How to migrate to GA4 is a crucial step for any website or app looking to leverage the latest Google Analytics features. This in-depth guide breaks down the entire process, from understanding the differences between Universal Analytics and GA4 to implementing tracking and analyzing data. We’ll cover everything you need to know, making the transition smooth and successful.
This guide covers the essential steps of planning, data import, implementation, and analysis. We’ll provide a roadmap, detailed explanations, and actionable advice, ensuring you’re well-equipped to navigate the complexities of the migration process.
Introduction to Google Analytics 4 (GA4) Migration

Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is the next-generation web analytics platform from Google, designed to provide a more comprehensive and adaptable way to track website and app performance. It offers a more robust and future-proof approach to data collection and analysis, emphasizing events over traditional session-based metrics. Moving to GA4 is crucial for businesses seeking to leverage advanced analytics capabilities and remain competitive in the evolving digital landscape.GA4 represents a significant shift from the previous Universal Analytics platform, offering a more robust and flexible framework for data collection and analysis.
This shift brings benefits such as improved data accuracy, enhanced reporting capabilities, and better integration with other Google services. It’s not just an upgrade; it’s a fundamental change in how you approach web and app analytics.
Benefits of Migrating to GA4
Migrating to GA4 provides several advantages. Improved data accuracy and comprehensive insights are key benefits. Enhanced reporting capabilities enable deeper understanding of user behavior and engagement, leading to more informed business decisions. Furthermore, GA4 is more future-proof, adapting better to evolving digital landscapes. It integrates seamlessly with other Google services, offering streamlined data workflows.
Differences Between Universal Analytics and GA4
Universal Analytics and GA4 differ fundamentally in their data models and collection methods. Universal Analytics relies on a hierarchical structure, primarily tracking sessions and page views. GA4, in contrast, uses an event-based model, capturing a wider range of user interactions, providing a more granular understanding of user journeys.
| Feature | Universal Analytics | GA4 |
|---|---|---|
| Data Model | Hierarchical | Event-Based |
| Reporting | Primarily reports on sessions and pages | Primarily reports on events |
| Data Collection | Cookie-based | Uses various methods including cookies and other identifiers |
The table above clearly Artikels the key distinctions. The event-based approach in GA4 provides a more nuanced view of user engagement, allowing for deeper insights into user behavior. This is in contrast to Universal Analytics, which primarily focused on tracking sessions and page views.
Migrating to GA4 is crucial for any website, but it’s not just about the technical aspects. A strong online presence is vital for any small business, and making a great first impression is key. Check out this article on making a big impression how to make your small tech firm look big for tips on projecting a professional image, which, in turn, can boost your credibility and encourage engagement.
Ultimately, a compelling website and solid analytics data, such as GA4, will help you attract the right audience and make your migration a success.
Key Considerations for a Successful GA4 Migration
A successful GA4 migration requires careful planning and execution. One crucial step is data integration, ensuring seamless transfer of historical data. Another vital consideration is understanding the new event-based model and defining relevant events for your specific business needs. Furthermore, testing the implementation thoroughly and addressing any potential issues is paramount to avoid disruptions in data collection.
Migrating to GA4 is a bit like cooking a delicious meal – you need the right ingredients and a good recipe. Understanding how to structure your data is key, but also thinking about how to create engaging content, similar to the “recipe of viral features” here , can boost your overall analytics. Ultimately, a successful GA4 migration involves meticulous planning and a focus on the user experience, so make sure you have a strong strategy in place.
Proper training of the analytics team is critical for successful adoption and interpretation of GA4’s features.
Planning Your GA4 Migration
Successfully migrating to Google Analytics 4 (GA4) requires careful planning. A well-defined strategy ensures a smooth transition, minimizing disruption and maximizing the benefits of the new platform. This phase sets the foundation for a successful implementation and data-driven future.A comprehensive migration plan Artikels the steps needed to move from Universal Analytics (UA) to GA4, ensuring a seamless transition.
This plan serves as a roadmap, guiding the project through various stages, from initial assessment to final launch. It facilitates the efficient allocation of resources and the timely completion of each task.
Key Steps in the Migration Planning
A robust migration plan involves several key steps. First, a thorough understanding of your current analytics setup is crucial. This includes identifying all existing data streams, reporting structures, and key performance indicators (KPIs). Second, defining clear objectives and goals for the GA4 implementation is essential. These objectives should be measurable and aligned with overall business strategies.
This step is vital for focusing efforts on the most relevant metrics and avoiding unnecessary complexity. Third, mapping your current UA data to GA4 equivalents is necessary. This step ensures data continuity and allows for the seamless transition of existing reporting. Finally, the creation of a detailed timeline and resource allocation plan is crucial. This will help in managing expectations and ensuring the project stays on track.
Essential Resources for the Migration
The successful GA4 migration relies on having the right resources. This includes a project manager who can oversee the entire process, stakeholders who represent various departments, and developers who can implement the technical changes. Analysts will be instrumental in interpreting the data and designing appropriate reports. A QA team is crucial for validating the accuracy and functionality of the migrated data.
Finally, the marketing team needs to be engaged to understand how GA4 will impact their work and to support the transition. Having a dedicated team of experts is key for efficient and effective migration.
Migration Checklist
A well-organized checklist streamlines the migration process. It provides a comprehensive list of tasks, ensuring nothing is overlooked.
- Define clear goals and objectives for the GA4 implementation.
- Assess existing Universal Analytics setup (data streams, reports, KPIs).
- Map UA data to GA4 equivalents.
- Identify and document all data sources feeding into UA.
- Create a detailed project timeline with milestones and deadlines.
- Assign responsibilities to team members for each task.
- Develop a plan for data validation and testing.
- Establish communication channels and a feedback mechanism.
- Prepare for potential issues and have contingency plans.
- Develop a plan to decommission the UA property.
Detailed Roadmap for GA4 Migration
A roadmap is crucial for visualizing the entire migration journey. It should break down the migration into manageable phases, outlining specific tasks for each phase and the corresponding timelines. This structured approach provides a clear view of the entire process and enables effective monitoring.
Migration Timeline and Tasks
This table details the timelines and tasks for each phase of the GA4 migration.
Data Import and Setup: How To Migrate To Ga4
Migrating from Universal Analytics (UA) to Google Analytics 4 (GA4) requires careful data import and setup. This crucial step ensures a smooth transition and preserves valuable historical data. Proper configuration of data streams, custom dimensions, and metrics is vital for accurate reporting and analysis in GA4. This section details the various methods for importing data, potential pitfalls, and the steps involved in setting up your GA4 environment.Data migration from Universal Analytics to GA4 is a critical phase in the transition.
A well-executed import process allows for a seamless continuation of your analytics efforts, maintaining the historical context of your data. A smooth setup enables analysis of your website or app’s performance within the GA4 platform.
Data Import Methods
Various methods are available for importing data from Universal Analytics to GA4. The best approach depends on your technical expertise, budget, and the scale of your data. Understanding the pros and cons of each method is essential for making an informed decision.
- Direct Import: This method involves directly importing data from your Universal Analytics property to a new GA4 property. This approach is often the fastest and least prone to errors, but it requires technical expertise and understanding of the configuration process. The direct import process generally avoids the complexity and potential issues associated with third-party tools.
- Data Migration Tools: Dedicated tools automate the data transfer process. They offer a degree of automation, potentially reducing the time required for migration. However, these tools typically come with a cost and a learning curve to master their functionality.
- Manual Import: This approach involves exporting data from Universal Analytics and importing it manually into GA4. It is the least expensive option, but it is also the most time-consuming and error-prone method. Carefully considering the time investment is crucial when choosing this approach.
Potential Data Loss or Discrepancies
Data migration can sometimes lead to loss or discrepancies. Understanding potential issues is vital for mitigating risks. The direct import method generally avoids these risks but may require more technical effort.
- Data Cleansing: Ensure that the data you’re importing is clean and consistent. Inconsistencies or errors in the source data can lead to inaccuracies in your GA4 reports. Prioritizing data quality in the import process is vital.
- Data Transformation: GA4 data models differ from Universal Analytics. Data transformations might be necessary to ensure compatibility. Understanding the differences between the data models is essential for successful migration.
- Data Volume: Large datasets can take longer to import and may require optimization. Consider data compression techniques and proper scheduling for large-scale imports to avoid delays.
Configuring Data Streams in GA4
Setting up data streams in GA4 is a crucial step. It involves connecting your website or app to GA4 to collect data. Proper configuration is essential for accurate data collection.
- Account Creation: Create a GA4 account and property. Proper account management ensures that data is collected and stored securely.
- Data Stream Setup: Configure data streams for your website or app. This involves setting up tracking codes and implementing the appropriate configuration for your platform.
- Verification: Verify that data is flowing correctly to GA4. Regular verification ensures accurate data capture and analysis.
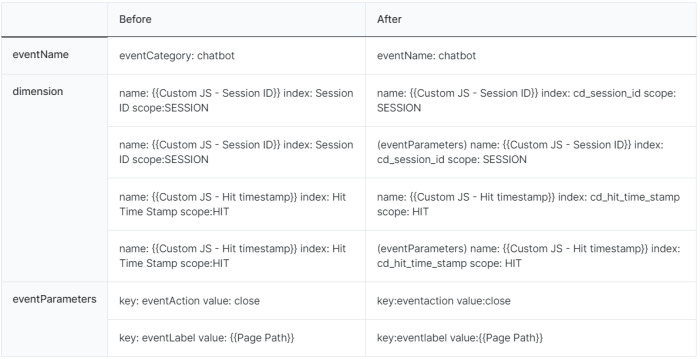
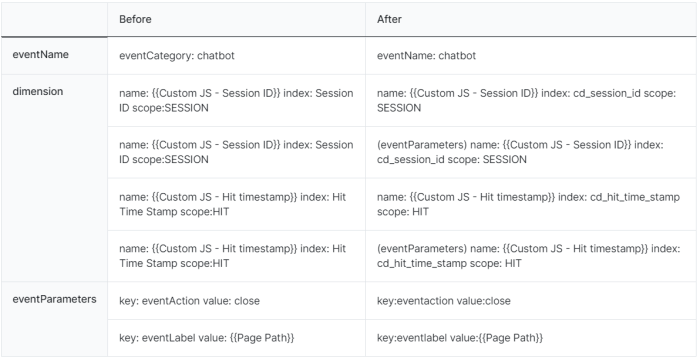
Configuring Custom Dimensions and Metrics
Custom dimensions and metrics allow you to track specific aspects of your data. These provide more in-depth insights.
- Custom Dimensions: Define custom dimensions to categorize and segment data. For example, you might track customer demographics or campaign sources.
- Custom Metrics: Define custom metrics to measure specific actions. Examples include the number of product views or the average time spent on a page.
- Implementation: Implementing custom dimensions and metrics involves modifying your tracking code to capture the desired data points. Proper implementation ensures that the data is accurately reflected in your reports.
Data Import Options Comparison
| Method | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Import | Direct transfer from UA to GA4 | Fastest, least error-prone | Requires technical expertise |
| Data Migration Tools | Tools automate the transfer | Automation, potentially faster | Cost, learning curve |
| Manual Import | Manual export/import | Lowest cost | Time-consuming, high risk of error |
Implementing GA4 Tracking
Getting your website or app set up for GA4 tracking is a crucial step in migrating to this enhanced analytics platform. This process involves integrating tracking codes and setting up events to capture valuable user interactions. Proper implementation ensures that you’re collecting the right data for informed decision-making.Implementing GA4 tracking involves more than just pasting a code snippet.
It necessitates understanding how to leverage the various features and parameters available to effectively collect and analyze the right data. This includes setting up different tags and tracking codes, and understanding how to track events, which can be a critical aspect of evaluating user behavior.
Setting Up Tags and Tracking Codes
The implementation process begins with integrating the GA4 tracking code into your website or application. This code snippet, provided by Google, is responsible for sending data about user interactions to Google Analytics 4. Different platforms require slightly different implementation methods.
Migrating to GA4 can feel overwhelming, but it’s totally doable! A key part of optimizing your website for better analytics is understanding how to structure your data for maximum insights. Knowing how to get rich snippets, for example, can significantly improve your search engine visibility, making your website stand out from the crowd. Once you’ve mastered those crucial rich snippet techniques, you’ll be well-equipped to truly harness the power of GA4 for your website’s performance.
Check out this comprehensive guide on how to get rich snippets for more tips on this. Ultimately, understanding both rich snippets and GA4 is essential for a well-rounded digital strategy.
- For websites: The GA4 tracking code is typically added to the ` ` section of your website’s HTML. You’ll find detailed instructions for various website platforms like WordPress, Wix, or Squarespace. Follow the instructions meticulously to avoid errors.
- For mobile apps: The implementation method differs, utilizing specific SDKs and libraries tailored for mobile app development. Consult the documentation for the specific mobile development platform you use (e.g., React Native, Flutter, Swift) for detailed implementation steps.
Tracking Events in GA4
Event tracking is fundamental to GA4, allowing you to monitor specific user actions. These actions can range from simple button clicks to complex interactions like product purchases. Setting up proper event tracking is essential for understanding user behavior and optimizing your website or app.
- Defining Events: Events are user actions you want to track, like page views, button clicks, video plays, or file downloads. You define these actions within your GA4 property, ensuring that the correct data points are captured.
- Event Parameters: Adding parameters to events provides further context. These parameters can include details like product names, product IDs, or transaction amounts. This detailed information helps in deeper analysis.
Best Practices for Tagging and Tracking
Adhering to best practices is crucial for accurate and reliable GA4 data collection. This includes ensuring that all events are properly defined, parameters are accurately populated, and that you’re tracking the right data points for your business objectives.
- Consistency: Maintain consistency in your tagging and tracking strategies across all pages and features. This uniformity allows for accurate comparisons and analysis.
- Clarity: Clearly define the events you track and the parameters associated with each event. This improves data interpretability and allows for better decision-making.
Implementing GA4 Tracking for E-commerce Sites
E-commerce sites require specific tracking to monitor user behavior related to product interactions and purchases. Proper implementation is vital for analyzing sales trends and optimizing the shopping experience.
- Product Interactions: Track events like product views, adds to cart, and purchases. The parameters should include product IDs, names, and prices to allow for detailed analysis.
- Purchase Tracking: Accurate purchase tracking is critical. Data on order IDs, amounts, and other relevant parameters should be included in the tracking setup.
Common GA4 Events and Parameters
The following table Artikels common events and their associated parameters for e-commerce tracking:
| Event Name | Event Category | Event Action | Event Label |
|---|---|---|---|
| Product View | Products | View | Product ID |
| Add to Cart | Cart | Add | Product ID |
| Purchase | Purchase | Complete | Order ID |
Analyzing GA4 Data
Unleashing the power of Google Analytics 4 (GA4) data requires more than just importing it. Effective analysis involves understanding the available reports, crafting custom views, and interpreting key metrics to gain actionable insights. This section dives into the practical application of GA4 data, enabling you to transform raw numbers into meaningful strategies.
GA4 Reports: A Comprehensive Overview, How to migrate to ga4
GA4 offers a suite of reports categorized into Acquisition, Behavior, Conversions, and Audience. These reports provide a holistic view of user interactions, traffic sources, and overall performance. Each report type provides crucial data for different aspects of your website or app analysis.
Custom Reports and Dashboards: Tailoring Your View
Custom reports and dashboards allow you to focus on specific metrics and dimensions relevant to your business goals. Instead of sifting through numerous default reports, you can create a personalized view that highlights your key performance indicators (KPIs). This targeted approach is essential for rapid identification of trends and patterns. Custom dashboards consolidate multiple reports into a single, interactive interface, simplifying your analysis process.
Advanced Segments and Filters: Refining Your Analysis
Advanced segments and filters in GA4 empower you to isolate specific user groups and interactions. You can segment users based on demographics, behavior, or conversion actions, allowing you to understand the nuances of different user groups. Filters refine your data by excluding irrelevant data points, focusing your analysis on the desired subsets of your user base. This granular level of control provides a deeper understanding of user behavior.
Interpreting Key Metrics: Engagement and Conversion Rates
Understanding engagement and conversion rates is critical for evaluating the success of your website or app. Engagement metrics, such as session duration and bounce rate, reveal user interaction levels. High engagement suggests users find your content valuable and engaging. Conversion rates, on the other hand, measure the percentage of users who complete a desired action, such as making a purchase or filling out a form.
Interpreting these metrics in conjunction with other data provides a clear picture of user journey and campaign performance.
Creating Custom Reports in GA4: A Practical Guide
Creating custom reports involves selecting the desired metrics and dimensions. The process is straightforward and offers flexibility in structuring your data. Start by identifying the metrics you want to track, then select the relevant dimensions for analysis. This allows for a deeper dive into specific aspects of user behavior, ultimately providing a more detailed understanding of your user base.
By defining specific dimensions, you can create a custom report to monitor the progress of different marketing channels or campaigns. A well-structured custom report enables efficient identification of successful and unsuccessful strategies.
Common GA4 Reports and Their Use Cases
| Report Type | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Acquisition | Understanding where your traffic is coming from (e.g., search engines, social media, referrals). This helps identify high-performing channels and areas for improvement. |
| Behavior | Analyzing user interactions on your website (e.g., page views, time on site, bounce rate). This provides insights into user engagement and areas where users might be dropping off. |
| Conversions | Tracking and measuring your website’s goals (e.g., purchases, sign-ups, form submissions). This allows you to measure the effectiveness of your campaigns and optimize your conversion funnel. |
| Audience | Understanding your website visitors (e.g., demographics, interests, behavior). This helps you tailor your content and marketing efforts to specific user segments. |
Concluding Remarks
Migrating to GA4 empowers you with a more robust and insightful analytics platform. This guide has equipped you with the knowledge and strategies needed for a seamless transition. Remember to meticulously plan, implement carefully, and analyze diligently to maximize the benefits of your GA4 setup. Happy analyzing!