Google UK lawsuit search dominance is thrusting the tech giant into the spotlight, igniting debate about its market power and potential impact on users and competitors. This investigation delves into the historical context of Google’s UK market position, examining the nature of the lawsuit, and analyzing the potential economic and user experience ramifications.
The lawsuit alleges that Google’s dominance in the UK search market stifles competition, potentially hindering innovation and negatively affecting smaller players. Key arguments focus on Google’s search algorithm, market share, and the implications for consumers. This analysis will explore potential changes to the user experience if Google’s dominance is challenged, and investigate alternative search engines currently available in the UK market.
The discussion will also consider the broader regulatory and policy implications of this landmark case, including potential impacts on global digital markets and user experience.
Historical Context of Google’s UK Market Position
Google’s dominance in the UK online search market isn’t a sudden phenomenon. Its rise reflects a complex interplay of technological advancements, evolving user habits, and regulatory landscapes. Understanding this historical context is crucial for evaluating the current legal challenges and the broader implications for the digital economy.The company’s journey in the UK has been shaped by the evolution of online search technology, alongside significant regulatory developments and shifts in consumer behaviour.
This evolution has been intertwined with Google’s strategic adaptations and responses to challenges posed by the changing market dynamics.
Google’s Early Presence and Growth
Google first established a significant presence in the UK in the late 1990s and early 2000s. Its innovative search algorithm, emphasizing relevance and user experience, rapidly gained popularity compared to existing search engines. This early success was fueled by the burgeoning internet adoption in the UK, leading to increased online activity and the need for efficient search tools.
The Google UK lawsuit surrounding search dominance is a fascinating case, highlighting the power of online search. This impacts how businesses advertise, and directly connects to the strategies used for driving demand generation through Google Ads, specifically checkout optimization for merchants. For example, google ads checkout on merchant demand gen is a critical area of focus for businesses navigating this complex landscape.
Ultimately, the lawsuit raises questions about the fairness and competitiveness of the digital advertising market.
Impactful Events Shaping Google’s Market Share
Several events significantly impacted Google’s market share in the UK. The rise of mobile internet access and the subsequent increase in mobile searches, beginning around the mid-2000s, fundamentally altered how users interacted with online information. This shift significantly influenced Google’s strategy, necessitating adaptation to the mobile-first environment. The emergence of social media platforms and the increasing use of search for information discovery and product research were other notable events impacting Google’s market position.
Evolution of Online Search Technology
The evolution of online search technology has directly contributed to Google’s dominance. The development of sophisticated algorithms, such as PageRank, and the integration of various data sources (including news, images, and videos) transformed the user experience and made Google a more comprehensive search engine. This technological advancement was instrumental in attracting and retaining users, leading to its substantial market share.
The increasing sophistication of search algorithms allowed Google to provide more accurate and tailored search results, further strengthening its position in the market.
Key Regulatory Changes Affecting Search Engine Markets
The UK has seen several key regulatory changes impacting search engine markets. The development and enforcement of regulations related to consumer protection, competition, and data privacy have influenced Google’s operations and market strategies. These regulations, such as those addressing data protection and competition, have sought to balance the benefits of market dominance with the needs of consumers and smaller competitors.
For example, changes in data protection legislation, like GDPR, required Google to adapt its data collection and usage practices, influencing its interactions with users in the UK. These evolving regulations continue to shape the digital landscape, creating a dynamic environment for companies like Google.
The Nature of the Lawsuit
The UK’s antitrust watchdog, the Competition and Markets Authority (CMA), launched a landmark investigation into Google’s alleged dominance in the UK search market. This investigation culminated in a formal lawsuit, alleging that Google’s practices unfairly stifle competition and harm consumers. The case, a significant test of market power and digital dominance, is attracting global attention.The core arguments presented in the lawsuit center around Google’s alleged abuse of its dominant position in the UK search market.
The CMA argues that Google’s practices have created an unfair playing field, hindering smaller competitors and ultimately impacting consumers. The lawsuit seeks to ensure a more competitive market, allowing for a wider range of options for users and potentially leading to better services and lower prices.
Core Arguments Presented
The CMA’s case hinges on the argument that Google’s search practices have created an unfair competitive landscape in the UK. They contend that Google’s prominent position gives it undue influence over the results displayed in search queries, effectively hindering rivals. This alleged manipulation of search results benefits Google, to the detriment of consumers.
Specific Allegations Against Google
The CMA alleges several specific actions by Google that contribute to its alleged market dominance. These include:
- Predatory pricing: Google is accused of using its market power to offer search services at artificially low prices, effectively pricing smaller competitors out of the market.
- Bundling and favoring own products: The CMA alleges Google favors its own products and services in search results, giving them a preferential position over competing offerings. This could lead to customers missing out on potentially better alternatives.
- Unfair algorithms: The case alleges that Google’s search algorithm is designed to favor its own products, pushing them to the top of search results.
Evidence Presented in the Case
The CMA likely presented a range of evidence to support its claims, including:
- Market share data: Detailed data on Google’s market share in the UK search market would be crucial evidence. This data would demonstrate the extent of Google’s dominance.
- Expert testimony: Economic experts and industry specialists would likely provide insights into the impact of Google’s practices on competition and consumer choice.
- Internal documents: Internal Google documents (if obtained through legal means) could shed light on the company’s strategies and decision-making processes related to search algorithms and ranking.
Legal Precedent Set by Similar Cases
The lawsuit draws upon legal precedent from similar cases globally. These cases often involve antitrust investigations into dominant tech companies. The CMA’s case will likely be influenced by existing legal interpretations of market dominance and anti-competitive practices in the digital realm.
Key Players Involved
- Competition and Markets Authority (CMA): The UK’s antitrust watchdog leading the investigation and lawsuit.
- Google: The company facing the allegations of market dominance and anti-competitive behavior.
- Legal teams for both parties: The legal teams representing the CMA and Google will play a crucial role in the legal process, presenting arguments and evidence.
Google’s Search Dominance in the UK
Google’s dominance in the UK search market is undeniable, a position that has drawn considerable attention and scrutiny, particularly in the context of the ongoing legal battle. This substantial market share, while beneficial for users in terms of convenience, raises concerns about the potential for reduced competition and innovation in the wider digital landscape.The sheer scale of Google’s operation, coupled with its sophisticated search algorithms, presents a formidable barrier to entry for smaller competitors.
Understanding this dominance is key to comprehending the nuances of the legal challenges and the wider implications for the digital economy.
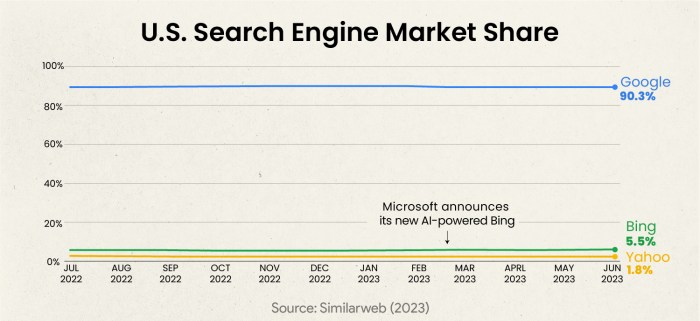
Google’s Market Share in the UK Search Engine Market
Google maintains a substantial and consistently high market share in the UK search engine market. Precise figures fluctuate, but publicly available data often place Google’s share significantly above its closest competitors. This dominance is a crucial factor in the legal challenges, as it raises concerns about the fairness and openness of the digital market.
Impact on Competition
Google’s dominance has the potential to significantly stifle competition. The sheer size and resources of Google allow it to dominate various aspects of the digital ecosystem, potentially leading to an uneven playing field. This can limit opportunities for innovation and the development of alternative search solutions. The large amount of user data Google collects through its search engine is also a significant concern.
This data can be leveraged to further enhance its search engine algorithms and products.
Impact on Smaller Search Engines or Upstarts
Smaller search engines or new entrants face considerable challenges in competing with Google’s established infrastructure and user base. The sheer scale of Google’s operations, coupled with its advanced search algorithms and user base, makes it very difficult for smaller competitors to gain traction. Existing search engines and new entrants face the significant hurdle of gaining a substantial user base.
Without a large user base, it’s difficult to attract advertisers and, subsequently, maintain a sustainable business model.
Comparison of Google’s Search Algorithm to Competitors
Google’s search algorithm is highly complex and constantly evolving, designed to provide users with the most relevant and useful search results. Other search engines use varying algorithms, often with different priorities and approaches to ranking results. For example, some algorithms may emphasize specific types of content, such as news articles or academic papers. The intricacies of these algorithms and their impact on search results are constantly in flux, with Google’s continuously evolving algorithms making it challenging for competitors to maintain a comparable level of relevance and efficiency.
Detailed Explanation of Google’s Search Algorithm and its Effects on Search Results, Google uk lawsuit search dominance
Google’s search algorithm is a sophisticated system of ranking and displaying results. It takes into account a vast array of factors, including relevance, website authority, user engagement, and geographic location. These factors, combined, affect how search results are ordered, impacting user experience and potentially creating biases. A well-optimized website is more likely to appear higher in search results, potentially giving a competitive advantage to those with the resources to optimize their presence.
Google’s algorithm prioritizes speed and relevance to user queries, aiming to deliver results quickly and accurately. This can lead to a more efficient search experience, but it also raises concerns about the potential for manipulation or bias. This complexity, however, is also a source of potential manipulation.
Economic Implications of the Lawsuit
The Google UK lawsuit, alleging search dominance, raises significant economic questions about market competition and its impact on various stakeholders. Understanding these implications is crucial to assessing the potential consequences for the UK economy, businesses, and consumers. This analysis will explore the potential ripple effects of the lawsuit on innovation, entrepreneurship, and the overall economic landscape.The outcome of the lawsuit could dramatically reshape the UK digital market.
If Google is found to have abused its dominant position, potential remedies could range from structural changes, like divesting certain assets, to regulatory fines. These interventions could potentially affect Google’s market share, and consequently, the competitive landscape for other search engine providers and related businesses.
Potential Effects on Consumers
Consumer welfare is a key consideration in antitrust cases. A dominant search engine could potentially limit consumer choice and increase prices for related services. For example, if Google’s dominance prevents the rise of alternative search engines, consumers might face higher prices or less innovation in the search experience. Consumers might also see a decline in the quality of results or tailored advertising if competition is suppressed.
Potential Effects on Businesses
Businesses, particularly smaller and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), rely heavily on online search. A significant ruling against Google could either enhance or constrain their access to potential customers. If Google’s dominance is challenged, this could lead to a more competitive market where SMEs can better compete for visibility and market share. Conversely, a less competitive market could negatively impact businesses that rely on Google’s services for marketing and sales.
Potential Effects on the Overall Economy
The UK economy benefits from a vibrant and competitive digital market. A successful challenge to Google’s dominance could lead to greater innovation and competition in the search market. Conversely, if the ruling fails to deter anti-competitive behavior, it could stifle innovation and entrepreneurship. The lawsuit’s impact could be felt across numerous sectors, from retail and tourism to finance and technology.
The overall economic impact depends heavily on the specific actions and remedies imposed by the court.
Potential Impacts on Innovation and Entrepreneurship
Innovation and entrepreneurship thrive in competitive environments. If the lawsuit fosters competition, it could open opportunities for new search engine technologies and innovative business models. This could lead to improved search functionality, personalized user experiences, and new avenues for online advertising. However, if the lawsuit doesn’t effectively curb anti-competitive practices, it could stifle new entrants and limit the development of potentially disruptive technologies.
Comparative Analysis of Potential Outcomes with Other Similar Cases
Analyzing previous antitrust cases against dominant tech companies provides valuable context. Cases like the Microsoft antitrust case in the US offer lessons about the potential economic consequences of challenging market dominance. However, the UK market and its unique characteristics need to be considered in assessing the likely outcomes. The specific nature of Google’s alleged anti-competitive practices and the remedies sought will be crucial in determining the ultimate economic impact.
A thorough evaluation of previous rulings and their economic effects is essential for understanding the potential consequences of this lawsuit.
Potential Impacts on User Experience

The ongoing lawsuit challenging Google’s search dominance in the UK raises significant questions about the future user experience. This exploration delves into potential shifts in search results, features, and the overall search landscape, considering both positive and negative outcomes. The potential impact on user satisfaction and the availability of alternative search engines are also crucial considerations.
Potential Changes in Search Results
Understanding how search results might change is vital for evaluating the impact on users. The current system, heavily reliant on Google’s algorithms, prioritizes certain results based on factors like relevance, popularity, and potential revenue streams. A breakup of Google’s dominance could lead to adjustments in this process.
| Potential Change | Impact on User Experience |
|---|---|
| Increased competition among search engines | Users might see more diverse results, potentially exposing them to a wider range of perspectives and information sources. |
| Differing algorithms prioritizing different factors | Users could encounter varying degrees of accuracy and relevance across different search engines, requiring adjustment to adapt to new search strategies. |
| Emphasis on diverse sources and viewpoints | Users might gain access to a more balanced representation of information, although biases in algorithms used by other search engines may also exist. |
| Increased emphasis on local and niche content | Users in specific geographic areas or with particular interests may find more relevant results, depending on the algorithms used by alternative search engines. |
Potential Changes in Search Features
Changes in search features could also significantly impact the user experience. Features like personalized search results, image search, and advanced search tools may evolve or even disappear depending on the new market structure.
- Personalized Search Results: Alternative search engines might adopt different personalization strategies, impacting the accuracy and relevance of results for individual users. For example, a search engine focusing on privacy might personalize results based on user-provided criteria and minimize data collection. This could result in users experiencing either improved or diminished personalized results, depending on their preference and the new algorithms used.
- Image Search: Competition in image search could lead to varied search results and functionalities. Different search engines might prioritize different aspects of image retrieval, like copyright compliance or image resolution. This could lead to users finding different types of results or experiencing delays in image retrieval.
- Advanced Search Tools: Alternative search engines may introduce their own advanced search features. These could focus on specialized fields, like academic research or legal documents, offering different perspectives and functionality. Some might enhance or reduce the existing advanced search features depending on the priorities and goals of the search engine.
Alternatives to Google Search
If the lawsuit succeeds and Google’s dominance is challenged, alternative search engines could emerge or gain market share. This could result in a more competitive search landscape.
- DuckDuckGo: DuckDuckGo, known for its privacy-focused approach, might gain significant traction. Users concerned about data privacy may find this a desirable alternative to Google.
- Ecosia: Ecosia, a search engine that donates a portion of its revenue to reforestation efforts, could attract users with environmentally conscious values.
- Other Competitors: Emerging or existing competitors could also potentially challenge Google’s dominance, offering unique features or focusing on specific niches.
Possible Outcomes for Users
The success of the lawsuit could lead to several possible scenarios for users.
- Improved Search Diversity: Users might encounter a wider variety of search results and features, exposing them to more diverse information sources and perspectives. This could result in improved overall search results.
- Increased Search Engine Choice: A more competitive market could provide users with greater choice and flexibility in selecting a search engine that best suits their needs and values. This is a positive development.
- Potential for Algorithm Bias: Other search engines might have their own biases in algorithms, potentially impacting the accuracy and relevance of search results. This could result in inconsistent user experience.
- Learning Curve: Users might need to adapt to new search engines, algorithms, and search strategies. This might be a short-term issue.
Regulatory and Policy Considerations
The Google UK lawsuit, focusing on search dominance, raises significant regulatory and policy questions. The outcome will likely shape how the UK and other countries approach digital market regulation in the future. This analysis delves into the key regulatory bodies, potential policy changes, and the broader impact on the global digital landscape.This section examines the UK’s regulatory framework for digital markets, evaluating how the lawsuit might alter current policies and influence future approaches to controlling the power of dominant tech companies.
It also considers the ripple effects of the case on global digital policy and the implications for other countries navigating similar challenges in their respective digital spheres.
Relevant UK Regulatory Bodies
The UK has several regulatory bodies with a stake in digital markets. These include the Competition and Markets Authority (CMA), which investigates mergers and anti-competitive practices, and the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO), responsible for data protection. The CMA has a crucial role in assessing the potential anti-competitive effects of Google’s market dominance in search, while the ICO’s role centers on ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
The Office for National Statistics (ONS) plays a supporting role by gathering and publishing data on the UK’s digital economy. Their analyses are essential for understanding market trends and for evaluating the impact of the lawsuit on the digital economy.
Potential Policy Changes
The lawsuit could lead to significant policy changes, potentially affecting market access and competition in the UK’s digital economy. One possible outcome is the introduction of stricter rules targeting the dominance of search engines, perhaps requiring greater transparency in algorithms or promoting competition through alternative search platforms. Another potential policy change is stricter enforcement of existing regulations, leading to increased scrutiny and potential fines for violations.
This might also include mandating greater data sharing among competing platforms to allow for fairer comparisons.
Impact on Broader Digital Markets
The Google UK lawsuit’s impact could extend beyond the UK’s borders. The outcome may influence the development of similar regulatory frameworks in other countries. If the UK courts find Google’s practices anti-competitive, this could create a precedent for similar cases elsewhere. For example, if the ruling favors the plaintiffs, other countries might face pressure to introduce regulations aimed at curbing the dominance of major tech companies.
The Google UK lawsuit surrounding search dominance is definitely a hot topic. It’s fascinating to consider how powerful search engines have become, and how a company’s control over the online space impacts everyone. Building a strong online presence often requires more than just technical SEO; developing valuable email newsletter thought leadership, like that found here , is increasingly important for businesses to stand out from the crowd.
Ultimately, the Google UK lawsuit highlights the importance of competition and fair play in the digital marketplace.
The outcome may affect the entire landscape of digital markets worldwide, influencing how tech giants operate in search, advertising, and other online services.
Influence on Global Digital Policy
The outcome of the Google UK lawsuit will significantly influence global digital policy discussions. If the case sets a precedent for antitrust action against dominant tech companies, it could spur a global wave of regulatory change. This is particularly relevant in the context of globalization and the increasingly interconnected nature of the digital economy. The case could lead to the creation of international standards for regulating the digital economy, which would help to establish a level playing field for businesses worldwide.
For instance, international collaborations between regulatory bodies could emerge to coordinate strategies for managing digital market dominance.
The Google UK lawsuit surrounding search dominance is a fascinating case, highlighting the power of online platforms. It’s a reminder that, in the digital age, building a strong online presence isn’t just about search engine optimization, but also about creating a truly authentic brand story. A compelling brand narrative, like the one explored in create authentic brand story , can help companies stand out and connect with their audience, even in the face of powerful competitors.
Ultimately, this lawsuit underscores the importance of maintaining fair competition in the online sphere, and authenticity in brand building plays a crucial role in that battle.
Implications for Other Countries
The case’s implications for other countries are multifaceted. The UK’s experience with regulating Google’s dominance could serve as a model for other jurisdictions. Countries facing similar challenges, such as concerns about search engine dominance or issues with digital market access, could adapt or develop regulations based on the UK’s case. The case might even encourage international cooperation to address global digital market concerns.
For instance, if the lawsuit is successful in establishing precedents for breaking up large tech companies, it could influence regulations in countries with significant digital economies, leading to increased competition and a more balanced digital landscape.
Alternatives to Google Search
Google’s dominance in the UK search market has spurred interest in alternative search engines. This section explores the current landscape of alternative search engines, providing a comparison of their strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these alternatives is crucial for evaluating the potential impacts of the ongoing lawsuit and the future of online search in the UK.
Available Alternative Search Engines in the UK Market
A variety of search engines are available beyond Google, catering to different user needs and preferences. These alternatives range from established players with broad appeal to niche services targeting specific demographics or functionalities. DuckDuckGo, a privacy-focused search engine, is a prominent example, while others, like Ecosia and Qwant, emphasize environmental responsibility and user data protection, respectively.
Comparison of Alternative Search Engines to Google
Evaluating alternative search engines necessitates a comparison to Google, the dominant player. Key criteria include search accuracy, user experience, and specific features. While Google excels in comprehensive indexing and sophisticated algorithms, alternative search engines may offer unique strengths. For instance, DuckDuckGo emphasizes user privacy by not tracking search history, which can be a valuable feature for users concerned about online surveillance.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Alternative Search Engines
Alternative search engines possess varying strengths and weaknesses. DuckDuckGo, prioritizing user privacy, lacks the comprehensive indexing of Google, potentially resulting in fewer results for complex queries. Ecosia, promoting environmental sustainability, might not always offer the same level of speed and accuracy as Google. Qwant, focusing on user data protection, may be less familiar to UK users compared to more established competitors.
Historical Context of Alternative Search Engines
Alternative search engines have existed alongside Google, but their market share has remained relatively small compared to Google’s. Early search engines like AltaVista and Lycos paved the way for Google’s dominance. The rise of privacy concerns and the evolution of search technologies have led to the development of new alternatives that focus on different aspects of the search experience.
The historical context reveals that while alternatives exist, Google’s strong brand recognition and extensive index have proven difficult for challengers to overcome.
Comparison Table of Different Search Engines
| Search Engine | Strengths | Weaknesses | Specific Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Comprehensive indexing, sophisticated algorithms, broad user base | Potential for biased results, data privacy concerns | Instant results, image search, knowledge graph | |
| DuckDuckGo | Prioritizes user privacy, no tracking of search history | May not return as many results as Google for complex queries | Privacy-focused interface, customizable search settings |
| Ecosia | Environmental focus, plants trees with every search | Potentially less comprehensive indexing than Google | Eco-friendly approach, promotes sustainability |
| Qwant | Focuses on user data protection, respects privacy | May not have the same level of brand recognition as Google | European roots, data protection compliance |
Public Opinion and Perceptions
Public perception of Google and this lawsuit is multifaceted, ranging from concerns about monopolistic practices to praise for its innovation and user-friendly services. The debate highlights a fundamental tension between technological advancement and the potential for market distortion. Different segments of the public hold varying perspectives, shaping the public discourse surrounding the case.
Varying Viewpoints on Google’s Dominance
Public opinion regarding Google’s dominance is highly polarized. Some view Google’s market position as a natural outcome of its innovative products and efficient algorithms, leading to a superior user experience. Others perceive this dominance as a consequence of anti-competitive practices, arguing that it stifles innovation and harms consumers by limiting choices. This divergence in viewpoints underscores the complexity of the issue and the absence of a clear consensus.
Examples of Public Discourse
Online forums, social media platforms, and news articles frequently feature discussions about the lawsuit. These discussions often reflect the differing perspectives. Some users express concern about the potential for reduced competition, while others argue that Google’s dominance has been beneficial for the development of the internet. These contrasting viewpoints are evident in the ongoing public discourse, emphasizing the complexity of the issue.
Interest Groups Involved
Numerous interest groups are involved in this case, each with its own set of motivations and perspectives. These groups include consumers, who may be concerned about choice and pricing; businesses, particularly smaller competitors, who may see Google’s dominance as an obstacle; and regulators, who are tasked with maintaining a healthy competitive market. Understanding the motivations of these diverse groups is crucial to comprehending the complexity of the situation.
Summary of Public Opinions
| Opinion Category | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Pro-Google | Emphasizes Google’s innovation, user-friendliness, and overall positive impact. Many argue that Google’s search engine has become an essential tool in modern life. | “Google has made searching the internet easier than ever.” “Google Maps is invaluable.” |
| Anti-Google | Focuses on concerns about Google’s market dominance and its potential to stifle competition. These concerns often include issues of user data privacy. | “Google’s dominance leads to a lack of alternatives.” “Google’s algorithms are biased.” |
| Neutral | Individuals who have a more balanced perspective, acknowledging both the benefits and potential drawbacks of Google’s dominance. | “Google’s dominance has some benefits, but it also presents challenges.” |
Elaboration on Interest Groups
Consumers are a key interest group, as they directly benefit from Google’s services but might also be concerned about the potential impact on choices and prices. Smaller businesses might feel stifled by Google’s dominance, as it may be difficult to compete with such a large player. Regulators, on the other hand, are responsible for ensuring fair competition and preventing monopolies, thus having a crucial role in the outcome of the case.
Epilogue: Google Uk Lawsuit Search Dominance
The Google UK lawsuit regarding search dominance raises significant questions about the future of online search and competition. This case is likely to have far-reaching consequences, impacting not only the UK market but potentially influencing digital policy globally. The outcome will be closely watched, and the potential alternatives to Google search will be carefully evaluated. The potential impacts on user experience, the economic consequences, and the regulatory considerations are all critical aspects to consider in understanding the implications of this legal battle.
The evolving public perception of Google and the case will also be a critical factor in shaping the future of the digital landscape.