially, followed by a stabilization and subsequent improvement. |
| News Publication B | Leveraged alternative data sources like page views, dwell time, and social media engagement. | Maintained valuable insights into audience preferences and engagement without compromising user privacy; reported success in retaining readership and ad revenue. |
| Travel Agency C | Focused on user journey analysis to understand overall customer preferences. | Identified high-demand travel routes and popular booking patterns, enabling targeted marketing campaigns without individual user tracking. |
Future Trends and Predictions
The shift towards privacy-focused analytics is not a fleeting trend; it’s a fundamental change in how we collect and utilize user data. This evolution demands a proactive approach from marketers and website owners to adapt and thrive in this new landscape. Understanding the potential future developments will be crucial for navigating the complexities of the evolving digital marketing environment.The future of privacy-focused analytics will be characterized by a greater emphasis on user consent, transparency, and the development of new, innovative methods for data collection and analysis.
The need for ethical data practices will continue to rise, shaping not only marketing strategies but also broader societal discussions about data ownership and control.
Potential Future Developments in Privacy-Focused Analytics
The development of new privacy-focused analytics tools and techniques will be a key driver in this area. Expect advancements in federated learning, differential privacy, and synthetic data generation to provide robust data analysis without compromising user privacy. These approaches will empower businesses to glean valuable insights from user behavior while upholding stringent privacy standards. These technologies promise to provide more nuanced and comprehensive insights, while maintaining respect for user data.
Long-Term Impact on the Digital Marketing Landscape, Google analytics adds new features for privacy era tracking
The long-term impact of these changes will reshape the digital marketing landscape by prioritizing user trust and experience. Businesses will need to demonstrate a commitment to ethical data practices and user privacy. This focus on user privacy will likely lead to a greater emphasis on personalization strategies that are transparent and respect user choices.
Evolution of User Data Privacy Policies
User data privacy policies will likely become more intricate and comprehensive. We can anticipate more detailed explanations of how data is collected, used, and shared. There will likely be increased emphasis on providing users with more granular control over their data, including options for opting out of specific data collection practices. Furthermore, international data privacy regulations are likely to influence the development of data privacy policies worldwide.
Timeline of Predicted Changes and Advancements
Predicting precise timelines for these advancements is challenging, but certain milestones are likely to occur within the next few years.
- Within the next 2-3 years, we can expect to see increased adoption of privacy-focused analytics tools and platforms by businesses.
- Within the next 5 years, the impact of privacy regulations will be more evident in the digital marketing landscape. Businesses will need to demonstrate their commitment to user privacy.
- Within the next 10 years, we may see significant breakthroughs in data anonymization and synthetic data generation, enabling advanced analytics without compromising user privacy.
Visual Representation of Future Trends in Data Collection
Imagine a graph with the X-axis representing time (years from now) and the Y-axis representing the degree of user control over data collection. A steadily increasing line on the graph would indicate a growing emphasis on user control over data. Initially, the line would show a gradual increase, signifying the initial adoption of privacy-focused practices. Later, a steeper incline would suggest the significant impact of new regulations and technologies, leading to a higher level of user control.
This visual representation illustrates the increasing importance of user data privacy and the ongoing evolution of data collection methods.
Closure
In conclusion, Google Analytics’ new privacy features represent a significant shift in how website owners collect and analyze data. While these changes present challenges, they also offer opportunities for more transparent and effective data collection. By understanding the new tracking methods, their impact, and alternative solutions, website owners can navigate this evolving landscape successfully. Adapting to these changes is crucial for maintaining a strong online presence in today’s privacy-conscious world.